Intro
Discover how ringworm infection affects humans, causing skin lesions, itching, and discomfort, with 5 key ways it impacts overall health, including fungal transmission, symptoms, and treatment options for this contagious fungal disease.
Ringworm, also known as tinea, is a common fungal infection that affects humans, causing a range of symptoms and complications. Despite its name, ringworm is not a worm, but rather a fungal infection that can affect various parts of the body, including the skin, hair, and nails. The importance of understanding ringworm cannot be overstated, as it can have significant impacts on a person's quality of life, social interactions, and overall well-being. In this article, we will delve into the various ways ringworm affects humans, exploring its symptoms, causes, and consequences.
Ringworm is a highly contagious infection that can be spread through direct contact with an infected person, animal, or contaminated surface. It can also be spread through indirect contact, such as sharing personal items or walking barefoot in areas where the fungus is present. The infection can affect anyone, regardless of age, gender, or background, making it a significant public health concern. As we explore the effects of ringworm on humans, it becomes clear that prompt treatment and prevention strategies are crucial in managing this condition.
The impact of ringworm on humans can be far-reaching, affecting not only physical health but also emotional and social well-being. For instance, ringworm can cause significant discomfort, pain, and embarrassment, leading to anxiety, depression, and social isolation. Furthermore, ringworm can also have economic implications, as it can lead to lost productivity, medical expenses, and decreased quality of life. As we examine the various ways ringworm affects humans, it becomes evident that a comprehensive approach to prevention, diagnosis, and treatment is necessary to mitigate its effects.
Ringworm Symptoms and Diagnosis
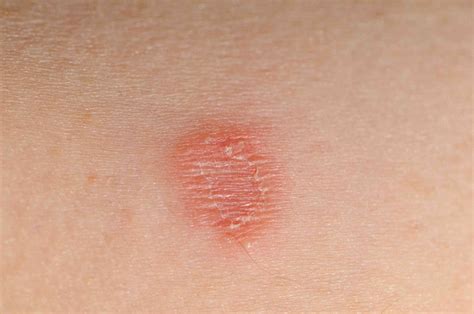
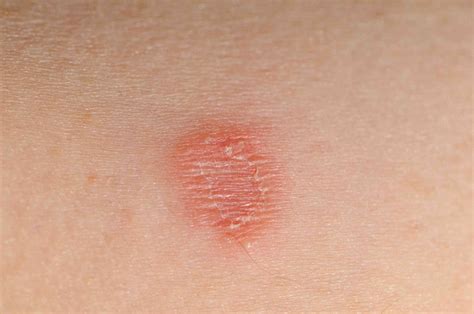
Types of Ringworm Infections
There are several types of ringworm infections, each affecting different parts of the body. These include: * Tinea corporis (body ringworm) * Tinea capitis (scalp ringworm) * Tinea pedis (athlete's foot) * Tinea unguium (nail ringworm) * Tinea cruris (jock itch) Each type of ringworm infection requires specific treatment and prevention strategies, highlighting the importance of accurate diagnosis and targeted interventions.Causes and Risk Factors of Ringworm
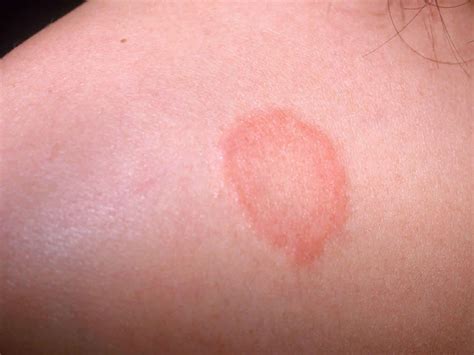
Prevention and Treatment of Ringworm
Preventing ringworm involves practicing good hygiene, avoiding contact with infected individuals or animals, and using antifungal medications. Treatment typically involves topical or oral antifungal medications, depending on the severity and location of the infection. In some cases, ringworm may require more aggressive treatment, such as laser therapy or surgical removal of infected tissue. It is essential to seek medical attention if symptoms persist or worsen over time, as untreated ringworm can lead to complications and long-term consequences.Complications and Consequences of Ringworm
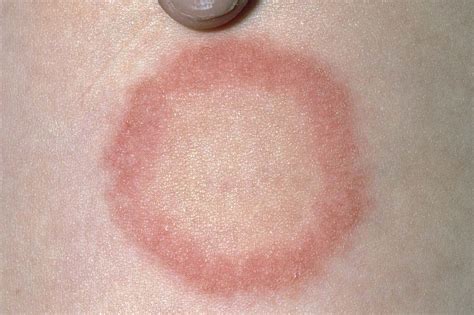
Ringworm in Special Populations
Ringworm can affect anyone, but certain populations are more susceptible to infection. These include: * Children: due to their increased exposure to other children and contaminated surfaces * Athletes: due to their increased exposure to sweat, moisture, and skin-to-skin contact * People with weakened immune systems: due to their reduced ability to fight off fungal infections * People with certain medical conditions: such as diabetes, eczema, or psoriasis Understanding the unique needs and risks of these populations is crucial in developing targeted prevention and treatment strategies.Ringworm and Mental Health
Coping with Ringworm
Coping with ringworm requires a comprehensive approach, incorporating medical treatment, lifestyle changes, and emotional support. This can include: * Practicing good hygiene and self-care * Avoiding triggers and risk factors * Seeking social support and counseling * Engaging in stress-reducing activities * Focusing on overall health and well-being By adopting a holistic approach to managing ringworm, individuals can reduce its impact on their lives, improve their mental health, and enhance their overall well-being.Conclusion and Future Directions

What is ringworm, and how is it transmitted?
+Ringworm is a fungal infection caused by a group of fungi, including Trichophyton, Microsporum, and Epidermophyton. It can be transmitted through direct contact with an infected person, animal, or contaminated surface, as well as through indirect contact, such as sharing personal items or walking barefoot in public areas.
What are the symptoms of ringworm, and how is it diagnosed?
+The symptoms of ringworm can vary depending on the affected area of the body, but common symptoms include red, itchy, and circular rashes, as well as hair loss, nail discoloration, and skin lesions. Diagnosing ringworm typically involves a physical examination, medical history, and laboratory tests, such as skin scrapings or biopsy.
How can ringworm be prevented and treated?
+Preventing ringworm involves practicing good hygiene, avoiding contact with infected individuals or animals, and using antifungal medications. Treatment typically involves topical or oral antifungal medications, depending on the severity and location of the infection. In some cases, ringworm may require more aggressive treatment, such as laser therapy or surgical removal of infected tissue.
