Intro
Act fast with 5 ways to respond to stroke symptoms, including warning signs, emergency response, and prevention methods, to minimize brain damage and improve recovery chances with prompt medical attention and timely treatment.
Strokes are a leading cause of disability and death worldwide, affecting millions of people each year. The impact of a stroke can be devastating, not only for the individual but also for their loved ones. However, with advancements in medical technology and a better understanding of stroke prevention, there are ways to reduce the risk of stroke and improve outcomes for those who have experienced one. In this article, we will explore five ways to act fast in the event of a stroke, as well as discuss the importance of stroke prevention and treatment.
The importance of acting quickly in the event of a stroke cannot be overstated. Every minute counts, as the sooner medical attention is received, the better the chances of survival and minimizing damage. Stroke awareness is crucial, and recognizing the signs of a stroke is the first step in taking action. The acronym FAST is often used to remember the signs of a stroke: Face, Arm, Speech, and Time. If someone's face is drooping, they are unable to lift their arm, or their speech is slurred, it's time to call for emergency services.
Strokes can be classified into three main types: ischemic, hemorrhagic, and transient ischemic attack (TIA). Ischemic strokes occur when a blood vessel in the brain is blocked, while hemorrhagic strokes occur when a blood vessel in the brain ruptures. TIAs, also known as "mini-strokes," are temporary and often a warning sign of a future stroke. Understanding the type of stroke is essential for determining the best course of treatment. With the right medical attention, it's possible to reduce the risk of long-term damage and improve outcomes.
Acting Fast in the Event of a Stroke
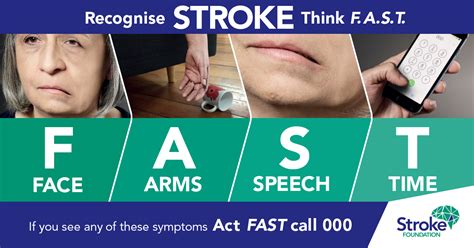
Recognizing the Signs of a Stroke
Recognizing the signs of a stroke is the first step in taking action. The FAST acronym is a useful tool for remembering the signs of a stroke: Face, Arm, Speech, and Time. If someone's face is drooping, they are unable to lift their arm, or their speech is slurred, it's time to call for emergency services. Other signs of a stroke may include sudden weakness or numbness in the face, arm, or leg, difficulty seeing or walking, and severe headache.Calling for Emergency Services

Providing Medical History
Providing medical history is crucial in the event of a stroke. This information can help medical professionals determine the best course of treatment and identify any potential underlying conditions that may have contributed to the stroke. Medical history should include any pre-existing medical conditions, medications, and allergies.Administering Medication

Seeking Follow-Up Care
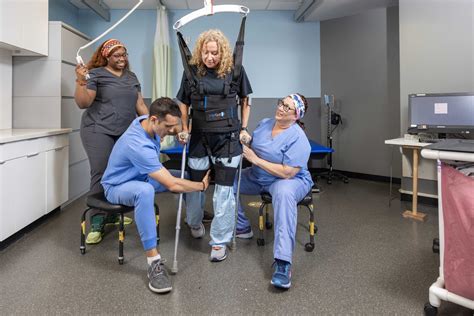
Seeking follow-up care is essential after a stroke. This may include rehabilitation, such as physical, occupational, and speech therapy, to help regain lost abilities. Follow-up care may also involve lifestyle changes, such as quitting smoking, exercising regularly, and eating a healthy diet, to reduce the risk of future strokes.Stroke Prevention

- Quitting smoking
- Exercising regularly
- Eating a healthy diet
- Maintaining a healthy weight
- Managing stress
- Getting enough sleep
- Monitoring blood pressure and cholesterol levels
By taking these steps, individuals can significantly reduce their risk of stroke and improve overall health.
Treatment Options

Recovery and Rehabilitation
Conclusion and Next Steps

What are the signs of a stroke?
+The signs of a stroke include sudden weakness or numbness in the face, arm, or leg, difficulty seeing or walking, and severe headache. The FAST acronym is a useful tool for remembering the signs of a stroke: Face, Arm, Speech, and Time.
How can I reduce my risk of stroke?
+There are several ways to reduce your risk of stroke, including quitting smoking, exercising regularly, eating a healthy diet, maintaining a healthy weight, managing stress, getting enough sleep, and monitoring blood pressure and cholesterol levels.
What are the treatment options for stroke?
+Treatment options for stroke vary depending on the type and severity of the stroke. In some cases, medication may be used to dissolve blood clots or prevent further clotting. In other cases, surgery may be necessary to remove blood clots or repair damaged blood vessels. Rehabilitation, such as physical, occupational, and speech therapy, may also be necessary to help regain lost abilities.
