Intro
Hypoglycemia, also known as low blood sugar, is a condition that occurs when the level of glucose in the blood falls below a certain threshold. This can happen to anyone, but it is more common in people with diabetes who take insulin or other medications to control their blood sugar levels. Recognizing the signs of hypoglycemia is crucial, as it can lead to serious health complications if left untreated. In this article, we will delve into the importance of understanding hypoglycemia, its causes, symptoms, and treatment options.
The importance of recognizing hypoglycemia cannot be overstated. When blood sugar levels drop too low, the body's cells are not able to function properly, which can lead to a range of symptoms, from mild to severe. If left untreated, hypoglycemia can cause confusion, seizures, and even loss of consciousness. In severe cases, it can be life-threatening. Therefore, it is essential to be aware of the signs of hypoglycemia and take prompt action to treat it.
Hypoglycemia can be caused by a variety of factors, including taking too much insulin or other diabetes medications, skipping meals or snacks, and engaging in strenuous physical activity without adjusting food or medication intake. Certain medical conditions, such as kidney or liver disease, can also increase the risk of developing hypoglycemia. Understanding the causes of hypoglycemia is key to preventing and managing the condition.
Understanding Hypoglycemia

Symptoms of Hypoglycemia
The symptoms of hypoglycemia can vary from person to person, but common signs include shakiness, dizziness, sweating, hunger, irritability, confusion, and difficulty speaking. In severe cases, hypoglycemia can cause seizures, loss of consciousness, and even death. It is essential to recognize the symptoms of hypoglycemia and take prompt action to treat it.Causes of Hypoglycemia

Risk Factors for Hypoglycemia
Certain individuals are at a higher risk of developing hypoglycemia, including: * People with diabetes who take insulin or other medications to control their blood sugar levels * Older adults * People with kidney or liver disease * Those who engage in strenuous physical activity * People who drink alcohol without eatingTreatment Options for Hypoglycemia
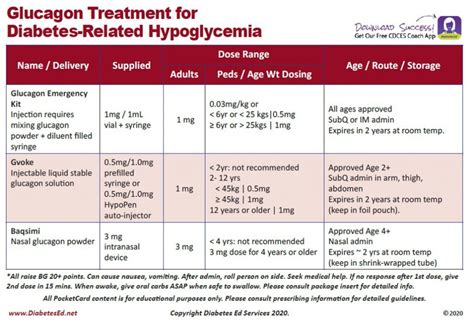
Preventing Hypoglycemia
Preventing hypoglycemia is crucial to managing the condition. This can be achieved by: * Monitoring blood sugar levels regularly * Eating regular meals and snacks * Adjusting insulin or medication doses based on food intake and physical activity * Avoiding strenuous physical activity without adjusting food or medication intake * Drinking alcohol in moderation and eating before or while drinkingLiving with Hypoglycemia

Coping with Hypoglycemia
Coping with hypoglycemia can be challenging, but there are several strategies that can help, including: * Keeping a log of blood sugar levels and symptoms * Developing a support network of family and friends * Engaging in regular physical activity to improve insulin sensitivity * Practicing stress-reducing techniques, such as meditation or yogaConclusion and Next Steps

We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with hypoglycemia in the comments below. Have you or someone you know been diagnosed with hypoglycemia? What steps have you taken to manage the condition? Share your story and help others understand the importance of recognizing and treating hypoglycemia.
What are the symptoms of hypoglycemia?
+The symptoms of hypoglycemia include shakiness, dizziness, sweating, hunger, irritability, confusion, and difficulty speaking. In severe cases, hypoglycemia can cause seizures, loss of consciousness, and even death.
How is hypoglycemia treated?
+Mild hypoglycemia can be treated by consuming a small amount of glucose, such as glucose tablets or juice. More severe cases may require medical attention, including the administration of intravenous glucose or glucagon.
Can hypoglycemia be prevented?
+Yes, hypoglycemia can be prevented by monitoring blood sugar levels regularly, eating regular meals and snacks, adjusting insulin or medication doses based on food intake and physical activity, and avoiding strenuous physical activity without adjusting food or medication intake.
