Intro
The hepatitis B vaccine is a crucial component in the prevention of hepatitis B, a potentially life-threatening liver infection caused by the hepatitis B virus (HBV). Hepatitis B is a major global health concern, with approximately 257 million people living with chronic HBV infection, and it is a leading cause of liver cirrhosis and liver cancer. The importance of hepatitis B vaccination cannot be overstated, as it has been proven to be highly effective in preventing the transmission of the virus and reducing the risk of chronic infection and its associated complications.
Hepatitis B is a highly infectious disease that can be spread through various routes, including blood, semen, and other bodily fluids. The virus can be transmitted from mother to child during birth, through sexual contact, and through sharing needles or other equipment that has come into contact with infected blood. The risk of chronic infection is highest among individuals who are infected at birth or in early childhood, as their immature immune systems are less capable of clearing the virus. The consequences of chronic hepatitis B infection can be severe, including liver damage, liver failure, and liver cancer.
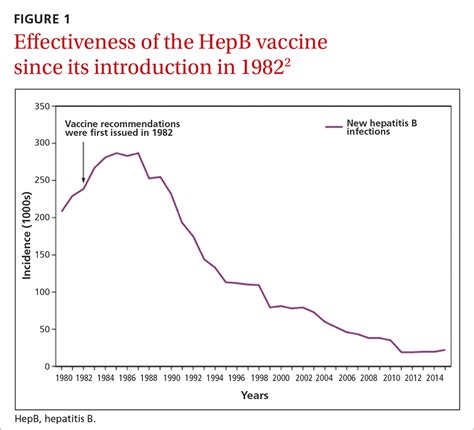
The hepatitis B vaccine has been widely used since its introduction in the 1980s and has been instrumental in reducing the incidence of hepatitis B worldwide. The vaccine is typically administered in a series of two to four doses, depending on the age and risk factors of the individual. The first dose is usually given at birth, followed by subsequent doses at 1-2 months, 4-6 months, and 12-18 months of age. The vaccine is also recommended for all individuals who are at increased risk of infection, including healthcare workers, individuals with multiple sex partners, and injecting drug users.
Hepatitis B Vaccine Mechanism
Benefits of Hepatitis B Vaccination

Who Should Get Vaccinated
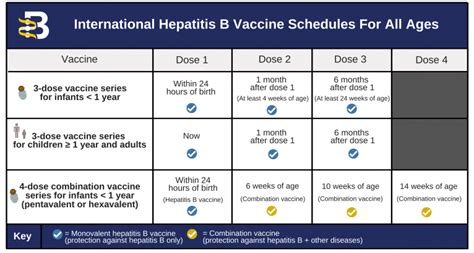
The hepatitis B vaccine is recommended for all individuals, regardless of age or risk factors. However, certain groups are at increased risk of infection and should be prioritized for vaccination. These groups include: * All newborns, as the risk of chronic infection is highest among individuals who are infected at birth * Children and adolescents who have not been previously vaccinated * Adults who are at increased risk of infection, including healthcare workers, individuals with multiple sex partners, and injecting drug users * Individuals who are traveling to or living in areas where hepatitis B is common * Individuals who have been exposed to the virus, such as through a needlestick injury or sexual contact with an infected partnerHepatitis B Vaccine Schedule
Common Side Effects
The hepatitis B vaccine is generally well-tolerated and has a good safety profile. However, as with any vaccine, there can be side effects. Common side effects include: * Pain, redness, or swelling at the injection site * Fatigue * Headache * Fever * Nausea or vomitingHepatitis B Vaccine Effectiveness
Challenges and Limitations
Despite the effectiveness of the hepatitis B vaccine, there are still challenges and limitations to its use. These include: * Limited access to vaccination in some parts of the world, particularly in low-income and middle-income countries * Limited awareness and understanding of the importance of hepatitis B vaccination * Limited resources and infrastructure for vaccine delivery and administration * Potential for vaccine hesitancy and refusalFuture Directions

Conclusion and Recommendations
In conclusion, the hepatitis B vaccine is a crucial component in the prevention of hepatitis B, a potentially life-threatening liver infection. The vaccine has been proven to be highly effective in preventing the transmission of the virus and reducing the risk of chronic infection and its associated complications. It is recommended that all individuals, regardless of age or risk factors, receive the hepatitis B vaccine as part of a comprehensive prevention strategy. Additionally, efforts should be made to increase access to vaccination, improve awareness and understanding of the importance of hepatitis B vaccination, and address potential challenges and limitations to vaccine use.What is hepatitis B?
+Hepatitis B is a potentially life-threatening liver infection caused by the hepatitis B virus (HBV).
How is hepatitis B transmitted?
+Hepatitis B can be transmitted through various routes, including blood, semen, and other bodily fluids, as well as through mother-to-child transmission during birth.
What are the benefits of hepatitis B vaccination?
+The benefits of hepatitis B vaccination include prevention of hepatitis B infection and its associated complications, reduction in the risk of chronic infection, and protection against mother-to-child transmission of the virus during birth.
Who should get vaccinated against hepatitis B?
+The hepatitis B vaccine is recommended for all individuals, regardless of age or risk factors, as well as for individuals who are at increased risk of infection, such as healthcare workers, individuals with multiple sex partners, and injecting drug users.
What is the hepatitis B vaccine schedule?
+The hepatitis B vaccine schedule typically involves a series of two to four doses, depending on the age and risk factors of the individual, with the first dose given at birth and subsequent doses given at 1-2 months, 4-6 months, and 12-18 months of age.
We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of the importance of hepatitis B vaccination and the benefits it offers. If you have any further questions or concerns, please do not hesitate to reach out to us. Additionally, we encourage you to share this article with others to help raise awareness about the importance of hepatitis B vaccination and to promote the prevention of this potentially life-threatening disease.
