Intro
Discover key facts about Sulfamethoxazole, a sulfonamide antibiotic, including its uses, side effects, and interactions, to understand its role in treating bacterial infections and diseases, such as UTIs and pneumonia.
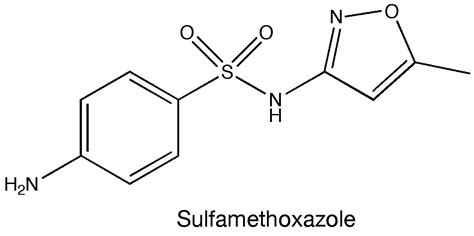
Sulfamethoxazole is an antibiotic that belongs to the sulfonamide class, which has been widely used to treat various bacterial infections. The importance of understanding this medication lies in its efficacy, potential side effects, and the growing concern of antibiotic resistance. As we delve into the world of sulfamethoxazole, it's crucial to recognize its role in modern medicine and how it impacts our health and wellbeing. With the rise of antibiotic-resistant bacteria, medications like sulfamethoxazole are under scrutiny, making it essential to explore their benefits and limitations. By examining the facts surrounding sulfamethoxazole, we can better comprehend its applications, risks, and the future of antibiotic treatment.
The use of sulfamethoxazole is not without controversy, as it has been associated with several side effects, ranging from mild to severe. Despite these concerns, sulfamethoxazole remains a vital component in the treatment of certain bacterial infections, particularly when used in combination with other antibiotics. Its mechanism of action, which involves inhibiting folic acid synthesis in bacteria, is effective against a broad spectrum of bacterial pathogens. However, the increasing prevalence of antibiotic resistance necessitates a cautious approach to prescribing sulfamethoxazole, emphasizing the need for responsible antibiotic use. As we navigate the complexities of sulfamethoxazole, it's essential to consider both its therapeutic potential and the potential risks associated with its use.
Sulfamethoxazole is often prescribed in combination with trimethoprim, another antibiotic, to enhance its effectiveness against a wider range of bacterial infections. This combination, known as co-trimoxazole, has been used to treat urinary tract infections, respiratory infections, and other conditions. The synergy between sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim allows for lower doses of each medication, potentially reducing side effects while maintaining therapeutic efficacy. Understanding the benefits and limitations of co-trimoxazole is vital for healthcare professionals and patients alike, as it informs treatment decisions and promotes the responsible use of antibiotics. By exploring the intricacies of sulfamethoxazole and its combinations, we can better appreciate the nuances of antibiotic therapy and the ongoing challenges in combating bacterial infections.
Introduction to Sulfamethoxazole
History of Sulfamethoxazole
The discovery of sulfamethoxazole dates back to the mid-20th century, when researchers were seeking to develop new antibiotics with improved efficacy and safety profiles. The sulfonamide class, to which sulfamethoxazole belongs, was one of the first groups of synthetic antibiotics, offering an alternative to natural antibiotics like penicillin. Over the years, sulfamethoxazole has undergone extensive clinical trials, demonstrating its effectiveness in treating various bacterial infections. Its combination with trimethoprim has further expanded its therapeutic applications, making co-trimoxazole a staple in modern medicine.Benefits of Sulfamethoxazole
Some of the key benefits of sulfamethoxazole include:
- Broad-spectrum activity against bacterial pathogens
- Enhanced efficacy when used in combination with trimethoprim
- Relatively low cost compared to other antibiotics
- Effective in preventing certain types of infections in immunocompromised individuals
- Wide range of therapeutic applications, including urinary tract infections, respiratory infections, and skin infections
Working Mechanism of Sulfamethoxazole
The working mechanism of sulfamethoxazole involves the inhibition of folic acid synthesis in bacteria. By competing with PABA, sulfamethoxazole prevents the production of dihydrofolic acid, which is necessary for the synthesis of tetrahydrofolic acid. Tetrahydrofolic acid is essential for the production of purines and pyrimidines, which are critical components of DNA and RNA. Without tetrahydrofolic acid, bacteria are unable to replicate, ultimately leading to their death. This mechanism of action makes sulfamethoxazole effective against a wide range of bacterial pathogens, including those responsible for urinary tract infections, respiratory infections, and skin infections.Risks and Side Effects of Sulfamethoxazole

Some of the key risks and side effects of sulfamethoxazole include:
- Gastrointestinal disturbances, such as nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea
- Allergic reactions, such as rash and itching
- Stevens-Johnson syndrome
- Toxic epidermal necrolysis
- Agranulocytosis
- Interactions with other medications, such as warfarin and phenytoin
Precautions and Contraindications
Sulfamethoxazole is contraindicated in individuals with a known hypersensitivity to sulfonamides or trimethoprim. Additionally, sulfamethoxazole should be used with caution in individuals with renal or hepatic impairment, as well as those with glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) deficiency. Pregnant women and breastfeeding mothers should also use sulfamethoxazole with caution, as it can cross the placenta and enter breast milk.Some of the key precautions and contraindications of sulfamethoxazole include:
- Hypersensitivity to sulfonamides or trimethoprim
- Renal or hepatic impairment
- Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) deficiency
- Pregnancy and breastfeeding
Future of Sulfamethoxazole
Some of the key considerations for the future of sulfamethoxazole include:
- Development of new antibiotics and alternative therapies
- Responsible use of sulfamethoxazole and other antibiotics
- Promotion of antibiotic stewardship
- Addressing the challenge of antibiotic resistance
Conclusion and Recommendations
In conclusion, sulfamethoxazole is a valuable antibiotic that has been used to treat a wide range of bacterial infections. While it is generally considered safe and effective, it is not without risks and side effects. To ensure the continued effectiveness of sulfamethoxazole, it is essential to promote antibiotic stewardship and develop new treatments. Additionally, individuals should be aware of the potential risks and side effects of sulfamethoxazole and use it only as directed by a healthcare professional.We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with sulfamethoxazole in the comments below. Have you or a loved one used sulfamethoxazole to treat a bacterial infection? What were your experiences with the medication? Share your story and help us raise awareness about the importance of responsible antibiotic use.
What is sulfamethoxazole used to treat?
+Sulfamethoxazole is used to treat a wide range of bacterial infections, including urinary tract infections, respiratory infections, and skin infections.
What are the potential side effects of sulfamethoxazole?
+The potential side effects of sulfamethoxazole include gastrointestinal disturbances, allergic reactions, and interactions with other medications.
Can sulfamethoxazole be used in combination with other medications?
+Yes, sulfamethoxazole can be used in combination with other medications, such as trimethoprim, to enhance its effectiveness against certain bacterial infections.
