Intro
Discover 5 ways Sjögrens syndrome impacts health, affecting autoimmune, inflammatory, and neurological systems, causing dryness, fatigue, and pain, with related conditions like lupus and rheumatoid arthritis.
The impact of Systemic Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis (sJIA) on health is a topic of great importance, as it affects not only the individuals diagnosed with the condition but also their families and caregivers. sJIA is a rare and chronic autoimmune disorder that causes inflammation in various parts of the body, including the joints, skin, and internal organs. Understanding the effects of sJIA on health is crucial for developing effective treatment plans and improving the quality of life for those affected. In this article, we will delve into the various ways sJIA impacts health, exploring the physical, emotional, and social consequences of the condition.
sJIA is a complex condition that can manifest differently in each individual, making it challenging to diagnose and treat. The symptoms of sJIA can range from mild to severe and may include fever, rash, joint pain and swelling, and inflammation of internal organs such as the liver and spleen. If left untreated or poorly managed, sJIA can lead to significant morbidity and mortality. Therefore, it is essential to recognize the signs and symptoms of sJIA and seek medical attention promptly.
The diagnosis of sJIA can be a life-altering event, affecting not only the individual but also their loved ones. The condition requires ongoing medical care, including regular check-ups, laboratory tests, and medications to manage symptoms and prevent complications. Additionally, individuals with sJIA may need to make lifestyle modifications, such as maintaining a healthy diet, exercising regularly, and getting sufficient rest, to help manage their condition. In this article, we will explore the five ways sJIA impacts health, including its effects on physical health, mental health, social relationships, daily activities, and overall well-being.
Physical Health Impacts
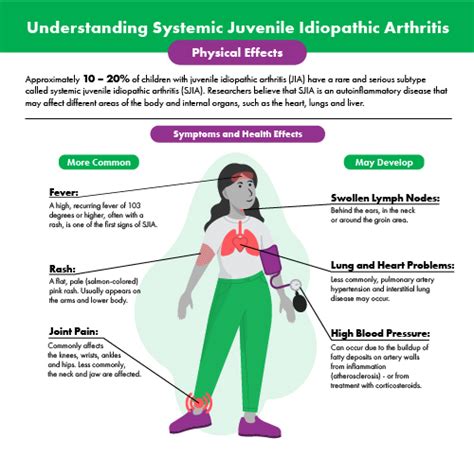
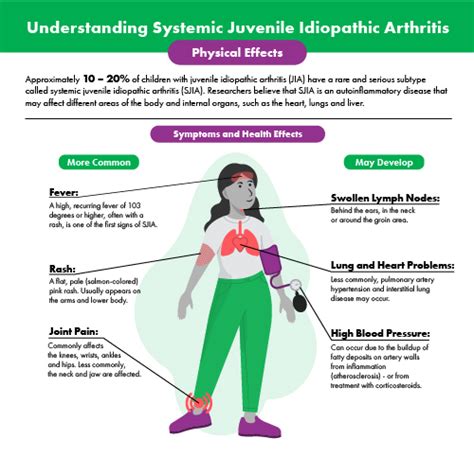
Some of the physical health impacts of sJIA include:
- Joint pain and swelling
- Limited mobility and flexibility
- Inflammation of internal organs
- Osteoporosis and increased risk of fractures
- Growth and development delays in children and adolescents
Mental Health Impacts
Some of the mental health impacts of sJIA include:
- Anxiety and depression
- Stress and emotional distress
- Fear and uncertainty related to symptoms and flares
- Body image issues and self-esteem problems
- Social withdrawal and isolation
Social Relationship Impacts
Some of the social relationship impacts of sJIA include:
- Social isolation and loneliness
- Decreased social support and networking
- Strained relationships with family and friends
- Difficulty maintaining romantic relationships
- Challenges in forming and maintaining friendships
Daily Activity Impacts

Some of the daily activity impacts of sJIA include:
- Decreased productivity and efficiency
- Reduced participation in hobbies and interests
- Difficulty maintaining a regular routine
- Challenges in performing daily tasks and chores
- Need for assistance with daily activities
Overall Well-being Impacts
Some of the overall well-being impacts of sJIA include:
- Decreased quality of life
- Increased emotional distress and psychological burden
- Social isolation and loneliness
- Decreased overall well-being and life satisfaction
- Need for ongoing medical care and support
Managing sJIA and Improving Health Outcomes
Managing sJIA requires a comprehensive approach, incorporating medical treatment, lifestyle modifications, and emotional support. Individuals with sJIA should work closely with their healthcare providers to develop a personalized treatment plan, including medications, physical therapy, and lifestyle modifications. Additionally, individuals with sJIA can benefit from emotional support, including counseling, support groups, and online resources.Some strategies for managing sJIA and improving health outcomes include:
- Working closely with healthcare providers to develop a personalized treatment plan
- Maintaining a healthy diet and exercising regularly
- Getting sufficient rest and practicing stress-reducing techniques
- Participating in support groups and online communities
- Staying informed about the latest research and treatment options
Future Directions and Research
Research into sJIA is ongoing, with scientists and healthcare providers working to develop new treatments and improve our understanding of the condition. Future directions for research include the development of more effective medications, the exploration of alternative therapies, and the investigation of the genetic and environmental factors that contribute to sJIA.Some areas of future research into sJIA include:
- Development of more effective medications and treatments
- Exploration of alternative therapies, such as acupuncture and mindfulness
- Investigation of the genetic and environmental factors that contribute to sJIA
- Development of personalized treatment plans and precision medicine approaches
- Improvement of healthcare outcomes and quality of life for individuals with sJIA
What are the most common symptoms of sJIA?
+The most common symptoms of sJIA include fever, rash, joint pain and swelling, and inflammation of internal organs such as the liver and spleen.
How is sJIA diagnosed?
+sJIA is diagnosed based on a combination of clinical features, laboratory tests, and imaging studies. A diagnosis of sJIA is typically made by a pediatric rheumatologist or other healthcare provider with expertise in the condition.
What are the treatment options for sJIA?
+Treatment options for sJIA include medications such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs), and biologic agents. Additionally, individuals with sJIA may benefit from physical therapy, occupational therapy, and lifestyle modifications such as maintaining a healthy diet and exercising regularly.
Can sJIA be cured?
+Currently, there is no cure for sJIA. However, with proper treatment and management, individuals with sJIA can experience significant improvement in their symptoms and quality of life.
What are the long-term complications of sJIA?
+The long-term complications of sJIA can include joint damage, osteoporosis, and increased risk of infections. Additionally, individuals with sJIA may be at increased risk for developing other autoimmune disorders and certain types of cancer.
In conclusion, sJIA is a complex and multifaceted condition that can have significant impacts on health, including physical, emotional, and social consequences. By understanding the effects of sJIA on health and working closely with healthcare providers, individuals with sJIA can develop effective treatment plans and improve their overall quality of life. We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with sJIA, and to join the conversation about this important topic. Together, we can work towards improving our understanding of sJIA and developing new and innovative treatments for this condition.
