Intro
Hyperglycemia, or high blood sugar, is a condition that occurs when the body has too much glucose in the blood. This can be a serious health issue if left untreated, as it can lead to a range of complications, including damage to the nerves, kidneys, and eyes. Hyperglycemia is often associated with diabetes, but it can also occur in people without diabetes due to other factors such as certain medications, hormonal imbalances, or medical conditions. Understanding the signs and symptoms of hyperglycemia is crucial for early detection and treatment.
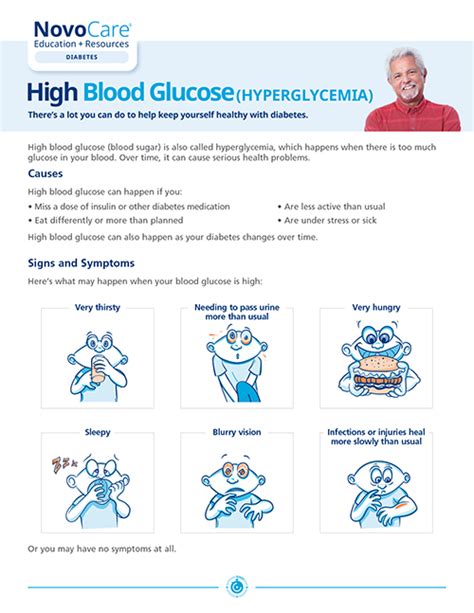
Hyperglycemia can manifest in different ways, and its symptoms can vary from person to person. Some individuals may experience mild symptoms, while others may have more severe symptoms that require immediate medical attention. Recognizing the signs of hyperglycemia is essential for managing the condition effectively and preventing long-term damage to the body. The symptoms of hyperglycemia can be acute or chronic, depending on the duration and severity of the condition.
The importance of recognizing and managing hyperglycemia cannot be overstated. If left untreated, high blood sugar levels can lead to serious health complications, including diabetic ketoacidosis, a life-threatening condition that requires immediate medical attention. Moreover, prolonged periods of hyperglycemia can increase the risk of cardiovascular disease, kidney failure, and blindness. Therefore, it is crucial to be aware of the signs and symptoms of hyperglycemia and to seek medical attention if they occur.
Understanding Hyperglycemia

Hyperglycemia occurs when the body is unable to regulate blood sugar levels effectively. This can happen for several reasons, including insulin resistance, insulin deficiency, or glucagon excess. Insulin is a hormone produced by the pancreas that helps to regulate blood sugar levels by facilitating the uptake of glucose by cells. When the body becomes resistant to insulin or is unable to produce enough insulin, glucose builds up in the blood, leading to hyperglycemia.
Causes Of Hyperglycemia
The causes of hyperglycemia can be broadly classified into two categories: diabetic and non-diabetic. Diabetic hyperglycemia occurs in people with diabetes, either due to insulin resistance or insulin deficiency. Non-diabetic hyperglycemia, on the other hand, can occur due to various factors, including certain medications, hormonal imbalances, or medical conditions.Signs And Symptoms Of Hyperglycemia

The signs and symptoms of hyperglycemia can vary from person to person, but common symptoms include:
- Increased thirst and urination
- Fatigue and weakness
- Blurred vision
- Slow healing of cuts and wounds
- Tingling or numbness in the hands and feet
- Recurring skin, gum, or bladder infections
These symptoms can be mild or severe, depending on the duration and severity of the condition. In some cases, people with hyperglycemia may not experience any symptoms at all, which is why regular blood sugar monitoring is crucial for early detection and treatment.
Acute Symptoms Of Hyperglycemia
Acute symptoms of hyperglycemia occur suddenly and can be severe. They include: * Diabetic ketoacidosis, a life-threatening condition that requires immediate medical attention * Hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state, a condition characterized by extremely high blood sugar levels and dehydration * Seizures or coma, which can occur if blood sugar levels become extremely highThese symptoms require immediate medical attention, as they can be life-threatening if left untreated.
Diagnosing Hyperglycemia

Diagnosing hyperglycemia involves a combination of physical examination, medical history, and laboratory tests. The most common test used to diagnose hyperglycemia is the fasting plasma glucose test, which measures blood sugar levels after an overnight fast. Other tests, such as the oral glucose tolerance test and the hemoglobin A1c test, may also be used to diagnose and monitor hyperglycemia.
Treatment Options For Hyperglycemia
Treatment for hyperglycemia depends on the underlying cause of the condition. For people with diabetes, treatment may involve lifestyle changes, such as diet and exercise, as well as medications to regulate blood sugar levels. For people without diabetes, treatment may involve addressing the underlying cause of the condition, such as discontinuing certain medications or treating hormonal imbalances.Managing Hyperglycemia
Managing hyperglycemia involves a combination of lifestyle changes and medical treatment. Lifestyle changes, such as diet and exercise, can help to regulate blood sugar levels and prevent complications. Medical treatment, such as medications and insulin therapy, may also be necessary to control blood sugar levels.
Preventing Hyperglycemia
Preventing hyperglycemia involves maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet and regular exercise. For people with diabetes, preventing hyperglycemia involves monitoring blood sugar levels regularly and adjusting treatment as needed. For people without diabetes, preventing hyperglycemia involves avoiding factors that can contribute to the condition, such as certain medications and hormonal imbalances.Complications Of Hyperglycemia

If left untreated, hyperglycemia can lead to a range of complications, including:
- Diabetic ketoacidosis, a life-threatening condition that requires immediate medical attention
- Hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state, a condition characterized by extremely high blood sugar levels and dehydration
- Cardiovascular disease, including heart attack, stroke, and peripheral artery disease
- Kidney failure, which can require dialysis or kidney transplantation
- Blindness, due to damage to the blood vessels in the eyes
These complications can be prevented or delayed with early detection and treatment of hyperglycemia.
Living With Hyperglycemia
Living with hyperglycemia requires a commitment to maintaining a healthy lifestyle and adhering to medical treatment. This includes monitoring blood sugar levels regularly, taking medications as prescribed, and making lifestyle changes, such as diet and exercise, to regulate blood sugar levels.Conclusion And Next Steps

In conclusion, hyperglycemia is a serious health condition that requires early detection and treatment to prevent complications. By understanding the signs and symptoms of hyperglycemia, people can take steps to manage the condition and prevent long-term damage to the body. If you are experiencing symptoms of hyperglycemia, it is essential to seek medical attention to determine the underlying cause of the condition and to develop a treatment plan.
We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with hyperglycemia in the comments below. If you have any questions or concerns, please do not hesitate to reach out to us. We are committed to providing you with accurate and helpful information to support your health and well-being.
What are the symptoms of hyperglycemia?
+The symptoms of hyperglycemia include increased thirst and urination, fatigue and weakness, blurred vision, slow healing of cuts and wounds, tingling or numbness in the hands and feet, and recurring skin, gum, or bladder infections.
How is hyperglycemia diagnosed?
+Hyperglycemia is diagnosed using a combination of physical examination, medical history, and laboratory tests, including the fasting plasma glucose test, the oral glucose tolerance test, and the hemoglobin A1c test.
What are the complications of hyperglycemia?
+The complications of hyperglycemia include diabetic ketoacidosis, hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state, cardiovascular disease, kidney failure, and blindness.
How can hyperglycemia be managed?
+Hyperglycemia can be managed using a combination of lifestyle changes, such as diet and exercise, and medical treatment, including medications and insulin therapy.
Can hyperglycemia be prevented?
+Yes, hyperglycemia can be prevented by maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet and regular exercise, and avoiding factors that can contribute to the condition, such as certain medications and hormonal imbalances.
