Intro
Discover the importance of balanced sodium blood levels, understanding hyponatremia and hypernatremia, and maintaining healthy electrolyte levels for overall well-being.
The human body relies on a delicate balance of various substances to function properly, and one of the most critical components is sodium. Sodium is an essential mineral that plays a vital role in maintaining proper fluid balance, nerve function, and muscle contraction. However, when sodium levels in the blood become imbalanced, it can lead to a range of health problems. In this article, we will delve into the world of sodium blood levels, exploring what they are, how they are regulated, and what happens when they become disrupted.
Sodium is a naturally occurring mineral that is found in many foods, and it is also an essential component of various bodily functions. The body uses sodium to regulate the amount of water in cells, transmit nerve impulses, and contract and relax muscles. When sodium levels in the blood are within the normal range, the body functions properly, and overall health is maintained. However, when sodium levels become elevated or decreased, it can lead to a range of health problems, including seizures, muscle weakness, and even death.
The regulation of sodium levels in the blood is a complex process that involves the kidneys, hormones, and other bodily systems. The kidneys play a crucial role in maintaining sodium balance by adjusting the amount of sodium that is excreted in the urine. When sodium levels in the blood become elevated, the kidneys increase sodium excretion, and when levels become decreased, the kidneys reduce sodium excretion. Hormones, such as aldosterone, also play a vital role in regulating sodium levels by stimulating the kidneys to retain sodium. Understanding how sodium levels are regulated is essential for appreciating the importance of maintaining proper sodium balance.
Sodium Blood Level Regulation
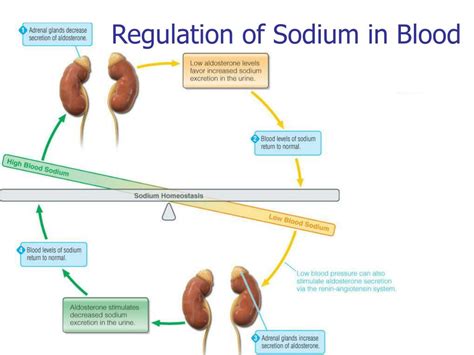
Importance of Sodium Balance
Maintaining proper sodium balance is essential for overall health and well-being. When sodium levels in the blood become imbalanced, it can lead to a range of health problems, including: * Seizures * Muscle weakness * Fatigue * Headaches * Nausea and vomiting * Abnormal heart rhythms Proper sodium balance is also essential for maintaining proper blood pressure, as elevated sodium levels can lead to high blood pressure, which is a major risk factor for heart disease, stroke, and kidney disease.Sodium Blood Level Imbalance

Treatment and Prevention
Treatment for a sodium imbalance typically involves addressing the underlying cause of the imbalance. For example, if dehydration is the cause, treatment may involve administering fluids and electrolytes to help restore proper sodium balance. If excessive sodium intake is the cause, treatment may involve reducing sodium intake and increasing potassium intake to help balance out the sodium levels. In some cases, medications may be prescribed to help regulate sodium levels.Prevention is also key when it comes to maintaining proper sodium balance. This can involve:
- Eating a balanced diet that is low in sodium
- Staying hydrated by drinking plenty of water
- Avoiding excessive sodium intake
- Getting regular check-ups to monitor sodium levels
- Managing underlying medical conditions, such as kidney disease or hormonal imbalances
Sodium Blood Level Testing

There are several types of sodium blood level tests, including:
- Fasting sodium test: This test involves measuring sodium levels in the blood after an overnight fast.
- Random sodium test: This test involves measuring sodium levels in the blood at any time of day.
- Urine sodium test: This test involves measuring the amount of sodium in the urine.
Interpreting Test Results
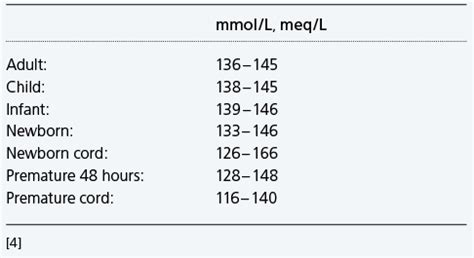
Interpreting sodium blood level test results can be complex, and it is essential to consult with a healthcare professional to understand the results. In general, a sodium level that is: * Below 135 mmol/L is considered low * Between 135 and 145 mmol/L is considered normal * Above 145 mmol/L is considered high However, the interpretation of test results can vary depending on the individual and the underlying medical condition.Sodium Blood Level Management
Role of Diet and Lifestyle
Diet and lifestyle play a critical role in managing sodium blood levels. A balanced diet that is low in sodium can help to maintain proper sodium balance, while a diet that is high in sodium can lead to sodium imbalances. Additionally, staying hydrated by drinking plenty of water can help to maintain proper sodium balance.Lifestyle factors, such as stress and physical activity, can also impact sodium blood levels. For example, stress can cause the body to retain sodium, leading to elevated sodium levels, while physical activity can help to reduce sodium levels.
Sodium Blood Level Complications
Long-Term Consequences
The long-term consequences of a sodium imbalance can be severe and include: * Kidney disease * Heart disease * Stroke * Osteoporosis * Cognitive impairment It is essential to manage sodium blood levels properly to prevent these long-term consequences.Sodium Blood Level and Other Medical Conditions

Impact on Quality of Life
Sodium imbalances can significantly impact quality of life, causing symptoms such as fatigue, weakness, and confusion. Additionally, sodium imbalances can increase the risk of long-term complications, such as kidney disease and heart disease.Sodium Blood Level Research

Future Directions
Future research on sodium blood levels is likely to focus on developing new treatments and prevention strategies. For example, researchers may develop new medications that can help to regulate sodium levels, or new dietary approaches that can help to prevent sodium imbalances.What is a normal sodium blood level?
+A normal sodium blood level is between 135 and 145 mmol/L, although this can vary slightly depending on the laboratory and the individual.
What are the symptoms of a sodium imbalance?
+The symptoms of a sodium imbalance can include seizures, muscle weakness, fatigue, headaches, nausea and vomiting, and abnormal heart rhythms.
How can I prevent a sodium imbalance?
+You can prevent a sodium imbalance by eating a balanced diet that is low in sodium, staying hydrated by drinking plenty of water, and managing underlying medical conditions, such as kidney disease or hormonal imbalances.
What are the long-term consequences of a sodium imbalance?
+The long-term consequences of a sodium imbalance can include kidney disease, heart disease, stroke, osteoporosis, and cognitive impairment.
How is a sodium imbalance diagnosed?
+A sodium imbalance is typically diagnosed with a blood test that measures the level of sodium in the blood.
In conclusion, maintaining proper sodium balance is essential for overall health and well-being. By understanding how sodium levels are regulated, the importance of sodium balance, and the complications that can occur when sodium levels become imbalanced, individuals can take steps to prevent sodium imbalances and maintain proper sodium balance. We encourage readers to share their thoughts and experiences with sodium imbalances in the comments below and to take action to prioritize their health by managing their sodium levels. Additionally, we invite readers to share this article with others who may be interested in learning more about sodium blood levels and how to maintain proper sodium balance.
