Intro
Discover how succinate boosts energy, supports heart health, and enhances mitochondrial function, exploring its 5 key benefits and mechanisms, including antioxidant properties and cellular respiration.
Succinate, a naturally occurring compound found in the body, plays a crucial role in various physiological processes. Its significance extends beyond being a simple metabolic intermediate, as it has been found to have numerous benefits for overall health and well-being. From energy production to immune system modulation, succinate's mechanisms of action are multifaceted and fascinating. As research continues to uncover the depths of succinate's potential, it becomes increasingly clear that this compound is more than just a footnote in the grand tome of human biochemistry.
The importance of succinate cannot be overstated, given its involvement in critical pathways such as the citric acid cycle (also known as the Krebs cycle or tricarboxylic acid cycle), where it serves as a key intermediate. Beyond its role in energy metabolism, succinate has been implicated in processes ranging from the regulation of blood pressure to the enhancement of exercise performance. Its impact on both mitochondrial function and the immune response underscores its broad significance in maintaining health.
Understanding succinate's modes of action and its implications for human health is essential for appreciating its potential therapeutic applications. Whether through dietary interventions, supplements, or pharmacological agents, manipulating succinate levels or its activity could offer novel strategies for managing a range of conditions. As the scientific community continues to explore succinate's properties and effects, it is becoming evident that this compound holds considerable promise for improving quality of life and treating diseases.
Introduction to Succinate Mechanisms
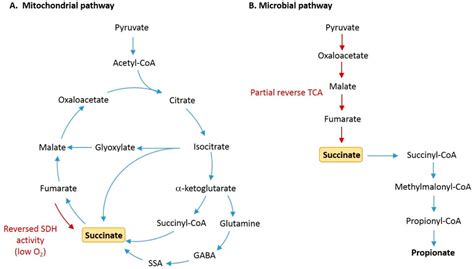
Energy Production and Succinate
The citric acid cycle is pivotal for the generation of ATP (adenosine triphosphate), the primary energy currency of the cell. Succinate, by being converted into fumarate, contributes to the production of FADH2 and NADH, which are then utilized in the electron transport chain to produce ATP. This process highlights succinate's critical role in meeting the energy demands of the cell, particularly under conditions of high energy requirement such as exercise.Succinate in Immune Response Modulation
Impact on Mitochondrial Function
Succinate's impact on mitochondrial function is profound, given that mitochondria are the site of the citric acid cycle and oxidative phosphorylation. By influencing the efficiency of these processes, succinate can affect cellular energy status and redox balance. Moreover, succinate has been implicated in the regulation of mitochondrial biogenesis and dynamics, further emphasizing its significance for mitochondrial health and, by extension, overall cellular function.Therapeutic Potential of Succinate

Exercise Performance and Succinate
Succinate supplementation has been explored as a means to improve exercise performance, given its role in energy metabolism. By potentially increasing the efficiency of energy production or enhancing endurance, succinate could offer benefits for athletes and individuals seeking to improve their physical performance. However, more research is needed to fully understand succinate's effects in this context and to establish optimal dosing regimens.Practical Applications of Succinate

Dietary Sources and Supplementation
Succinate is naturally found in various foods, although the amounts may not be sufficient to achieve therapeutic effects. Supplementation, therefore, represents a viable means to increase succinate intake. However, it is crucial to approach supplementation with caution, ensuring that any regimen is guided by scientific evidence and, if necessary, monitored by a healthcare professional.Future Directions for Succinate Research

Challenges and Considerations
While succinate holds considerable promise, there are challenges to its development as a therapeutic agent. These include the need for more comprehensive clinical trials to establish efficacy and safety, as well as a deeper understanding of its pharmacokinetics and potential side effects. Additionally, the regulatory framework surrounding succinate supplementation will need to be navigated carefully to ensure that products are both safe and effective.Conclusion and Next Steps

We invite you to share your thoughts on the potential of succinate and its implications for human health. Whether you are a healthcare professional, a researcher, or simply an individual interested in the latest developments in biochemistry, your insights and questions are valuable. Please feel free to comment below, sharing your perspectives on how succinate might be harnessed to improve our understanding and treatment of various diseases.
What is succinate and its role in the body?
+Succinate is a naturally occurring compound that plays a crucial role in energy production, immune response modulation, and mitochondrial function. It is a key intermediate in the citric acid cycle and has been found to have numerous benefits for overall health and well-being.
How does succinate influence the immune system?
+Succinate acts as a signaling molecule that can modulate the activity of immune cells, influencing the production of pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory cytokines. This ability to modulate the immune response suggests its potential as a therapeutic target for inflammatory diseases.
What are the potential therapeutic applications of succinate?
+The therapeutic potential of succinate is vast, with applications ranging from metabolic disorders to inflammatory diseases. Its ability to enhance energy production, modulate immune responses, and protect against oxidative stress positions succinate as a promising candidate for addressing a variety of pathological conditions.
