Intro
Identify ear infection symptoms, including ear pain, discharge, and hearing loss, and learn about otitis media, inner ear infections, and eustachian tube issues, to seek timely treatment and relief.
Ear infections are a common health issue that can affect anyone, regardless of age. They occur when bacteria or viruses infect the middle ear, causing inflammation and fluid buildup. Ear infections can be painful and uncomfortable, and if left untreated, can lead to more serious complications. It is essential to recognize the symptoms of an ear infection to seek medical attention promptly.
Ear infections can be caused by a variety of factors, including colds, allergies, and exposure to cigarette smoke. They can also be caused by anatomical issues, such as a narrow Eustachian tube, which connects the middle ear to the back of the throat. When the Eustachian tube is blocked, fluid can build up in the middle ear, creating an ideal environment for bacteria and viruses to grow. Understanding the causes of ear infections can help individuals take preventive measures to reduce their risk of developing the condition.
Recognizing the symptoms of an ear infection is crucial for seeking medical attention and receiving proper treatment. The symptoms of an ear infection can vary depending on the individual and the severity of the infection. Common symptoms include ear pain, fever, and difficulty hearing. In some cases, individuals may experience a feeling of fullness or pressure in the ear, and they may have trouble sleeping due to the discomfort. It is essential to seek medical attention if symptoms persist or worsen over time.
Understanding Ear Infection Symptoms
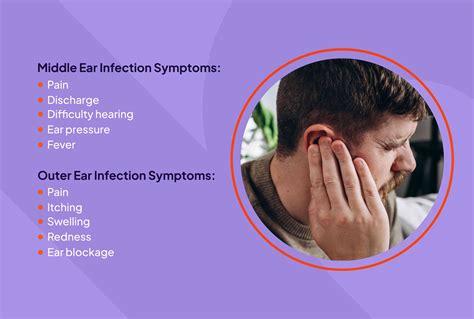
Ear infection symptoms can be categorized into two main types: acute and chronic. Acute ear infections are short-term and typically resolve on their own within a few days. Chronic ear infections, on the other hand, are long-term and can persist for weeks or even months. Understanding the differences between acute and chronic ear infections can help individuals seek the right treatment and prevent further complications.
Acute Ear Infection Symptoms
Acute ear infections are typically caused by bacteria or viruses and can be accompanied by a range of symptoms. Common symptoms of acute ear infections include: * Ear pain or discomfort * Fever * Difficulty hearing * Feeling of fullness or pressure in the ear * Discharge or fluid leaking from the ear * Trouble sleeping due to discomfort * Loss of appetite * IrritabilityDiagnosing Ear Infections
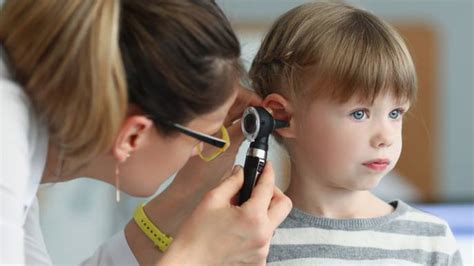
Diagnosing ear infections typically involves a physical examination and a review of the individual's medical history. A doctor may use an otoscope to examine the ear canal and eardrum, looking for signs of inflammation or fluid buildup. In some cases, a doctor may also perform a tympanometry test to assess the movement of the eardrum and the conduction of sound.
Treatment Options for Ear Infections
Treatment for ear infections depends on the severity of the infection and the individual's overall health. Mild ear infections may resolve on their own without treatment, while more severe infections may require antibiotics or other medications. In some cases, a doctor may recommend ear drops or pain relievers to help manage symptoms.Preventing Ear Infections

Preventing ear infections requires a combination of good hygiene, a healthy lifestyle, and regular medical check-ups. Individuals can reduce their risk of developing ear infections by:
- Practicing good hygiene, such as washing hands regularly
- Avoiding close contact with individuals who have colds or other illnesses
- Getting regular vaccinations, such as the flu vaccine
- Avoiding exposure to cigarette smoke
- Using ear protection, such as earplugs, when swimming or engaging in loud activities
Complications of Untreated Ear Infections
Untreated ear infections can lead to a range of complications, including: * Permanent hearing loss * Speech delays or difficulties * Balance problems * Increased risk of future ear infections * Spread of infection to other parts of the body, such as the brain or spinal cordManaging Ear Infection Symptoms
Managing ear infection symptoms requires a combination of self-care and medical treatment. Individuals can help manage their symptoms by:
- Getting plenty of rest
- Using a warm compress to relieve ear pain
- Taking over-the-counter pain relievers, such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen
- Using ear drops or other medications as prescribed by a doctor
- Staying hydrated by drinking plenty of fluids
When to Seek Medical Attention
Individuals should seek medical attention if they experience any of the following symptoms: * Severe ear pain or discomfort * Fever over 102°F (39°C) * Difficulty hearing or speaking * Discharge or fluid leaking from the ear * Trouble sleeping due to discomfort * Loss of appetite * IrritabilityConclusion and Next Steps

In conclusion, ear infections are a common health issue that can affect anyone, regardless of age. Recognizing the symptoms of an ear infection and seeking medical attention promptly can help prevent complications and promote effective treatment. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for ear infections, individuals can take proactive steps to protect their hearing and overall health.
We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with ear infections in the comments below. If you have any questions or concerns, please don't hesitate to reach out. Share this article with others who may be interested in learning more about ear infections and their symptoms.
What are the common symptoms of an ear infection?
+Common symptoms of an ear infection include ear pain, fever, difficulty hearing, and a feeling of fullness or pressure in the ear.
How are ear infections diagnosed?
+Ear infections are typically diagnosed through a physical examination and a review of the individual's medical history. A doctor may also use an otoscope to examine the ear canal and eardrum.
What are the treatment options for ear infections?
+Treatment for ear infections depends on the severity of the infection and the individual's overall health. Mild ear infections may resolve on their own without treatment, while more severe infections may require antibiotics or other medications.
Can ear infections be prevented?
+Yes, ear infections can be prevented by practicing good hygiene, avoiding close contact with individuals who have colds or other illnesses, and getting regular vaccinations.
What are the complications of untreated ear infections?
+Untreated ear infections can lead to a range of complications, including permanent hearing loss, speech delays or difficulties, balance problems, and increased risk of future ear infections.
