Intro
Discover 5 key simvastatin facts, including its uses, side effects, and interactions, to manage cholesterol and heart health effectively with statin therapy and medication management.
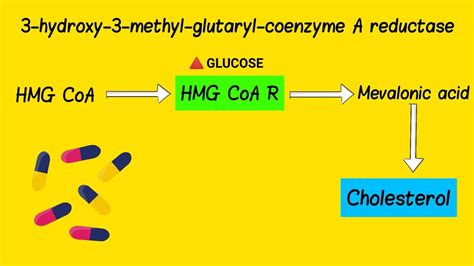
Simvastatin is a medication widely used to lower cholesterol levels in the blood, reducing the risk of heart disease. It belongs to a group of drugs known as statins, which work by inhibiting an enzyme in the liver (HMG-CoA reductase) that is necessary for the production of cholesterol. With its introduction in the late 1980s, simvastatin has become one of the most prescribed medications globally, due to its efficacy in managing hypercholesterolemia (high cholesterol) and preventing cardiovascular events. Understanding simvastatin's mechanism of action, its benefits, potential side effects, and how it compares to other statins can provide valuable insights into its role in modern medicine.
The importance of managing cholesterol levels cannot be overstated, given the significant impact high cholesterol can have on health. Elevated levels of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol, often referred to as "bad" cholesterol, can lead to the buildup of plaque in arteries, known as atherosclerosis. This condition can result in reduced or blocked blood flow, leading to heart attacks, strokes, and other cardiovascular diseases. Simvastatin, by reducing LDL cholesterol levels, plays a critical role in preventing these outcomes. Moreover, its use has been expanded to include individuals at high risk of cardiovascular events, even if their cholesterol levels are not significantly elevated, highlighting its potential in primary prevention.
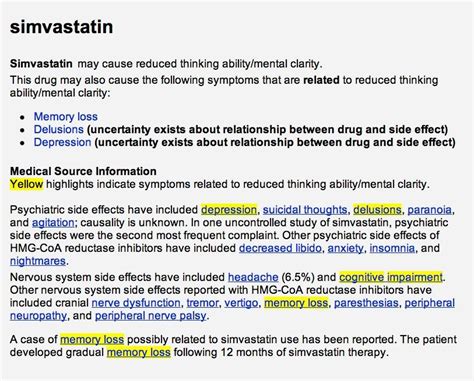
Simvastatin's effectiveness and relatively favorable side effect profile have contributed to its widespread adoption. However, like all medications, it is not without potential drawbacks. Side effects can include muscle pain, liver enzyme elevations, and, in rare cases, more severe conditions such as rhabdomyolysis (a serious syndrome due to direct or indirect muscle injury). It is also important to consider drug interactions, as simvastatin can be affected by other medications, either enhancing its effects or increasing the risk of side effects. Despite these considerations, for many patients, the benefits of simvastatin in reducing the risk of heart disease outweigh the potential risks, making it a cornerstone in the management of hypercholesterolemia.
