Intro
Identify Urinary Tract Infection signs, symptoms, and causes. Learn about UTI treatment, prevention, and management, including bladder infection, kidney infection, and recurring infections, to alleviate discomfort and promote urinary health.
Urinary tract infections, commonly referred to as UTIs, are a prevalent health issue affecting millions of people worldwide. These infections occur when bacteria, fungi, or viruses invade the urinary system, which includes the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra. Understanding the signs and symptoms of UTIs is crucial for early detection and treatment, as untreated infections can lead to severe complications, including kidney damage and sepsis. The importance of recognizing UTI signs cannot be overstated, as prompt medical intervention can significantly improve outcomes and reduce the risk of long-term health consequences.
UTIs can affect anyone, regardless of age or gender, although certain demographic groups are more susceptible. Women, for instance, are more likely to develop UTIs due to their shorter urethra, which facilitates bacterial entry into the bladder. Additionally, individuals with underlying medical conditions, such as diabetes, or those with compromised immune systems are at a higher risk of developing UTIs. The economic burden of UTIs is also significant, with millions of dollars spent annually on healthcare costs, lost productivity, and research into prevention and treatment strategies.
The impact of UTIs on quality of life should not be underestimated. Beyond the physical discomfort and pain, UTIs can cause emotional distress, disrupt daily routines, and lead to anxiety about future infections. This is why education on UTI prevention, recognition of signs and symptoms, and adherence to treatment plans is vital. By empowering individuals with knowledge, we can work towards reducing the incidence of UTIs and improving overall health outcomes. Understanding the complexities of UTIs, from their causes to their consequences, is the first step in managing and preventing these infections.
Understanding UTIs

Causes of UTIs
The primary cause of UTIs is the presence of pathogens in the urinary system. Escherichia coli (E. coli) is the most common bacteria responsible for UTIs, accounting for approximately 80% of cases. Other bacteria, such as Klebsiella pneumoniae and Pseudomonas aeruginosa, can also cause UTIs, especially in individuals with compromised immune systems or those using urinary catheters. Factors that increase the risk of UTIs include poor hygiene, sexual activity, use of certain types of birth control, and underlying medical conditions.Signs and Symptoms of UTIs
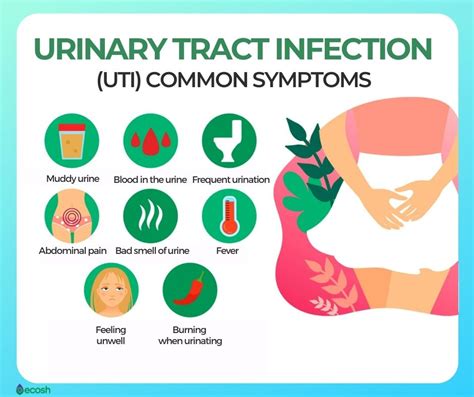
Differences in Symptoms by Age and Gender
Symptoms of UTIs can vary significantly across different age groups and genders. In infants and young children, UTIs may not present with the typical symptoms seen in adults. Instead, parents or caregivers may notice nonspecific signs such as fever, vomiting, or irritability. In older adults, UTIs can sometimes present with confusion or altered mental status, rather than the classic urinary symptoms.Diagnosis of UTIs
Importance of Accurate Diagnosis
Accurate diagnosis is crucial for effective treatment and prevention of complications. Misdiagnosis or delayed diagnosis can lead to prolonged suffering, increased risk of complications, and the development of antibiotic-resistant bacteria. Healthcare providers must consider the patient's symptoms, medical history, and laboratory results to make an informed diagnosis and develop an appropriate treatment plan.Treatment and Management of UTIs
