Intro
The journey of embryonic development is a fascinating and complex process that transforms a fertilized egg into a fully formed baby. Understanding the size of an embryo by week is crucial for expectant parents, healthcare providers, and researchers alike. As we delve into the world of embryonic growth, it's essential to appreciate the remarkable transformations that occur during this critical period.
The early stages of embryonic development are characterized by rapid cell division, differentiation, and organization. During the first few weeks, the embryo undergoes a series of intricate processes, including implantation, gastrulation, and organogenesis. As the embryo grows and develops, its size increases significantly, and by the end of the embryonic period, it has formed all the major organs and body systems.
The size of an embryo by week is a vital indicator of its developmental progress. Healthcare providers use various methods, including ultrasound and fetal measurement, to monitor embryonic growth and detect any potential abnormalities. By tracking the size of the embryo, healthcare providers can assess its overall health and identify any potential risks or complications early on.
Embryo Size By Week
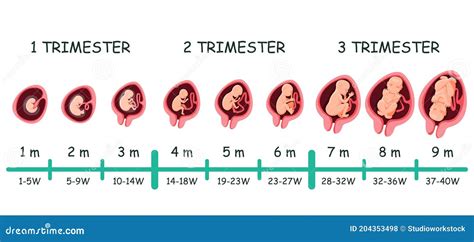
To better understand the growth trajectory of an embryo, let's break down its size by week:
- Week 1: The fertilized egg, now called a zygote, measures approximately 0.1-0.2 mm in diameter.
- Week 2: The zygote undergoes several cell divisions, forming a blastocyst that measures around 0.2-0.5 mm.
- Week 3: The blastocyst implants in the uterine lining, and its size increases to about 0.5-1 mm.
- Week 4: The embryo measures around 1-2 mm, and its major organs, such as the heart and liver, begin to form.
- Week 5: The embryo grows to approximately 2-3 mm, and its limbs, digits, and facial features start to develop.
- Week 6: The embryo measures around 3-4 mm, and its senses, including vision, hearing, and taste, begin to form.
- Week 7: The embryo grows to about 4-5 mm, and its nervous system, including the brain and spinal cord, starts to develop.
- Week 8: The embryo measures approximately 5-6 mm, and its major organs and body systems continue to mature.
Factors Influencing Embryo Size
Several factors can influence the size of an embryo, including:
- Genetic factors: The genetic material inherited from the parents can affect the embryo's growth rate and size.
- Environmental factors: Exposure to certain environmental toxins, such as pesticides or heavy metals, can impact embryonic development and size.
- Maternal health: The mother's overall health, including her nutrition, lifestyle, and medical conditions, can influence the embryo's growth and size.
- Multiple pregnancies: In cases of multiple pregnancies, such as twins or triplets, the embryos may be smaller than average due to shared resources.
Ultrasound Measurements
Ultrasound technology plays a vital role in monitoring embryonic growth and size. Healthcare providers use ultrasound measurements to: * Confirm pregnancy and detect any potential complications * Monitor embryonic growth and development * Detect any abnormalities or congenital defects * Estimate gestational age and due dateEmbryo Developmental Stages
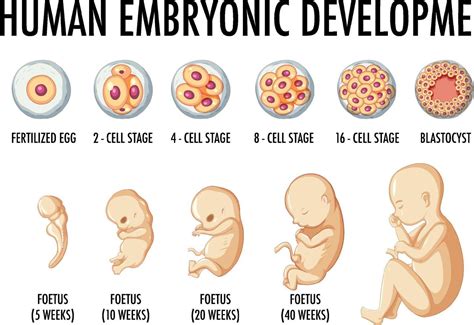
The embryonic period is divided into several stages, each characterized by significant developmental milestones:
- Cleavage stage (Week 1-2): The zygote undergoes several cell divisions, forming a blastocyst.
- Gastrulation stage (Week 2-3): The blastocyst undergoes gastrulation, forming the three primary germ layers: ectoderm, endoderm, and mesoderm.
- Organogenesis stage (Week 3-8): The germ layers differentiate into major organs and body systems.
- Fetal stage (Week 9-38): The embryo is now called a fetus, and its organs and body systems continue to mature and develop.
Common Embryo Size Measurements
Common embryo size measurements include: * Crown-rump length (CRL): Measures the length of the embryo from the crown of the head to the buttocks. * Biparietal diameter (BPD): Measures the diameter of the embryo's head. * Head circumference (HC): Measures the circumference of the embryo's head. * Abdominal circumference (AC): Measures the circumference of the embryo's abdomen.Importance Of Embryo Size Monitoring

Monitoring embryo size is essential for:
- Detecting potential growth restrictions or abnormalities
- Identifying multiple pregnancies or congenital defects
- Estimating gestational age and due date
- Providing personalized prenatal care and support
Potential Complications
Potential complications associated with abnormal embryo size include: * Growth restriction: The embryo may not be growing at a normal rate, which can increase the risk of stillbirth or low birth weight. * Congenital defects: Abnormal embryo size can be a sign of underlying congenital defects, such as heart defects or neural tube defects. * Multiple pregnancies: Abnormal embryo size can be a sign of multiple pregnancies, which can increase the risk of complications during pregnancy and childbirth.Conclusion And Next Steps

In conclusion, understanding the size of an embryo by week is crucial for monitoring its developmental progress and detecting any potential complications. By tracking embryo size, healthcare providers can provide personalized prenatal care and support, reducing the risk of complications and improving outcomes for both mother and baby. If you have any questions or concerns about embryo size or prenatal care, we encourage you to consult with your healthcare provider or leave a comment below.
What is the average size of an embryo at 6 weeks?
+The average size of an embryo at 6 weeks is approximately 3-4 mm.
How is embryo size measured during pregnancy?
+Embryo size is typically measured using ultrasound technology, which provides accurate and non-invasive measurements of the embryo's length, width, and other parameters.
What are the potential complications associated with abnormal embryo size?
+Potential complications associated with abnormal embryo size include growth restriction, congenital defects, and multiple pregnancies.