How Simvastatin Works
Benefits of Simvastatin

Statins and Primary Prevention
The use of simvastatin and other statins in primary prevention has been a subject of considerable debate. Guidelines generally recommend statin therapy for primary prevention in individuals with elevated cardiovascular risk, defined by factors such as age, sex, cholesterol levels, blood pressure, diabetes, and smoking status. Simvastatin, due to its efficacy and cost-effectiveness, is often considered a first-line option for these patients. The decision to initiate statin therapy should be based on a comprehensive assessment of the patient's risk factors and a discussion of the potential benefits and risks of treatment.Potential Side Effects
Drug Interactions
Simvastatin, like other statins, is metabolized by the cytochrome P450 enzyme system in the liver, specifically the CYP3A4 enzyme. Drugs that inhibit this enzyme, such as certain antibiotics, antifungals, and protease inhibitors, can increase simvastatin levels in the blood, enhancing its effects and potentially increasing the risk of side effects. Conversely, drugs that induce CYP3A4 can decrease simvastatin levels, reducing its efficacy. It is crucial for patients to inform their healthcare provider about all medications they are taking to minimize the risk of adverse interactions.Comparison with Other Statins
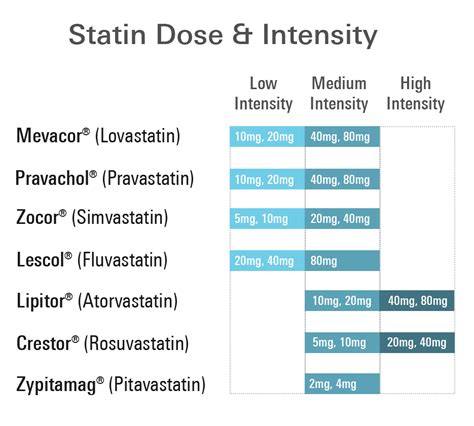
Dosing and Administration
Simvastatin is typically administered once daily in the evening, with or without food. The usual starting dose is 20-40 mg, which can be adjusted based on the patient's response to treatment. The maximum recommended dose is 80 mg per day, although this is rarely needed and should be used with caution due to an increased risk of side effects. Regular monitoring of cholesterol levels and liver function tests is recommended to assess the efficacy and safety of simvastatin therapy.Long-Term Use and Safety
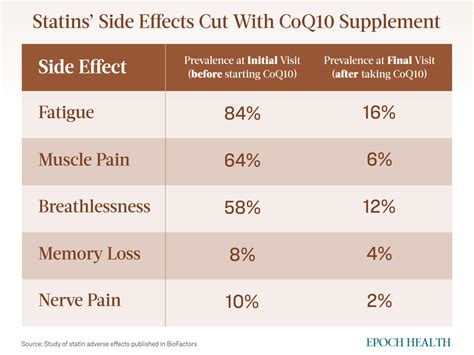
Patient Adherence and Education
Adherence to simvastatin therapy is crucial for achieving optimal lipid-lowering effects and reducing cardiovascular risk. Patient education plays a significant role in promoting adherence, as it helps patients understand the importance of their medication, how to manage potential side effects, and the need for regular follow-up appointments. Healthcare providers should also be mindful of the potential for statin intolerance and work with patients to find alternative treatments if necessary.Future Directions
Personalized Medicine
The future of statin therapy, including simvastatin, may lie in personalized medicine approaches, where treatment is tailored to the individual's genetic profile, lipid profile, and overall risk factors. Genetic testing can identify variants that affect an individual's response to statins, potentially guiding the choice of medication and dose. This personalized approach could optimize the benefits of simvastatin while minimizing risks, representing a significant advancement in the management of hypercholesterolemia and cardiovascular disease prevention.What is simvastatin used for?
+Simvastatin is used to lower cholesterol levels in the blood, reducing the risk of heart disease and stroke.
What are the common side effects of simvastatin?
+Common side effects include headache, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and muscle pain. More serious but rare side effects include myopathy and liver damage.
Can simvastatin be used in primary prevention?
+Yes, simvastatin can be used in primary prevention to reduce the risk of a first cardiovascular event in individuals with elevated cardiovascular risk factors.
How does simvastatin compare to other statins?
+Simvastatin is one of several statins available, each with its own profile. The choice of statin depends on factors including the patient's lipid profile, other medical conditions, potential drug interactions, and cost.
Is simvastatin safe for long-term use?
+The long-term safety of simvastatin has been extensively studied, and it is generally considered safe for most patients. However, regular monitoring is recommended to assess efficacy and safety.
As we conclude our in-depth exploration of simvastatin, it's clear that this medication has revolutionized the management of hypercholesterolemia and the prevention of cardiovascular disease. With its well-documented benefits, relatively favorable side effect profile, and cost-effectiveness, simvastatin remains a cornerstone in the treatment of high cholesterol. We invite you to share your thoughts, experiences, or questions about simvastatin in the comments below. Whether you're a healthcare professional seeking to deepen your understanding of statin therapy or an individual looking to manage your cholesterol levels, your engagement and feedback are invaluable. Let's work together to promote heart health and reduce the global burden of cardiovascular disease.
