Intro
Maintaining healthy blood sugar levels is crucial for overall well-being, as it directly impacts energy levels, weight management, and the risk of developing chronic diseases like diabetes and heart disease. The importance of monitoring and managing blood sugar levels cannot be overstated, especially for individuals who are at risk or have been diagnosed with diabetes. Regular blood sugar tests are a vital tool in this management, providing insights into how the body is processing glucose. Understanding the results of these tests is essential for making informed decisions about diet, exercise, and, if necessary, medication.
The process of monitoring blood sugar involves pricking the skin to draw a small amount of blood, which is then tested with a glucometer. This simple procedure can be done at home, making it accessible for individuals to keep track of their blood glucose levels regularly. The results are typically measured in milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL) in the United States and millimoles per liter (mmol/L) in most other countries. Knowing what these numbers mean and how they relate to health is key to effective management.
For many, the concept of blood sugar levels and how they are classified can be confusing. Generally, blood sugar levels are categorized into several ranges, each indicating a different status of glucose processing in the body. Normal levels typically range from 70 to 140 mg/dL, though these can slightly vary based on factors such as the time of day and when the last meal was consumed. Understanding these ranges and what they signify is vital for individuals looking to maintain healthy blood sugar levels and prevent complications associated with diabetes.
Understanding Blood Sugar Levels

Understanding blood sugar levels involves recognizing the different ranges and what they indicate about an individual's health. For people without diabetes, normal blood sugar levels are typically between 70 and 140 mg/dL after eating. However, these levels can fluctuate based on various factors, including diet, physical activity, and the timing of the last meal. It's also important to consider fasting blood sugar levels, which are usually taken in the morning before eating or drinking anything. Normal fasting blood sugar levels are typically below 100 mg/dL.
Factors Influencing Blood Sugar Levels
Several factors can influence blood sugar levels, including diet, physical activity, medications, and underlying health conditions. For instance, consuming foods high in simple carbohydrates can cause a rapid spike in blood sugar levels, whereas regular physical activity can help lower blood sugar levels by increasing the body's sensitivity to insulin. Medications, especially those prescribed for diabetes, can also significantly impact blood sugar levels, and it's crucial to follow the prescribed dosage and timing to avoid fluctuations.Importance of Regular Blood Sugar Testing
Regular blood sugar testing is essential for managing diabetes and preventing its complications. By monitoring blood sugar levels, individuals can identify patterns and make informed decisions about their diet, exercise, and medication. This proactive approach can help prevent severe fluctuations in blood sugar levels, which can lead to serious health issues such as diabetic ketoacidosis or hypoglycemia. Moreover, regular monitoring can provide insights into how different factors, such as stress or illness, affect blood sugar levels, allowing for more personalized management strategies.
Benefits of Blood Sugar Monitoring
The benefits of blood sugar monitoring are numerous. It not only helps in the early detection of diabetes but also in the management of the condition. By keeping track of blood sugar levels, individuals can adjust their lifestyle choices to maintain healthy levels, reducing the risk of long-term complications such as heart disease, kidney damage, and nerve damage. Furthermore, monitoring can help identify any issues with medication or insulin dosages, ensuring that the treatment plan is effective and safe.Interpreting Blood Sugar Test Results

Interpreting blood sugar test results requires understanding the different ranges and what they indicate. Generally, results are categorized as follows:
- Normal: Below 140 mg/dL (after eating) and below 100 mg/dL (fasting).
- Elevated: Between 140 and 199 mg/dL (after eating) and between 100 and 125 mg/dL (fasting), indicating prediabetes.
- Diabetes: 200 mg/dL or higher (after eating) and 126 mg/dL or higher (fasting).
Understanding Prediabetes
Prediabetes is a condition where blood sugar levels are higher than normal but not high enough to be classified as diabetes. It's a critical phase because lifestyle changes can still prevent the development of type 2 diabetes. Understanding and managing prediabetes involves adopting a healthier diet, increasing physical activity, and maintaining a healthy weight. Regular monitoring of blood sugar levels is also crucial during this phase to track progress and make adjustments as necessary.Managing Blood Sugar Levels

