Intro
Sickle cell disease is a genetic disorder that affects the production of hemoglobin, a protein in red blood cells that carries oxygen to different parts of the body. It is characterized by the presence of abnormal hemoglobin, known as hemoglobin S, which causes red blood cells to be misshapen and break down. Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial to managing the condition and preventing complications. In this article, we will discuss the importance of sickle cell tests and the various types of tests available.
The importance of sickle cell tests cannot be overstated. These tests help diagnose sickle cell disease, identify carriers of the disease, and monitor the condition's progression. They also enable healthcare providers to develop effective treatment plans and provide genetic counseling to individuals and families affected by the disease. With the advancement of medical technology, several sickle cell tests have been developed, each with its unique characteristics and purposes.
Sickle cell tests are essential for individuals who are at risk of developing the disease, particularly those with a family history of sickle cell disease. They are also crucial for newborns, as early diagnosis and treatment can significantly improve their quality of life. Additionally, sickle cell tests are necessary for individuals who are experiencing symptoms of the disease, such as anemia, jaundice, and recurring infections. By undergoing these tests, individuals can receive a definitive diagnosis and begin treatment promptly.
Introduction to Sickle Cell Tests
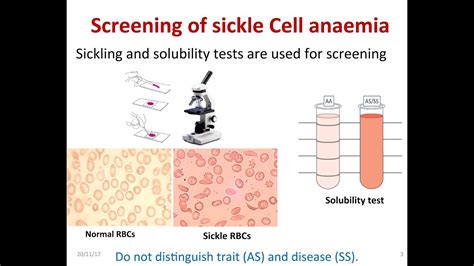
Types of Sickle Cell Tests
Sickle cell tests can be broadly classified into several categories, including blood tests, genetic tests, and prenatal tests. Blood tests are used to detect the presence of abnormal hemoglobin and diagnose sickle cell disease. Genetic tests, on the other hand, are used to identify carriers of the disease and diagnose sickle cell disease in newborns. Prenatal tests are used to diagnose sickle cell disease in fetuses and provide genetic counseling to parents.Blood Tests for Sickle Cell Disease

Complete Blood Counts
Complete blood counts are blood tests that measure the levels of different blood cells, including red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. These tests are used to diagnose and monitor sickle cell disease. They can detect anemia, which is a common complication of sickle cell disease. Anemia occurs when the body does not have enough red blood cells or when red blood cells are not functioning properly.Genetic Tests for Sickle Cell Disease

Amino Acid Analysis
Amino acid analysis is a genetic test that analyzes the amino acid sequence of hemoglobin. This test can detect any mutations in the genes that code for hemoglobin and diagnose sickle cell disease. Amino acid analysis is a highly sensitive and specific test that can detect even small changes in the amino acid sequence of hemoglobin.Prenatal Tests for Sickle Cell Disease
Chorionic Villus Sampling
Chorionic villus sampling is a prenatal test that involves removing a small sample of tissue from the placenta. This test can detect the presence of abnormal hemoglobin and diagnose sickle cell disease in fetuses. Chorionic villus sampling is a highly sensitive and specific test that can detect even small changes in the genes that code for hemoglobin.Benefits of Sickle Cell Tests
Improved Quality of Life
Sickle cell tests can improve the quality of life for individuals with sickle cell disease. Early diagnosis and treatment can reduce the risk of complications, such as anemia, jaundice, and recurring infections. Sickle cell tests also enable healthcare providers to monitor the condition's progression and adjust treatment plans accordingly.Steps to Take After Receiving Sickle Cell Test Results
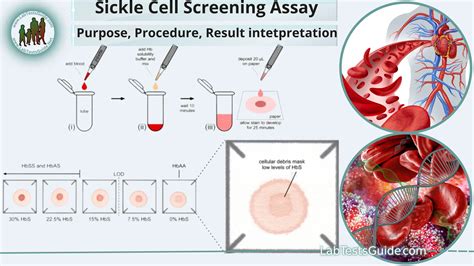
Seeking Medical Attention
Individuals who test positive for sickle cell disease should seek medical attention promptly. They should consult with their healthcare provider to develop an effective treatment plan. Healthcare providers can help individuals manage their condition, reduce the risk of complications, and improve their quality of life.What are the symptoms of sickle cell disease?
+The symptoms of sickle cell disease include anemia, jaundice, and recurring infections. Individuals with sickle cell disease may also experience pain episodes, swelling, and fatigue.
How is sickle cell disease diagnosed?
+Sickle cell disease is diagnosed using blood tests, genetic tests, and prenatal tests. These tests can detect the presence of abnormal hemoglobin and diagnose sickle cell disease.
What are the benefits of sickle cell tests?
+The benefits of sickle cell tests include early diagnosis and treatment, improved quality of life, and reduced risk of complications. Sickle cell tests can also enable healthcare providers to develop effective treatment plans and provide genetic counseling to individuals and families affected by the disease.
How can I manage my sickle cell disease?
+Individuals with sickle cell disease can manage their condition by following their treatment plans, practicing self-care, and seeking medical attention promptly. They should also stay hydrated, avoid extreme temperatures, and get plenty of rest.
Can sickle cell disease be cured?
+Currently, there is no cure for sickle cell disease. However, early diagnosis and treatment can significantly improve the quality of life for individuals with the condition. Researchers are also working to develop new treatments and therapies to manage sickle cell disease.
In conclusion, sickle cell tests are essential for diagnosing and managing sickle cell disease. These tests can detect the presence of abnormal hemoglobin, identify carriers of the disease, and monitor the condition's progression. By undergoing these tests, individuals can receive a definitive diagnosis and begin treatment promptly. We encourage readers to share this article with others, particularly those who are at risk of developing sickle cell disease. By raising awareness about sickle cell tests and their importance, we can improve the quality of life for individuals with sickle cell disease and reduce the risk of complications. If you have any questions or comments, please feel free to leave them below.
