Intro
Learn about Sickle Cell Disease, a genetic disorder affecting hemoglobin, causing sickling, anemia, and pain crises, with related terms like sickle cell anemia, hemoglobinopathy, and blood disorders explained in detail.
Sickle cell disease is a genetic disorder that affects millions of people worldwide, causing a wide range of health problems. It is a condition where the red blood cells are not shaped like they should be, which can lead to blockages in the blood vessels and a lack of oxygen being delivered to the body's tissues. This can cause a variety of symptoms, including pain, fatigue, and increased risk of infections. Understanding sickle cell disease is crucial for providing proper care and management, as well as for developing new treatments and therapies.
The importance of understanding sickle cell disease cannot be overstated. It is a condition that affects not only the individual but also their family and community. The financial burden of sickle cell disease is significant, with costs associated with medical care, lost productivity, and other related expenses. Furthermore, the emotional and psychological impact of living with sickle cell disease can be substantial, affecting a person's quality of life and overall well-being. By learning more about sickle cell disease, we can work towards improving the lives of those affected and reducing the disparities in healthcare that exist for this condition.
Sickle cell disease is a complex condition that requires a comprehensive approach to management. This includes not only medical treatment but also lifestyle modifications, such as maintaining a healthy diet, staying hydrated, and avoiding triggers that can cause sickling. Additionally, there are many resources available to support individuals with sickle cell disease, including support groups, educational materials, and advocacy organizations. By taking a proactive approach to managing sickle cell disease, individuals can reduce their risk of complications and improve their overall health and well-being.
What is Sickle Cell Disease?
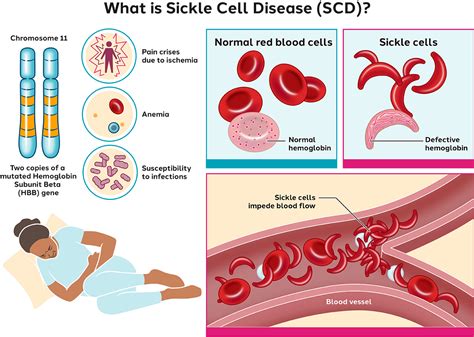
Types of Sickle Cell Disease
There are several types of sickle cell disease, including: * Sickle cell anemia (HbSS): This is the most common and severe form of sickle cell disease, where an individual inherits two copies of the mutated HBB gene (one from each parent). * Sickle cell trait (HbAS): This is a milder form of sickle cell disease, where an individual inherits one copy of the mutated HBB gene and one normal copy. * Sickle-hemoglobin C disease (HbSC): This is a form of sickle cell disease where an individual inherits one copy of the mutated HBB gene and one copy of the HbC gene. * Sickle-beta thalassemia (HbS-βthal): This is a form of sickle cell disease where an individual inherits one copy of the mutated HBB gene and one copy of the β-thalassemia gene.Causes and Risk Factors

Symptoms of Sickle Cell Disease
The symptoms of sickle cell disease can vary in severity and frequency, but common symptoms include: * Pain: Sickle cell disease can cause episodes of pain, which can range from mild to severe. * Fatigue: Sickle cell disease can cause fatigue, as the body's tissues are not receiving enough oxygen. * Increased risk of infections: Sickle cell disease can increase the risk of infections, particularly in children. * Swelling: Sickle cell disease can cause swelling in the hands and feet. * Jaundice: Sickle cell disease can cause jaundice, a yellowing of the skin and eyes.Diagnosis and Treatment
Complications of Sickle Cell Disease
Sickle cell disease can increase the risk of several complications, including: * Stroke: Sickle cell disease can increase the risk of stroke, particularly in children. * Kidney damage: Sickle cell disease can cause kidney damage and increase the risk of kidney failure. * Respiratory problems: Sickle cell disease can increase the risk of respiratory problems, such as pneumonia and acute chest syndrome. * Vision problems: Sickle cell disease can cause vision problems, including blindness.Living with Sickle Cell Disease

Coping with Sickle Cell Disease
Coping with sickle cell disease requires a proactive approach to management, including: * Keeping a pain diary: Keeping a pain diary can help individuals track their pain episodes and identify triggers. * Seeking medical attention: Seeking medical attention promptly can help prevent complications and improve outcomes. * Practicing stress-reducing techniques: Practicing stress-reducing techniques, such as meditation and deep breathing, can help manage stress and reduce the risk of sickling. * Staying connected: Staying connected with family, friends, and support groups can help individuals with sickle cell disease cope with the emotional and psychological impact of the condition.Current Research and Future Directions

Gene Therapy for Sickle Cell Disease
Gene therapy is a promising area of research for sickle cell disease, with the goal of correcting the genetic mutation that causes the condition. Several gene therapy approaches are being explored, including: * Gene editing: Gene editing technologies, such as CRISPR/Cas9, can be used to correct the genetic mutation that causes sickle cell disease. * Gene transfer: Gene transfer technologies can be used to introduce a healthy copy of the HBB gene into the body's cells. * Stem cell transplantation: Stem cell transplantation can be used to replace the body's bone marrow with healthy stem cells that can produce normal red blood cells.Conclusion and Final Thoughts

We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with sickle cell disease in the comments below. If you have any questions or would like to learn more about sickle cell disease, please don't hesitate to reach out. Together, we can work towards improving the lives of individuals with sickle cell disease and reducing the disparities in healthcare that exist for this condition.
What is sickle cell disease?
+Sickle cell disease is a genetic disorder that affects the production of hemoglobin, a protein in red blood cells that carries oxygen to the body's tissues.
What are the symptoms of sickle cell disease?
+The symptoms of sickle cell disease can vary in severity and frequency, but common symptoms include pain, fatigue, increased risk of infections, swelling, and jaundice.
How is sickle cell disease diagnosed?
+Sickle cell disease is typically diagnosed through a blood test, which can detect the presence of abnormal hemoglobin.
What are the treatment options for sickle cell disease?
+Treatment for sickle cell disease usually involves a combination of medications, lifestyle modifications, and other interventions, such as pain management, hydroxyurea, blood transfusions, and lifestyle modifications.
Is there a cure for sickle cell disease?
+Currently, there is no cure for sickle cell disease, but researchers are working to develop new treatments and therapies, including gene therapy and stem cell transplantation.
