Intro
Learn about Strep B in pregnancy risks, symptoms, and prevention methods, including Group B strep testing, transmission, and treatment options to minimize newborn complications and ensure a healthy delivery.
Pregnancy is a time of great joy and anticipation, but it can also be a time of concern for expectant mothers. One of the many things that pregnant women worry about is the risk of Group B strep (GBS) infection. Group B strep is a type of bacteria that can be present in the vagina and rectum of healthy women, and it can be passed to the baby during delivery. While GBS is not typically a cause for concern in healthy adults, it can be a serious problem for newborns. In this article, we will explore the risks of strep B in pregnancy, the symptoms and diagnosis, and the treatment options available.
The importance of understanding the risks of strep B in pregnancy cannot be overstated. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), GBS is a leading cause of illness and death among newborns. In fact, it is estimated that 1 in 4 pregnant women carry GBS, and if left untreated, it can pose a significant risk to the health of the baby. This is why it is essential for pregnant women to be aware of the risks and take steps to minimize them.
The risks associated with strep B in pregnancy are significant. If a woman has GBS, she can pass it to her baby during delivery, which can lead to serious health problems, including sepsis, pneumonia, and meningitis. These conditions can be life-threatening and require immediate medical attention. Additionally, GBS can also increase the risk of premature birth, low birth weight, and stillbirth. It is essential for pregnant women to be aware of these risks and take steps to minimize them.
Understanding Group B Strep

Group B strep is a type of bacteria that is commonly found in the vagina and rectum of healthy women. It is estimated that up to 25% of healthy women carry GBS, although it is not typically a cause for concern. However, during pregnancy, GBS can pose a significant risk to the health of the baby. This is because the bacteria can be passed to the baby during delivery, where it can cause serious health problems.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
The symptoms of GBS can vary, but they often include fever, chills, and flu-like symptoms. In some cases, women may not experience any symptoms at all. The diagnosis of GBS typically involves a vaginal and rectal swab test between 35 and 37 weeks of pregnancy. This test can detect the presence of GBS and help healthcare providers determine the best course of treatment.Risks of Strep B in Pregnancy
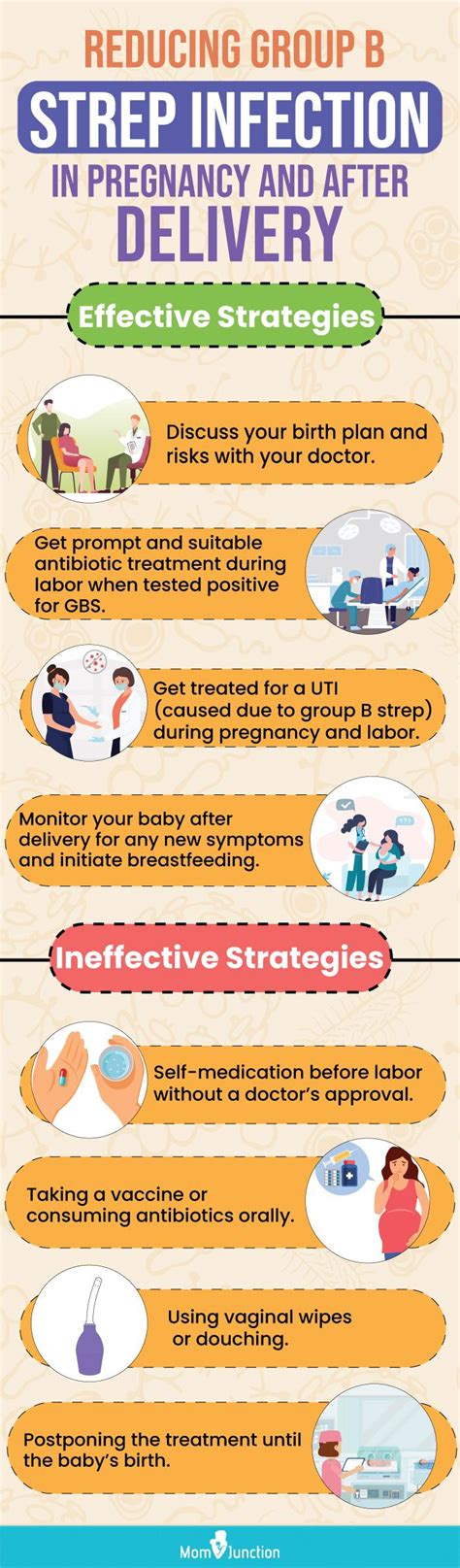
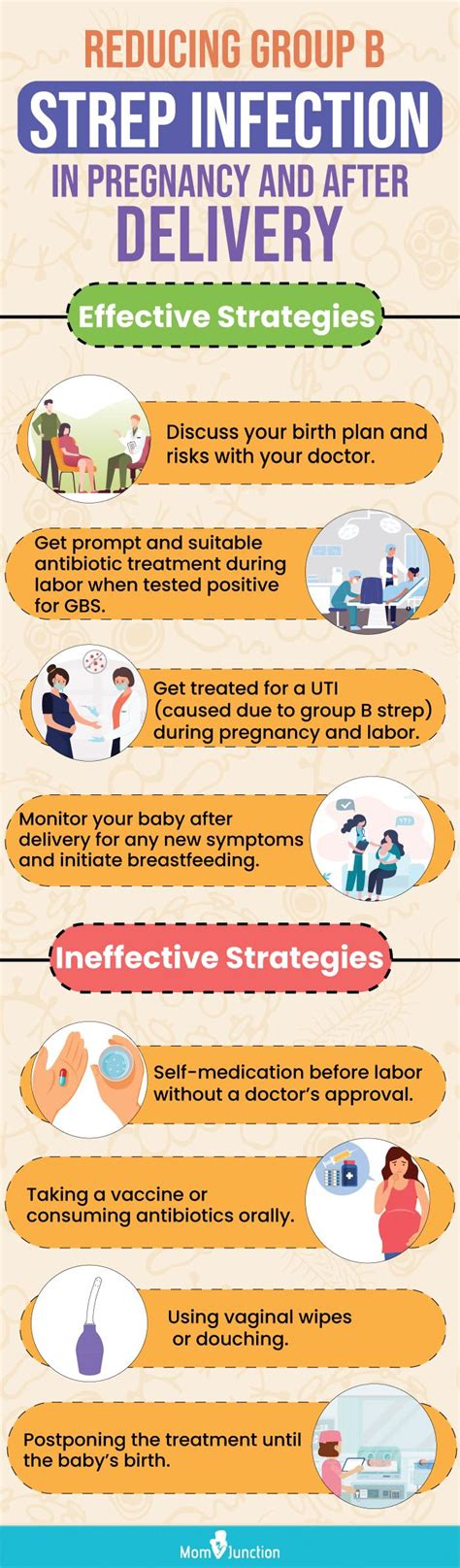
The risks of strep B in pregnancy are significant. If a woman has GBS, she can pass it to her baby during delivery, which can lead to serious health problems. These risks include:
- Sepsis: a life-threatening condition that occurs when the body's response to an infection becomes uncontrolled and causes widespread inflammation.
- Pneumonia: a serious infection that can cause inflammation of the lungs and make it difficult for the baby to breathe.
- Meningitis: a serious infection that can cause inflammation of the membranes surrounding the brain and spinal cord.
- Premature birth: GBS can increase the risk of premature birth, which can lead to a range of health problems for the baby.
- Low birth weight: GBS can also increase the risk of low birth weight, which can lead to a range of health problems for the baby.
- Stillbirth: in some cases, GBS can increase the risk of stillbirth, which is the death of a baby before birth.
Treatment Options
If a woman is diagnosed with GBS, there are several treatment options available. These include: * Antibiotics: antibiotics can be given to the mother during labor to reduce the risk of passing GBS to the baby. * Monitoring: healthcare providers may monitor the baby closely after birth to watch for signs of infection. * Supportive care: in some cases, supportive care may be necessary to help the baby recover from an infection.Prevention and Management

