Intro
Discover common Rhinovirus symptoms in adults, including cold-like signs, respiratory issues, and infection risks, to identify and manage the virus effectively.
Rhinoviruses are a common cause of respiratory infections, particularly the common cold, and can affect people of all ages. In adults, rhinovirus symptoms can range from mild to severe and may vary depending on the individual's overall health and the specific strain of the virus. Understanding the symptoms of rhinovirus infections in adults is crucial for seeking appropriate medical care and preventing the spread of the infection to others.
Rhinoviruses are highly contagious and can be spread through direct contact with an infected person, contaminated surfaces, or through the air when an infected person coughs or sneezes. Adults who are infected with rhinovirus may experience a range of symptoms, including nasal congestion, runny nose, sore throat, cough, and fatigue. In some cases, rhinovirus infections can lead to more severe complications, such as bronchitis, pneumonia, or exacerbation of underlying respiratory conditions like asthma or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
The impact of rhinovirus infections on adults can be significant, particularly in terms of lost productivity and decreased quality of life. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), the common cold, which is often caused by rhinoviruses, is one of the most common reasons for missed workdays and school days. Furthermore, rhinovirus infections can also lead to secondary bacterial infections, such as sinusitis or otitis media, which can require additional medical treatment and antibiotics.
Rhinovirus Infection Mechanism
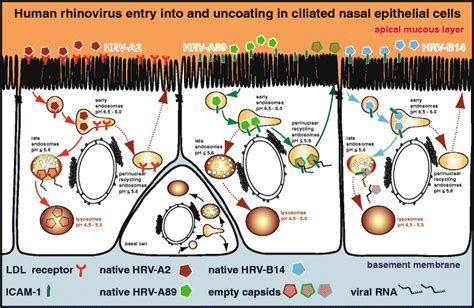
Types of Rhinoviruses
There are over 150 different strains of rhinoviruses, which can be divided into three main groups: A, B, and C. Each group has different characteristics and can cause different symptoms and severity of illness. Group A rhinoviruses are the most common cause of the common cold and are often associated with mild symptoms. Group B rhinoviruses are less common and can cause more severe symptoms, particularly in older adults and individuals with underlying health conditions. Group C rhinoviruses are the least common and are often associated with more severe respiratory illnesses, such as bronchiolitis and pneumonia.Rhinovirus Symptoms in Adults
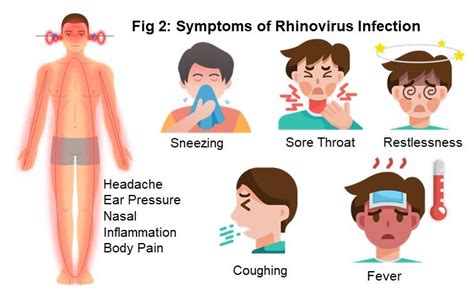
Rhinovirus Diagnosis
Diagnosing rhinovirus infections can be challenging, as the symptoms are often similar to those of other respiratory viruses. A healthcare provider may perform a physical examination and take a medical history to determine the cause of the symptoms. In some cases, a rapid antigen test or a PCR (polymerase chain reaction) test may be performed to confirm the diagnosis. However, these tests are not always necessary, and treatment is often based on the individual's symptoms and medical history.Rhinovirus Treatment and Prevention
Rhinovirus Complications
Rhinovirus infections can lead to several complications, particularly in older adults and individuals with underlying health conditions. These complications can include: * Bronchitis and pneumonia, which can require hospitalization and antibiotic treatment * Exacerbation of underlying respiratory conditions, such as asthma or COPD * Secondary bacterial infections, such as sinusitis or otitis media * Wheezing and shortness of breath, which can be life-threatening in severe casesRhinovirus and Asthma
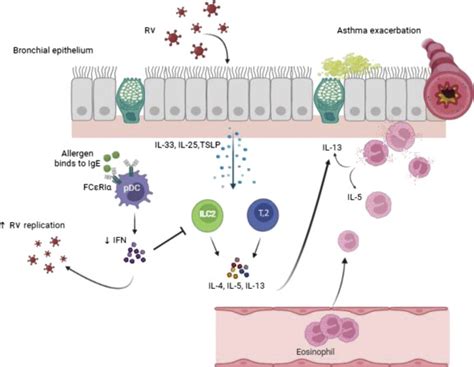
Rhinovirus and COPD