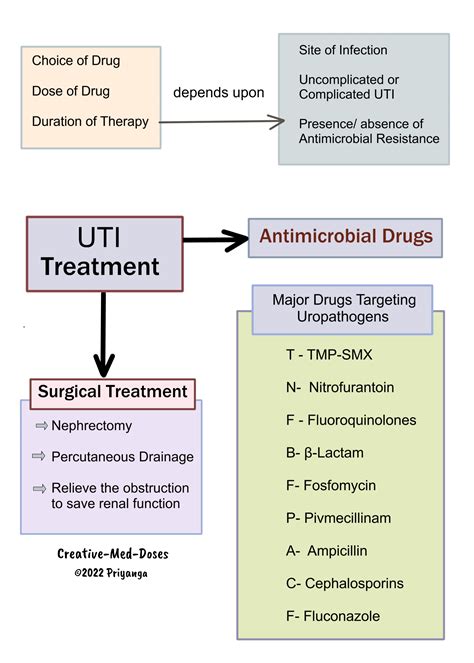
Self-Care Measures
In addition to antibiotic treatment, several self-care measures can help alleviate symptoms and support recovery. Drinking plenty of water to help flush out bacteria, avoiding irritants such as caffeine and spicy foods, and applying heat to the lower abdomen may help reduce discomfort. Practicing good hygiene, such as wiping from front to back after using the bathroom and urinating after sexual intercourse, can also help prevent recurrent infections.Prevention of UTIs
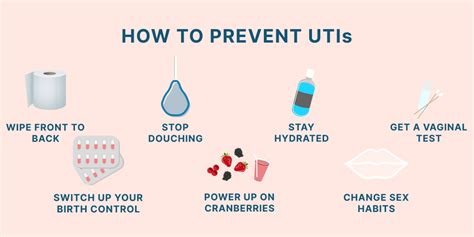
Role of Diet and Nutrition
Diet and nutrition play a significant role in UTI prevention. A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can help support immune function and reduce the risk of infection. Certain foods, such as cranberries, blueberries, and foods high in vitamin C, may have specific benefits in preventing UTIs due to their potential to prevent bacterial adhesion to the bladder and urinary tract walls.Complications of Untreated UTIs
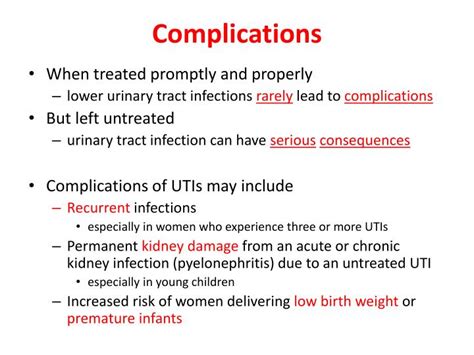
Long-Term Consequences
The long-term consequences of UTIs, especially if they become recurrent or chronic, can significantly impact quality of life. Individuals may experience persistent discomfort, anxiety about future infections, and the financial burden of ongoing medical care. Addressing the root causes of UTIs, whether through lifestyle changes, medical interventions, or a combination of both, is essential for preventing long-term consequences and improving overall health outcomes.Future Directions in UTI Management
Conclusion and Next Steps
In conclusion, urinary tract infections are a significant health concern that requires prompt attention and effective management. By understanding the signs and symptoms, causes, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention strategies for UTIs, individuals can take proactive steps to protect their health. It is essential for healthcare providers, researchers, and the public to work together to address the challenges posed by UTIs, from improving diagnosis and treatment to preventing recurrent infections. As we look to the future, our goal should be to reduce the incidence and impact of UTIs, enhancing the quality of life for millions of people worldwide.To further your understanding and stay updated on the latest developments in UTI management, consider the following steps:
- Engage with healthcare professionals and patient support groups to learn from their experiences and expertise.
- Stay informed about the latest research findings and clinical guidelines.
- Advocate for increased funding and support for UTI research and awareness campaigns.
- Share your knowledge with others to help prevent UTIs and promote better health outcomes.
What are the most common symptoms of a UTI?
+The most common symptoms of a UTI include a strong, persistent urge to urinate, burning sensation while urinating, passing frequent, small amounts of urine, and urine that appears cloudy, dark, or has a strong odor.
How are UTIs typically treated?
+UTIs are typically treated with antibiotics. The choice of antibiotic and duration of treatment depend on the severity of the infection, the type of bacteria causing the infection, and the patient's overall health.
Can UTIs be prevented?
+Yes, UTIs can be prevented through a combination of lifestyle modifications and hygiene practices. Drinking enough water, urinating when the need arises, practicing good hygiene, and avoiding irritants can help reduce the risk of UTIs.