Managing blood sugar levels effectively involves a combination of diet, exercise, and, if prescribed, medication or insulin therapy. A healthy diet that is low in simple carbohydrates and added sugars and high in fiber and lean proteins can help regulate blood sugar levels. Regular physical activity, such as walking or more intense workouts, can also improve insulin sensitivity, helping the body to more efficiently use insulin.
Lifestyle Changes for Blood Sugar Management
Lifestyle changes are fundamental in managing blood sugar levels. This includes: - Eating a balanced diet that is rich in whole foods and low in processed and sugary foods. - Engaging in regular physical activity, such as walking, jogging, or other exercises that improve cardiovascular health. - Maintaining a healthy weight, as excess weight can increase insulin resistance. - Managing stress through techniques like meditation or yoga, as chronic stress can affect blood sugar levels.Treatment Options for Diabetes
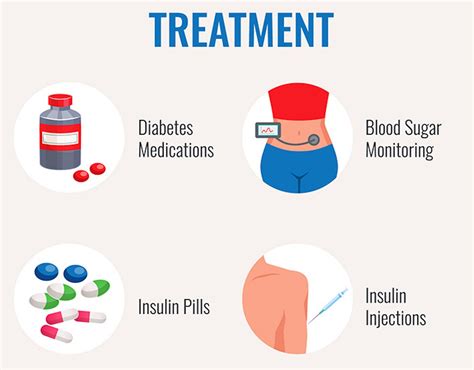
For individuals diagnosed with diabetes, various treatment options are available, depending on the type of diabetes and the severity of the condition. Type 1 diabetes is typically managed with insulin therapy, as the body does not produce enough insulin. Type 2 diabetes may be managed through lifestyle changes alone or in combination with oral medications or insulin therapy. The goal of treatment is to maintain blood sugar levels within a target range to prevent complications.
Medications for Diabetes
Several medications are available for managing type 2 diabetes, each working in a different way to lower blood sugar levels. These include metformin, sulfonylureas, meglitinides, thiazolidinediones, and SGLT2 inhibitors, among others. The choice of medication depends on the individual's health status, other medications they are taking, and the potential side effects of the medication.Preventing Diabetes Complications
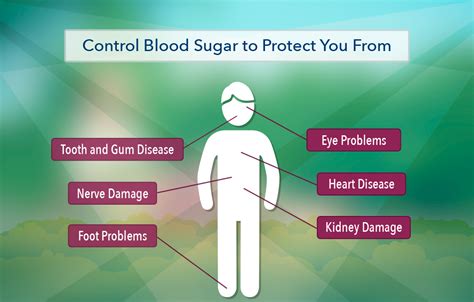
Preventing diabetes complications involves maintaining good blood sugar control, monitoring blood pressure and cholesterol levels, and adopting a healthy lifestyle. Regular check-ups with healthcare providers are crucial for early detection and management of any complications. Additionally, staying informed about diabetes and its management can empower individuals to take control of their health, making informed decisions about their care.
Importance of Regular Health Check-Ups
Regular health check-ups are vital for individuals with diabetes. These visits provide an opportunity for healthcare providers to monitor the effectiveness of the current treatment plan, check for any signs of complications, and make adjustments as necessary. They also offer a chance for individuals to ask questions, learn more about their condition, and receive support and guidance on managing their diabetes.What is the normal range for blood sugar levels?
+Normal blood sugar levels are typically between 70 and 140 mg/dL after eating and below 100 mg/dL when fasting.
How often should I check my blood sugar levels?
+The frequency of checking blood sugar levels depends on the individual's health status and the type of diabetes they have. Generally, it's recommended to check levels at least once a day, but this can vary based on the treatment plan and the healthcare provider's advice.
What are the symptoms of high blood sugar levels?
+Symptoms of high blood sugar levels can include increased thirst and urination, fatigue, blurred vision, and slow healing of cuts and wounds. If these symptoms persist, it's essential to consult with a healthcare provider.
In conclusion, maintaining healthy blood sugar levels is a multifaceted process that involves understanding the importance of blood sugar testing, interpreting test results, and adopting lifestyle changes and treatment options as necessary. By staying informed and proactive about diabetes management, individuals can significantly reduce the risk of complications and improve their overall quality of life. We invite you to share your experiences, ask questions, or seek advice on managing blood sugar levels in the comments below. Your engagement and feedback are invaluable in creating a supportive community for those navigating the complexities of diabetes care.