While there is no surefire way to prevent GBS, there are several steps that pregnant women can take to minimize the risks. These include:
- Getting tested for GBS between 35 and 37 weeks of pregnancy.
- Following good hygiene practices, such as washing hands regularly and avoiding close contact with anyone who is sick.
- Avoiding close contact with anyone who has a weakened immune system.
- Getting regular prenatal care to monitor the health of the baby and detect any potential problems early.
Reducing the Risk of Transmission
If a woman is diagnosed with GBS, there are several steps that can be taken to reduce the risk of transmission to the baby. These include: * Receiving antibiotics during labor to reduce the risk of passing GBS to the baby. * Having a cesarean delivery, which can reduce the risk of transmission. * Avoiding rupture of membranes, which can reduce the risk of transmission.Coping with a GBS Diagnosis

Receiving a diagnosis of GBS can be stressful and overwhelming. However, there are several steps that pregnant women can take to cope with the diagnosis and minimize the risks. These include:
- Following the recommended treatment plan, which may include antibiotics during labor.
- Staying informed about GBS and the risks associated with it.
- Seeking support from healthcare providers, family, and friends.
- Practicing good self-care, such as getting plenty of rest and eating a healthy diet.
Support and Resources
There are several resources available to support pregnant women who have been diagnosed with GBS. These include: * Healthcare providers, who can provide guidance and support throughout the pregnancy. * Online support groups, which can provide a safe and supportive community for women to connect with others who have been diagnosed with GBS. * Educational materials, which can provide information and resources to help women understand GBS and the risks associated with it.Conclusion and Next Steps
In conclusion, strep B in pregnancy is a serious condition that requires prompt attention and treatment. While the risks associated with GBS are significant, there are several steps that pregnant women can take to minimize them. By understanding the risks and taking steps to prevent transmission, pregnant women can help ensure a healthy pregnancy and a healthy baby.
We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with strep B in pregnancy in the comments below. If you have any questions or concerns, please don't hesitate to reach out to your healthcare provider. Additionally, if you found this article informative and helpful, please share it with others who may be interested.
What is Group B strep?
+Group B strep is a type of bacteria that can be present in the vagina and rectum of healthy women. It can be passed to the baby during delivery, where it can cause serious health problems.
What are the symptoms of GBS?
+The symptoms of GBS can vary, but they often include fever, chills, and flu-like symptoms. In some cases, women may not experience any symptoms at all.
How is GBS diagnosed?
+The diagnosis of GBS typically involves a vaginal and rectal swab test between 35 and 37 weeks of pregnancy. This test can detect the presence of GBS and help healthcare providers determine the best course of treatment.
What are the risks of GBS in pregnancy?
+The risks of GBS in pregnancy include sepsis, pneumonia, meningitis, premature birth, low birth weight, and stillbirth. These risks can be minimized by following the recommended treatment plan and taking steps to prevent transmission.
How can I reduce the risk of transmission?
+To reduce the risk of transmission, women can receive antibiotics during labor, have a cesarean delivery, and avoid rupture of membranes. Additionally, following good hygiene practices and avoiding close contact with anyone who is sick can also help minimize the risks.
