Intro
Discover Suboxones generic name, Buprenorphine, a medication for opioid addiction treatment, offering recovery solutions with opioid dependence therapy and narcotic addiction management.
The importance of understanding Suboxone and its generic name, buprenorphine, cannot be overstated, especially in the context of addressing opioid addiction. Opioid addiction is a pervasive issue that affects millions of people worldwide, causing immense suffering for individuals and their loved ones. The need for effective treatments is critical, and medications like Suboxone have been at the forefront of these efforts. Suboxone, which combines buprenorphine and naloxone, is a medication used to treat opioid use disorder, helping individuals manage withdrawal symptoms and reduce cravings.
As the opioid crisis continues to evolve, the role of medications such as Suboxone has become increasingly vital. These medications are part of a broader approach known as medication-assisted treatment (MAT), which combines pharmaceutical interventions with counseling and behavioral therapy to provide a comprehensive treatment plan. The generic name, buprenorphine, refers specifically to the active ingredient in Suboxone that interacts with the brain's opioid receptors, mitigating the effects of opioid withdrawal and reducing the desire to use opioids.
Understanding how Suboxone works, its benefits, and its potential side effects is essential for individuals considering this treatment option. Furthermore, recognizing the distinction between Suboxone and its generic counterpart, buprenorphine, can help in making informed decisions about treatment. The difference lies not only in the formulation, with Suboxone containing both buprenorphine and naloxone, but also in how these medications are perceived and prescribed within the medical community. Naloxone, an opioid antagonist, is added to discourage misuse of the medication, as it can precipitate withdrawal if the medication is injected.
Introduction to Buprenorphine
Buprenorphine, the generic name for Suboxone, is a partial opioid agonist, meaning it activates the opioid receptors in the brain but to a lesser extent than full agonists like heroin or methadone. This partial activation is sufficient to suppress withdrawal symptoms and reduce cravings without producing the intense "high" or dangerous side effects associated with full opioid agonists. The unique pharmacological profile of buprenorphine makes it an attractive option for treating opioid addiction, as it provides a safer alternative for managing withdrawal and maintaining sobriety.
Benefits of Buprenorphine
The benefits of buprenorphine are multifaceted, including its efficacy in reducing withdrawal symptoms, its safety profile compared to full opioid agonists, and its flexibility in dosing. Buprenorphine can be administered in various forms, including sublingual tablets and films, as well as implants and injectables, offering a range of options for patients. Its long-acting nature means that it can provide around-the-clock management of opioid cravings and withdrawal, which is crucial for individuals in the early stages of recovery.Working Mechanism of Suboxone
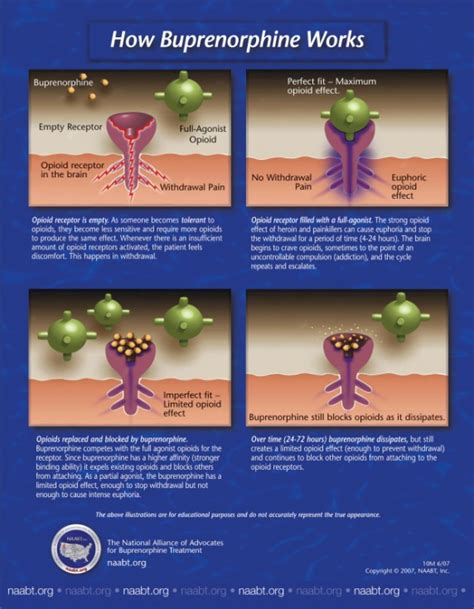
Suboxone works by combining buprenorphine, which acts as a partial opioid agonist, and naloxone, an opioid antagonist. The buprenorphine component helps to alleviate withdrawal symptoms and reduce cravings, while the naloxone component is included to deter misuse. If Suboxone is taken as prescribed (sublingually), the naloxone has minimal effect. However, if the medication is crushed and injected, the naloxone can precipitate withdrawal, thus discouraging intravenous use.
Steps to Initiate Treatment with Suboxone
Initiating treatment with Suboxone involves several steps, including: - **Assessment and Diagnosis**: A healthcare provider assesses the individual's opioid use disorder and determines if Suboxone is an appropriate treatment option. - **Induction**: The process of starting Suboxone, which typically occurs when the individual is in a state of mild to moderate withdrawal. This timing is crucial to minimize discomfort and ensure the medication's efficacy. - **Stabilization**: After the initial induction phase, the dosage of Suboxone may be adjusted to find the optimal level for managing withdrawal symptoms and cravings. - **Maintenance**: The long-term phase of treatment, where the goal is to maintain sobriety and prevent relapse.Benefits and Side Effects of Suboxone
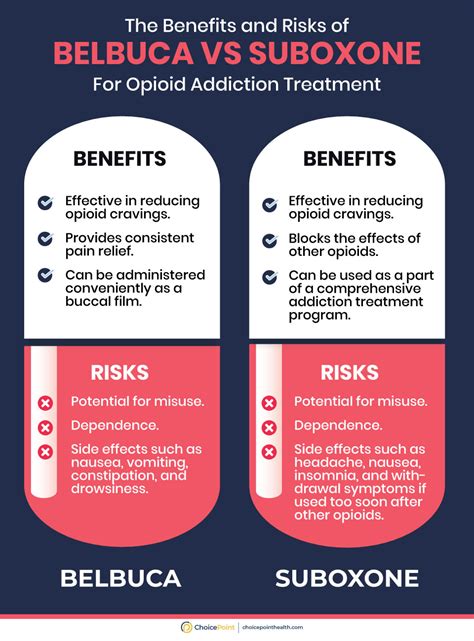
The benefits of Suboxone include its effectiveness in treating opioid addiction, its safety profile, and its role in reducing the risk of overdose. However, like all medications, Suboxone can have side effects, which may include nausea, headache, constipation, and insomnia. In rare cases, more serious side effects can occur, such as respiratory problems or allergic reactions.
Practical Examples and Statistical Data
Studies have shown that Suboxone is highly effective in treating opioid addiction, with success rates significantly higher than placebo. For example, a study published in the Journal of the American Medical Association (JAMA) found that buprenorphine-naloxone combination (Suboxone) was more effective than placebo in reducing illicit opioid use. Additionally, data from the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA) indicate that medications like Suboxone are a critical component of opioid addiction treatment, highlighting their role in reducing overdose rates and improving treatment outcomes.FAQs About Suboxone and Buprenorphine
What is the difference between Suboxone and buprenorphine?
+Suboxone is a brand name medication that contains buprenorphine and naloxone, while buprenorphine is the generic name for the active ingredient in Suboxone that treats opioid addiction.
How does Suboxone work?
+Suboxone works by combining buprenorphine, a partial opioid agonist, and naloxone, an opioid antagonist, to alleviate withdrawal symptoms, reduce cravings, and deter misuse.
What are the benefits of using Suboxone for opioid addiction treatment?
+The benefits include its efficacy in reducing withdrawal symptoms and cravings, its safety profile compared to full opioid agonists, and its flexibility in dosing options.
In conclusion, understanding Suboxone and its generic name, buprenorphine, is crucial for addressing opioid addiction effectively. By recognizing the benefits, working mechanisms, and potential side effects of these medications, individuals can make informed decisions about their treatment. As the medical community continues to combat the opioid crisis, medications like Suboxone will remain vital components of treatment plans, offering hope for recovery and a chance to rebuild lives affected by opioid addiction. We invite readers to share their thoughts and experiences with Suboxone and buprenorphine, and to explore further resources on medication-assisted treatment for opioid use disorder.
