Intro
Identify premature labor symptoms early with our guide, covering signs, causes, and risks, including contractions, back pain, and vaginal bleeding, to ensure timely medical attention.
Premature labor is a serious health concern that can affect pregnant women and their unborn babies. It is essential to recognize the signs of premature labor symptoms to ensure timely medical attention and prevent potential complications. Premature labor occurs when the body prepares for birth before the 37th week of pregnancy, which can lead to premature birth. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), approximately 15 million babies are born prematurely every year, and this number is increasing due to various factors such as multiple pregnancies, chronic health conditions, and lifestyle factors.
Premature labor can be caused by a combination of factors, including hormonal changes, uterine distension, and cervical insufficiency. Women who have experienced premature labor in previous pregnancies are at a higher risk of experiencing it again. Additionally, women with certain medical conditions, such as diabetes, hypertension, and obesity, are also at a higher risk of premature labor. It is crucial for pregnant women to be aware of the signs of premature labor symptoms to seek medical attention promptly. Early recognition and treatment can significantly improve the outcomes for both the mother and the baby.
Pregnant women should be aware of the physical and emotional changes that occur during pregnancy. While some changes are normal, others can be indicative of premature labor. It is essential to monitor these changes and seek medical attention if any concerns arise. Regular prenatal check-ups can help identify potential issues early on, and women should always discuss any concerns or symptoms with their healthcare provider. By being informed and proactive, pregnant women can reduce the risk of premature labor and ensure a healthy pregnancy.
Understanding Premature Labor Symptoms
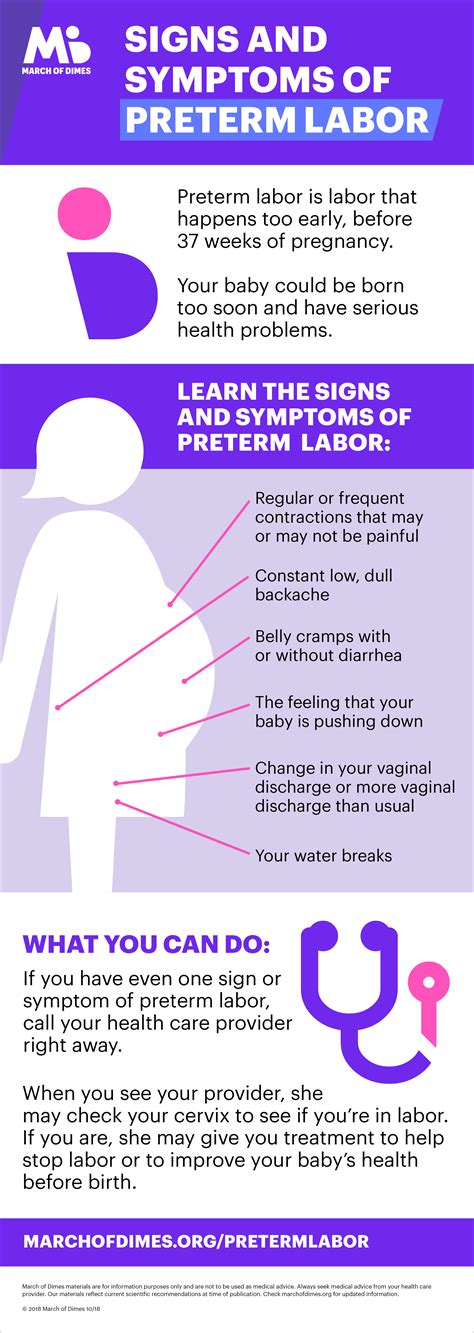
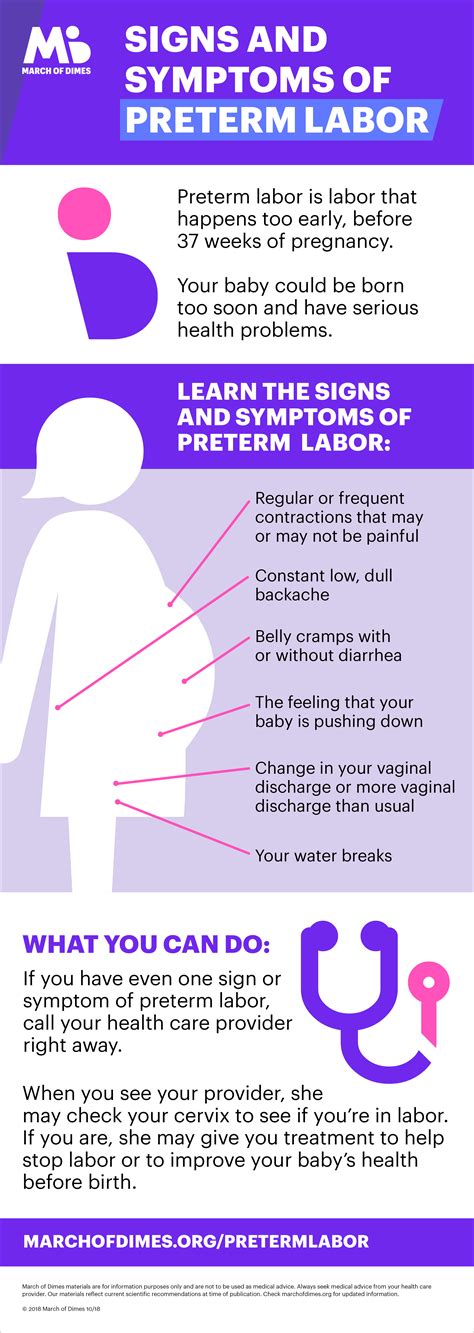
Premature labor symptoms can be subtle, and it is crucial to recognize them early to prevent complications. Some common signs of premature labor include mild cramping, back pain, and vaginal discharge. Women may also experience a sudden gush of fluid, which can be a sign of the amniotic sac breaking. Other symptoms include contractions that are more frequent and intense than usual, a low, dull backache, and a feeling of pressure in the pelvis. It is essential to seek medical attention immediately if any of these symptoms occur.
Types of Premature Labor
Premature labor can be classified into different types, including preterm labor, preterm premature rupture of membranes (PPROM), and cervical insufficiency. Preterm labor occurs when the body prepares for birth before the 37th week of pregnancy, while PPROM occurs when the amniotic sac breaks before the 37th week. Cervical insufficiency occurs when the cervix begins to dilate and efface before the 37th week, increasing the risk of premature birth. Understanding the different types of premature labor can help women identify the symptoms and seek medical attention promptly.Risk Factors for Premature Labor

