Intro
Learn about the stages of kidney disease, from mild kidney damage to end-stage renal failure, and understand chronic kidney disease symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options for each stage.
Kidney disease is a serious health condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It is a progressive disease, meaning that it can worsen over time if left untreated or poorly managed. Understanding the stages of kidney disease is crucial for patients, caregivers, and healthcare professionals to provide effective care and management. In this article, we will delve into the different stages of kidney disease, their characteristics, and the importance of early detection and treatment.
Kidney disease can be caused by a variety of factors, including diabetes, high blood pressure, family history, and age. The disease can progress slowly over many years, and symptoms may not appear until the later stages. This is why it is essential to be aware of the risk factors and to undergo regular check-ups to detect any potential problems early on. Early detection and treatment can significantly slow down the progression of kidney disease and improve the quality of life for patients.
The progression of kidney disease can be divided into five distinct stages, each with its own set of characteristics and treatment options. Understanding these stages is vital for developing effective treatment plans and improving patient outcomes. In the following sections, we will explore each stage of kidney disease in detail, including its symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options.
Introduction to Kidney Disease Stages
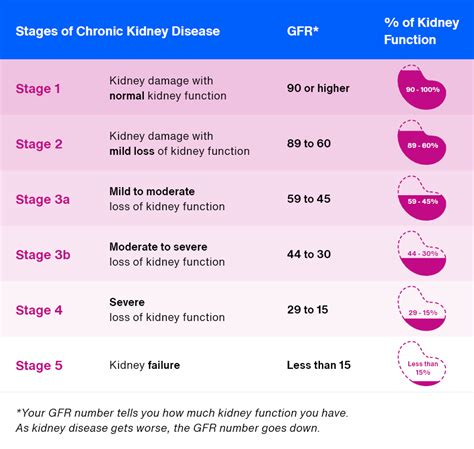
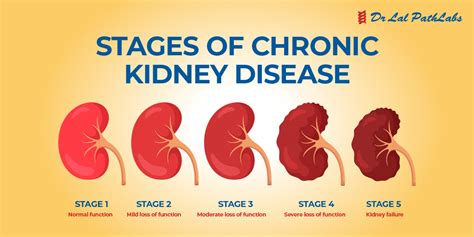
Stage 1: Kidney Damage with Normal GFR
In stage 1, the kidneys are damaged, but the GFR is still within the normal range. This stage is often asymptomatic, and patients may not be aware that they have kidney disease. However, it is essential to address any underlying conditions, such as high blood pressure or diabetes, to prevent further damage to the kidneys.Stage 2: Kidney Damage with Mild Decrease in GFR
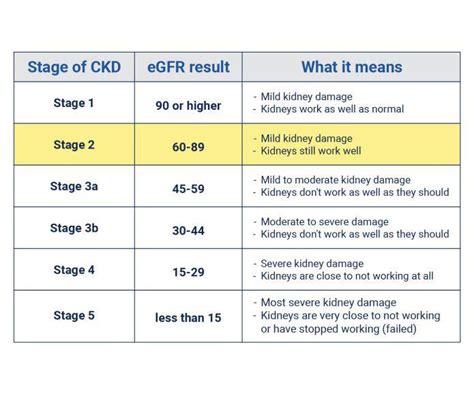
Stage 3: Moderate Decrease in GFR
Stage 3 is divided into two sub-stages: 3A and 3B. In stage 3A, the GFR is moderately decreased, and patients may start to experience symptoms such as fatigue, swelling, and frequent urination. In stage 3B, the GFR is further decreased, and patients may experience more severe symptoms, including anemia, bone disease, and cardiovascular disease.Stage 4: Severe Decrease in GFR
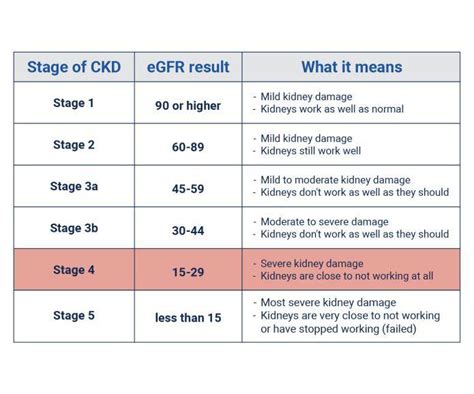
Treatment Options for Kidney Disease
Treatment options for kidney disease vary depending on the stage and severity of the disease. In the early stages, lifestyle modifications, such as a healthy diet and regular exercise, can help slow down the progression of the disease. In later stages, medications, dialysis, or a kidney transplant may be necessary to manage symptoms and improve quality of life.Stage 5: End-Stage Renal Disease (ESRD)
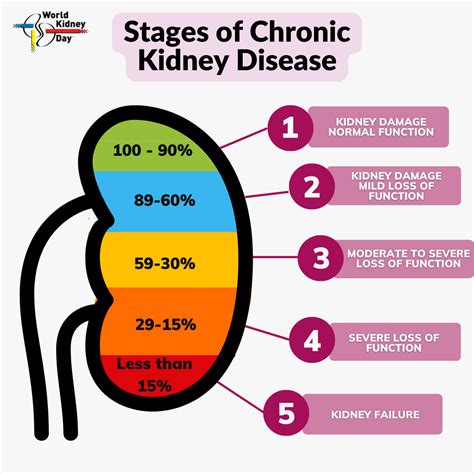