Rhinovirus infections can also exacerbate COPD, particularly in individuals with severe disease. The virus can cause inflammation and airway constriction, leading to symptoms such as wheezing, coughing, and shortness of breath. In some cases, rhinovirus infections can also lead to life-threatening COPD exacerbations, which require hospitalization and aggressive treatment.Rhinovirus and Other Respiratory Conditions
Rhinovirus and Immunocompromised Individuals
Rhinovirus infections can be particularly severe in immunocompromised individuals, such as those with HIV/AIDS, cancer, or taking immunosuppressive medications. The virus can cause prolonged and severe illness, and can also lead to life-threatening complications, such as pneumonia and sepsis. In these individuals, rhinovirus infections require prompt medical attention and aggressive treatment to prevent serious complications.Rhinovirus and Pregnancy
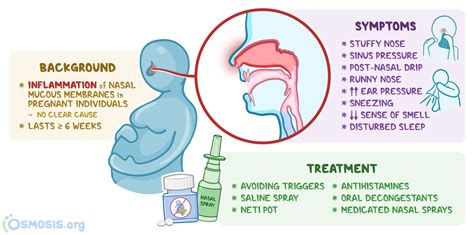
Rhinovirus and Children
Rhinovirus infections can also affect children, particularly those under the age of 5. The virus can cause symptoms such as runny nose, cough, and fever, and can also lead to more severe complications, such as bronchiolitis and pneumonia. Children with rhinovirus infections require prompt medical attention and close monitoring to prevent serious complications.Rhinovirus Research and Development

Rhinovirus Future Directions
The future of rhinovirus research and development is promising, with several new treatments and vaccines on the horizon. Additionally, advances in diagnostic testing and biomarkers will improve our understanding of the virus and its impact on human health. As our knowledge of rhinoviruses continues to grow, we can expect to see new and innovative approaches to preventing and treating these infections.In conclusion, rhinovirus infections are a significant public health concern, particularly in adults. Understanding the symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of these infections is crucial for reducing the risk of complications and improving quality of life. By staying informed and taking steps to prevent infection, individuals can reduce their risk of rhinovirus infections and stay healthy.
We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with rhinovirus infections in the comments below. Have you or a loved one had a rhinovirus infection? What were your symptoms, and how did you manage them? Share your story and help others understand the impact of rhinovirus infections on adults.
What are the most common symptoms of rhinovirus infections in adults?
+The most common symptoms of rhinovirus infections in adults include nasal congestion, runny nose, sore throat, cough, and fatigue.
How are rhinovirus infections diagnosed?
+Rhinovirus infections are often diagnosed based on symptoms and medical history. In some cases, a rapid antigen test or a PCR (polymerase chain reaction) test may be performed to confirm the diagnosis.
What are the best ways to prevent rhinovirus infections?
+The best ways to prevent rhinovirus infections include practicing good hygiene, such as washing hands frequently and avoiding close contact with individuals who are sick, avoiding touching the eyes, nose, and mouth, and getting plenty of rest and maintaining a healthy diet to keep the immune system strong.
Can rhinovirus infections be treated with antibiotics?
+No, rhinovirus infections cannot be treated with antibiotics. Antibiotics are only effective against bacterial infections, and rhinoviruses are caused by a virus.
What are the potential complications of rhinovirus infections in adults?
+Potential complications of rhinovirus infections in adults include bronchitis, pneumonia, exacerbation of underlying respiratory conditions, such as asthma or COPD, and secondary bacterial infections, such as sinusitis or otitis media.