Several risk factors can increase the likelihood of premature labor. These include a history of premature birth, multiple pregnancies, and certain medical conditions such as diabetes and hypertension. Women who experience vaginal bleeding during pregnancy are also at a higher risk of premature labor. Additionally, women who have a family history of premature birth or have experienced cervical surgery may also be at a higher risk. It is essential to discuss these risk factors with a healthcare provider to determine the best course of action.
Preventing Premature Labor
While it is not possible to eliminate all risk factors, there are steps that women can take to reduce the risk of premature labor. Maintaining a healthy weight, eating a balanced diet, and staying hydrated can help reduce the risk of premature labor. Women should also avoid smoking and excessive alcohol consumption, as these can increase the risk of premature birth. Regular prenatal check-ups can help identify potential issues early on, and women should always discuss any concerns or symptoms with their healthcare provider.Diagnosing Premature Labor
Diagnosing premature labor typically involves a physical examination, medical history, and laboratory tests. A healthcare provider will perform a pelvic exam to check for cervical dilation and effacement. They may also use ultrasound to check the fetal age and weight. Laboratory tests, such as a urinalysis and blood tests, can help identify any underlying infections or conditions that may be contributing to premature labor. In some cases, a healthcare provider may recommend bed rest or hospitalization to monitor the pregnancy and prevent premature birth.
Treatment Options for Premature Labor
Treatment options for premature labor depend on the gestational age and the severity of the symptoms. In some cases, bed rest or hospitalization may be recommended to monitor the pregnancy and prevent premature birth. Medications, such as corticosteroids and tocolytics, may be prescribed to reduce the risk of premature birth and promote fetal lung maturity. In severe cases, a healthcare provider may recommend delivery, either vaginally or via cesarean section.Complications of Premature Labor

Premature labor can lead to several complications, including low birth weight, respiratory distress syndrome, and neonatal intensive care unit (NICU) admission. Premature babies may also be at a higher risk of developmental delays, vision and hearing problems, and learning disabilities. Women who experience premature labor may also be at a higher risk of postpartum hemorrhage, infection, and emotional distress. It is essential to seek medical attention promptly if any symptoms of premature labor occur to reduce the risk of complications.
Coping with Premature Labor
Coping with premature labor can be challenging, both physically and emotionally. Women may experience anxiety, fear, and uncertainty about the outcome of the pregnancy. It is essential to have a support system, including family, friends, and a healthcare provider, to help navigate the challenges of premature labor. Women should also prioritize self-care, including rest, nutrition, and stress management, to reduce the risk of complications and promote a healthy pregnancy.Conclusion and Next Steps

In conclusion, premature labor is a serious health concern that requires prompt medical attention. Recognizing the signs of premature labor symptoms, understanding the risk factors, and taking steps to prevent premature labor can help reduce the risk of complications. Women should prioritize prenatal care, maintain a healthy lifestyle, and seek medical attention immediately if any symptoms of premature labor occur. By working together with a healthcare provider, women can reduce the risk of premature labor and promote a healthy pregnancy.
What are the signs of premature labor symptoms?
+Premature labor symptoms can include mild cramping, back pain, and vaginal discharge. Women may also experience a sudden gush of fluid, which can be a sign of the amniotic sac breaking.
What are the risk factors for premature labor?
+Risk factors for premature labor include a history of premature birth, multiple pregnancies, and certain medical conditions such as diabetes and hypertension.
How is premature labor diagnosed?
+Diagnosing premature labor typically involves a physical examination, medical history, and laboratory tests, including a pelvic exam, ultrasound, and urinalysis.
What are the treatment options for premature labor?
+Treatment options for premature labor depend on the gestational age and the severity of the symptoms, and may include bed rest, hospitalization, medications, and delivery.
How can women reduce the risk of premature labor?
+Women can reduce the risk of premature labor by maintaining a healthy weight, eating a balanced diet, staying hydrated, avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption, and attending regular prenatal check-ups.
We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of premature labor symptoms, risk factors, and treatment options. If you have any further questions or concerns, please do not hesitate to comment below or share this article with others who may benefit from this information. Remember, premature labor is a serious health concern that requires prompt medical attention, and by being informed and proactive, women can reduce the risk of complications and promote a healthy pregnancy.