Importance of Early Detection and Treatment
Early detection and treatment of kidney disease are crucial to slow down the progression of the disease and improve patient outcomes. Regular check-ups, monitoring of kidney function, and lifestyle modifications can help prevent or delay the onset of kidney disease. In addition, early treatment can help manage symptoms, slow down disease progression, and improve quality of life for patients.Kidney Disease Management and Prevention
Common Causes of Kidney Disease
Kidney disease can be caused by a variety of factors, including: * Diabetes * High blood pressure * Family history * Age * Obesity * Smoking * Certain medicationsDiagnosis and Testing for Kidney Disease
Treatment Options for Kidney Disease
Treatment options for kidney disease vary depending on the stage and severity of the disease. The following are some common treatment options: * Lifestyle modifications * Medications * Dialysis * Kidney transplantLiving with Kidney Disease
Coping with Kidney Disease
Coping with kidney disease can be challenging, both physically and emotionally. Patients may experience a range of emotions, including anxiety, depression, and frustration. The following tips can help patients cope with kidney disease: * Seek support from family and friends * Join a support group * Practice stress-reducing techniques, such as meditation or yoga * Focus on positive aspects of lifeKidney Disease and Mental Health

Conclusion and Next Steps
In conclusion, kidney disease is a serious health condition that requires early detection, treatment, and ongoing management. By understanding the stages of kidney disease, patients and healthcare professionals can work together to develop effective treatment plans and improve patient outcomes. If you or someone you know has kidney disease, it is essential to seek medical attention and follow a comprehensive treatment plan to manage the condition and improve quality of life.What are the symptoms of kidney disease?
+The symptoms of kidney disease can vary depending on the stage and severity of the disease. Common symptoms include fatigue, swelling, frequent urination, nausea, and vomiting.
How is kidney disease diagnosed?
+Kidney disease is diagnosed using a combination of physical exams, medical history, laboratory tests, and imaging studies.
What are the treatment options for kidney disease?
+Treatment options for kidney disease vary depending on the stage and severity of the disease. Common treatment options include lifestyle modifications, medications, dialysis, and kidney transplant.
Can kidney disease be prevented?
+Yes, kidney disease can be prevented or delayed by maintaining a healthy diet and weight, exercising regularly, monitoring and controlling blood pressure and blood sugar levels, and avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption.
What is the prognosis for kidney disease?
+The prognosis for kidney disease varies depending on the stage and severity of the disease. With early detection and treatment, patients can manage their condition and improve their quality of life.
