Intro
Discover the 7 gabapentin side effects, including dizziness, fatigue, and mood changes, and learn how to manage neuropathic pain treatment risks, withdrawal symptoms, and interactions with seizures, anxiety, and depression medications.
The use of gabapentin, a medication primarily prescribed to treat epilepsy, nerve pain, and hot flashes, has become increasingly common. While it can be effective in managing these conditions, it's essential to be aware of the potential side effects associated with its use. Gabapentin side effects can range from mild to severe and may impact daily life. Understanding these side effects is crucial for patients to make informed decisions about their treatment.
Gabapentin's mechanism of action, though not fully understood, is believed to involve the modulation of calcium channels in the nervous system, which in turn reduces the release of excitatory neurotransmitters. This action can lead to various systemic effects, some of which are undesirable. The importance of recognizing and managing gabapentin side effects cannot be overstated, as it directly affects the quality of life and adherence to medication regimens.
The prevalence of gabapentin side effects varies among individuals, with some people experiencing minimal issues while others may encounter more severe reactions. Factors such as dosage, duration of treatment, individual health status, and concurrent medications can influence the likelihood and intensity of side effects. It's crucial for healthcare providers to monitor patients closely and adjust treatment plans as necessary to mitigate adverse effects.
Common Gabapentin Side Effects

Common side effects of gabapentin are often mild and may include dizziness, drowsiness, fatigue, and nausea. These effects are usually transient and may diminish as the body adjusts to the medication. However, in some cases, they can be persistent and bothersome, necessitating a review of the treatment plan. It's also important to note that gabapentin can cause mood changes, such as irritability, anxiety, or depression, in some individuals.
Less Common but Significant Side Effects
Less common but potentially more serious side effects of gabapentin include weight gain, increased appetite, and swelling in the feet and hands. These effects can have significant implications for overall health, particularly in terms of metabolic changes and cardiovascular risk. Furthermore, gabapentin has been associated with an increased risk of suicidal thoughts and behaviors in some patients, highlighting the need for close monitoring, especially in those with a history of mental health issues.Gabapentin and Weight Gain
Weight gain is a notable side effect of gabapentin, affecting a significant portion of patients. This can be attributed to increased appetite and water retention. Managing weight while on gabapentin involves a combination of dietary changes, increased physical activity, and, in some cases, the use of weight management medications. It's essential for patients to discuss weight concerns with their healthcare provider to develop a personalized plan.
Psychological Effects of Gabapentin
Gabapentin can have psychological effects, ranging from mild mood alterations to more severe mental health issues. Patients may experience euphoria, which, while seemingly positive, can be a concern, especially in individuals with a history of substance abuse. Conversely, some patients may feel emotionally numb or detached, which can impact their relationships and overall well-being. The psychological impact of gabapentin underscores the importance of regular follow-up appointments with healthcare providers to adjust the treatment plan as needed.Gabapentin in Pregnancy and Breastfeeding

The use of gabapentin during pregnancy and breastfeeding is a topic of concern. While gabapentin is sometimes prescribed during pregnancy for conditions like epilepsy, its safety profile in this context is not fully understood. Animal studies have suggested potential risks, but human data are limited. For breastfeeding mothers, gabapentin is excreted in breast milk, and its effects on infants are not well characterized. Women who are pregnant or breastfeeding should discuss the potential risks and benefits of gabapentin with their healthcare provider to make informed decisions.
Withdrawal from Gabapentin
Withdrawal from gabapentin can occur when the medication is stopped abruptly or the dosage is significantly reduced. Symptoms of gabapentin withdrawal may include anxiety, insomnia, nausea, pain, and sweating. The risk of withdrawal highlights the importance of tapering off gabapentin under medical supervision. Gradually reducing the dosage over time can minimize the risk of severe withdrawal symptoms.Gabapentin Interactions with Other Medications
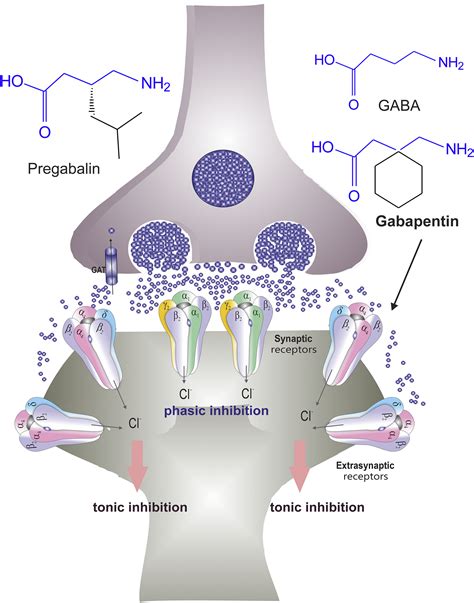
Gabapentin can interact with a variety of medications, including other antiepileptics, sedatives, and opioids. These interactions can lead to enhanced sedative effects, increased risk of respiratory depression, or altered gabapentin efficacy. It's crucial for patients to inform their healthcare providers about all medications they are taking to avoid potential drug interactions.
Managing Gabapentin Side Effects
Managing gabapentin side effects involves a multifaceted approach, including lifestyle modifications, monitoring by healthcare providers, and, in some cases, adjustments to the treatment regimen. Patients should maintain open communication with their healthcare team, reporting any changes in their condition or concerns about side effects. Regular follow-up appointments are essential for monitoring the efficacy of the medication and its impact on overall health.Alternatives to Gabapentin
For patients who experience intolerable side effects or inadequate relief from gabapentin, alternative treatments may be considered. These alternatives can include other medications, such as pregabalin, or non-pharmacological approaches like physical therapy, cognitive-behavioral therapy, or alternative pain management strategies. The choice of alternative treatment depends on the underlying condition, patient preferences, and the potential benefits and risks associated with each option.
Conclusion and Future Directions
In conclusion, while gabapentin can be an effective medication for various conditions, its potential side effects must be carefully considered. Ongoing research and clinical trials are aimed at better understanding the mechanisms of gabapentin and developing strategies to mitigate its adverse effects. As our understanding of gabapentin and its impact on health evolves, so too will the approaches to managing its side effects, ultimately leading to more personalized and effective treatment plans.Final Thoughts on Gabapentin Side Effects

The management of gabapentin side effects is a dynamic process that requires collaboration between patients and healthcare providers. By staying informed about the potential risks and benefits of gabapentin, individuals can make empowered decisions about their health. As research continues to uncover more about gabapentin's effects on the body, the hope is that future treatments will offer improved efficacy with reduced side effects, enhancing the quality of life for those who rely on this medication.
What are the most common side effects of gabapentin?
+The most common side effects of gabapentin include dizziness, drowsiness, fatigue, and nausea. These effects are usually mild and transient but can be persistent in some individuals.
Can gabapentin cause weight gain?
+Yes, gabapentin can cause weight gain in some patients, attributed to increased appetite and water retention. Managing weight while on gabapentin involves dietary changes, increased physical activity, and possibly weight management medications.
Is gabapentin safe during pregnancy and breastfeeding?
+The safety of gabapentin during pregnancy and breastfeeding is not fully understood. While it may be prescribed for certain conditions during pregnancy, its use should be carefully considered and monitored by a healthcare provider. Gabapentin is excreted in breast milk, and its effects on infants are not well characterized.
We invite you to share your experiences or questions about gabapentin side effects in the comments below. Your insights can help others better understand the potential impacts of this medication and how to manage its side effects effectively. Additionally, if you found this article informative, please consider sharing it with others who may benefit from this information.
