Intro
Discover the normal range for Sed Rate, a blood test measuring inflammation. Learn about ESR normal values, sedimentation rate, and related conditions like anemia and arthritis, to understand your test results and overall health.
The sed rate, also known as the erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR), is a blood test that measures how quickly erythrocytes (red blood cells) settle at the bottom of a test tube containing a blood sample. It indirectly measures how much inflammation is in the body. The sed rate is a non-specific test, meaning it can be elevated in a wide range of conditions, including infections, autoimmune disorders, and cancers.
The importance of understanding the sed rate normal range cannot be overstated, as it plays a crucial role in diagnosing and monitoring various medical conditions. A sed rate test can help doctors determine the severity of inflammation in the body and monitor the effectiveness of treatment. Moreover, an abnormal sed rate can indicate the presence of an underlying condition that requires medical attention. In this article, we will delve into the world of sed rates, exploring what they are, how they are measured, and what the normal range is.
The sed rate test is a simple and inexpensive procedure that can provide valuable information about a person's health. It is often used in conjunction with other tests, such as the C-reactive protein (CRP) test, to diagnose and monitor conditions like rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, and other inflammatory diseases. By understanding the sed rate normal range, healthcare professionals can make informed decisions about patient care and develop effective treatment plans.
What is Sed Rate?
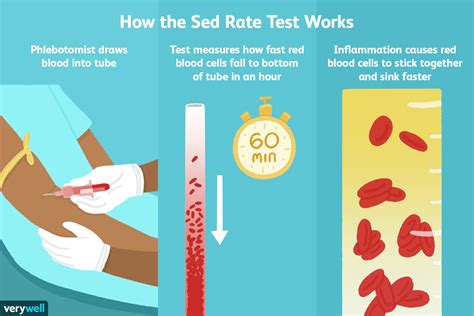
The sed rate is influenced by several factors, including the presence of inflammatory proteins, such as fibrinogen and immunoglobulins, which can cause red blood cells to clump together and settle more quickly. The test is not specific to any particular disease or condition, but rather provides a general indication of the level of inflammation in the body.
How is Sed Rate Measured?
The sed rate is typically measured in millimeters per hour (mm/h). The test is performed using a specialized device called a sed rate analyzer, which measures the distance that the red blood cells have settled over a period of time. The results are then compared to a reference range to determine if the sed rate is normal or abnormal.The sed rate can be measured using different methods, including the Westergren method and the Wintrobe method. The Westergren method is the most commonly used method and involves measuring the distance that the red blood cells have settled over a period of one hour. The Wintrobe method, on the other hand, involves measuring the distance that the red blood cells have settled over a period of one hour, but uses a different type of test tube.
Sed Rate Normal Range
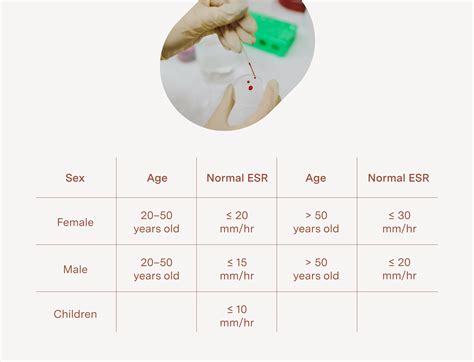
- Men: 0-15 mm/h
- Women: 0-20 mm/h
For children, the normal range is:
- Newborns: 0-2 mm/h
- Infants: 0-10 mm/h
- Children: 0-15 mm/h
It's essential to note that the sed rate can be influenced by various factors, such as age, sex, and the presence of underlying medical conditions. Therefore, the results of the test should be interpreted in conjunction with other clinical findings and laboratory results.
Factors that Affect Sed Rate
Several factors can affect the sed rate, including:- Age: The sed rate tends to increase with age.
- Sex: Women tend to have a higher sed rate than men.
- Pregnancy: The sed rate can increase during pregnancy.
- Inflammation: The presence of inflammatory proteins can cause the sed rate to increase.
- Infection: The presence of an infection can cause the sed rate to increase.
- Autoimmune disorders: Conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis and lupus can cause the sed rate to increase.
- Cancer: Certain types of cancer, such as lymphoma and multiple myeloma, can cause the sed rate to increase.
Abnormal Sed Rate Results
- Inflammation or infection
- Autoimmune disorder
- Cancer
- Pregnancy
- Aging
On the other hand, a low sed rate can indicate:
- Lack of inflammation
- Normal health
- Certain medical conditions, such as polycythemia vera
It's essential to note that an abnormal sed rate result should be interpreted in conjunction with other clinical findings and laboratory results. A healthcare professional can help determine the cause of an abnormal sed rate result and develop an appropriate treatment plan.
Treatment for Abnormal Sed Rate
The treatment for an abnormal sed rate depends on the underlying cause of the condition. For example:- Inflammation or infection: Treatment may involve anti-inflammatory medications, antibiotics, or other medications to reduce inflammation and fight infection.
- Autoimmune disorder: Treatment may involve immunosuppressive medications, corticosteroids, or other medications to reduce inflammation and modulate the immune system.
- Cancer: Treatment may involve chemotherapy, radiation therapy, or other medications to treat the underlying cancer.
- Pregnancy: Treatment may involve close monitoring of the pregnancy and the sed rate, as well as treatment of any underlying conditions that may be contributing to the abnormal sed rate.
Conclusion and Next Steps
We encourage you to share your thoughts and experiences with sed rate tests in the comments section below. Have you had a sed rate test recently? What were your results, and how did you feel about the experience? Share your story with us, and let's start a conversation about sed rates and their importance in healthcare.
What is the normal range for sed rate in adults?
+The normal range for sed rate in adults is 0-15 mm/h for men and 0-20 mm/h for women.
What factors can affect the sed rate?
+Several factors can affect the sed rate, including age, sex, pregnancy, inflammation, infection, autoimmune disorders, and cancer.
What does an abnormal sed rate result indicate?
+An abnormal sed rate result can indicate the presence of an underlying medical condition, such as inflammation, infection, autoimmune disorder, or cancer.
How is the sed rate test performed?
+The sed rate test is performed by measuring the distance that red blood cells have settled over a period of time, usually one hour, using a specialized device called a sed rate analyzer.
What is the significance of the sed rate in healthcare?
+The sed rate is a valuable tool for diagnosing and monitoring various medical conditions, including inflammatory diseases, autoimmune disorders, and cancer.
