Intro
The world of diabetes management has witnessed a significant shift in recent years, with the introduction of SGLT 2 inhibitors revolutionizing the way we approach this chronic condition. As a result, there is a growing interest in understanding the role of these medications in improving glycemic control and reducing the risk of complications associated with diabetes. In this article, we will delve into the world of SGLT 2 inhibitors, exploring their benefits, working mechanisms, and practical applications, as well as addressing common questions and concerns.
The importance of effective diabetes management cannot be overstated, with the condition affecting millions of people worldwide and posing a significant burden on healthcare systems. Traditional treatments, such as metformin and sulfonylureas, have been the cornerstone of diabetes care for decades, but they often come with limitations and side effects. The emergence of SGLT 2 inhibitors has provided a new avenue for patients and healthcare providers, offering a novel approach to managing blood sugar levels and mitigating the risks of diabetes-related complications.
As we navigate the complexities of diabetes care, it is essential to recognize the significance of SGLT 2 inhibitors in modern treatment regimens. These medications have been shown to improve glycemic control, reduce body weight, and lower blood pressure, making them an attractive option for patients with type 2 diabetes. Furthermore, SGLT 2 inhibitors have been found to have a favorable safety profile, with a low risk of hypoglycemia and minimal impact on liver and kidney function.
What are SGLT 2 Inhibitors?
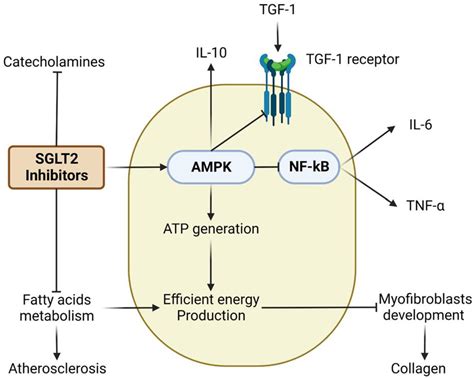
Benefits of SGLT 2 Inhibitors
The benefits of SGLT 2 inhibitors are multifaceted, with these medications offering a range of advantages over traditional diabetes treatments. Some of the key benefits include: * Improved glycemic control: SGLT 2 inhibitors have been shown to reduce HbA1c levels, indicating better blood sugar control. * Weight loss: By increasing glucose excretion in the urine, SGLT 2 inhibitors can lead to weight loss, which is a significant advantage for patients with type 2 diabetes. * Blood pressure reduction: SGLT 2 inhibitors have been found to lower blood pressure, which can reduce the risk of cardiovascular complications. * Low risk of hypoglycemia: Unlike traditional diabetes medications, SGLT 2 inhibitors do not increase the risk of hypoglycemia, making them a safer option for patients.How do SGLT 2 Inhibitors Work?
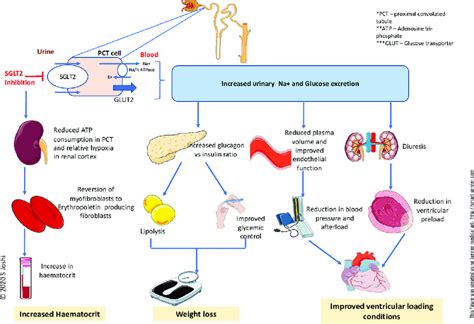
Types of SGLT 2 Inhibitors
There are several types of SGLT 2 inhibitors available, each with its own unique characteristics and benefits. Some of the most common SGLT 2 inhibitors include: * Canagliflozin (Invokana) * Dapagliflozin (Farxiga) * Empagliflozin (Jardiance) * Ertugliflozin (Steglatro) * Sotagliflozin (Zynquista)Practical Applications of SGLT 2 Inhibitors
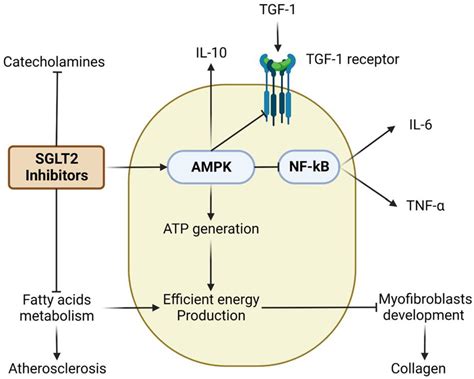
Common Side Effects of SGLT 2 Inhibitors
While SGLT 2 inhibitors are generally well-tolerated, they can cause a range of side effects, including: * Genital mycotic infections: SGLT 2 inhibitors can increase the risk of genital mycotic infections, such as thrush. * Urinary tract infections: SGLT 2 inhibitors can increase the risk of urinary tract infections, particularly in women. * Dehydration: SGLT 2 inhibitors can cause dehydration, particularly in patients who are not drinking enough fluids.Future Directions for SGLT 2 Inhibitors
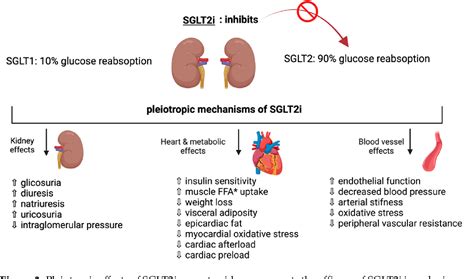
Conclusion and Final Thoughts
In conclusion, SGLT 2 inhibitors have revolutionized the way we approach diabetes care, offering a novel approach to managing blood sugar levels and reducing the risk of complications. As research continues to uncover the benefits and mechanisms of these medications, it is likely that they will play an increasingly important role in the treatment of type 2 diabetes. Whether you are a patient or a healthcare provider, it is essential to stay informed about the latest developments in SGLT 2 inhibitors and their potential applications in diabetes care.We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with SGLT 2 inhibitors in the comments section below. Have you used these medications to manage your diabetes? What benefits or challenges have you encountered? Your feedback and insights can help others better understand the role of SGLT 2 inhibitors in modern diabetes care.
What are the most common side effects of SGLT 2 inhibitors?
+The most common side effects of SGLT 2 inhibitors include genital mycotic infections, urinary tract infections, and dehydration.
Can SGLT 2 inhibitors be used in combination with other diabetes medications?
+Yes, SGLT 2 inhibitors can be used in combination with other diabetes medications, such as metformin or sulfonylureas, to improve glycemic control.
What is the mechanism of action of SGLT 2 inhibitors?
+SGLT 2 inhibitors work by inhibiting the reabsorption of glucose in the kidneys, leading to increased glucose excretion in the urine.
