Intro
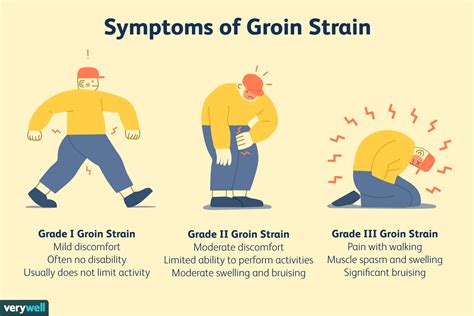
Identify 5 common groin pull symptoms, including pain, swelling, and limited mobility, and learn about strains, tears, and treatment options for inner thigh injuries, athletic groin pulls, and adductor strains.
Groin pull symptoms are a common issue among athletes and individuals who engage in physical activities that involve sudden changes of direction, quick turns, or rapid acceleration. The groin area is a complex region that includes several muscles, tendons, and ligaments, making it prone to injuries. Understanding the symptoms of a groin pull is essential for proper diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of further complications.
The groin area is a vital part of the human body, and any injury to this region can significantly impact an individual's quality of life. A groin pull, also known as a groin strain, occurs when the muscles or tendons in the groin area are stretched or torn. This type of injury is common in sports that involve running, jumping, or quick changes of direction, such as soccer, basketball, and football. Groin pull symptoms can vary in severity, ranging from mild to severe, and can have a significant impact on an individual's ability to perform daily activities.
Groin pull symptoms can be acute or chronic, and it is essential to recognize the signs and symptoms to seek medical attention promptly. Acute groin pull symptoms occur suddenly, often during physical activity, and can be severe. Chronic groin pull symptoms, on the other hand, develop over time and can be mild to moderate. Recognizing the symptoms of a groin pull is crucial for preventing further injury and promoting proper healing. In this article, we will discuss the common symptoms of a groin pull, their causes, and treatment options.
Groin Pull Symptoms
Causes of Groin Pull Symptoms
The causes of groin pull symptoms can be attributed to various factors, including overuse, poor training techniques, and inadequate warm-up routines. Overuse injuries occur when the muscles or tendons in the groin area are subjected to repetitive stress, leading to inflammation and damage. Poor training techniques, such as sudden changes of direction or quick turns, can also contribute to groin pull symptoms. Inadequate warm-up routines can increase the risk of injury, as the muscles and tendons are not properly prepared for physical activity.Treatment Options for Groin Pull Symptoms
Physical Therapy for Groin Pull Symptoms
Physical therapy is an essential component of treating groin pull symptoms. A physical therapist can help individuals develop a personalized exercise program to improve flexibility, strength, and range of motion. Physical therapy can also help reduce pain and inflammation, promoting proper healing and preventing further injury. Common physical therapy exercises for groin pull symptoms include stretching, strengthening, and plyometric exercises.Prevention of Groin Pull Symptoms

Risk Factors for Groin Pull Symptoms
Several risk factors can increase the likelihood of developing groin pull symptoms. These include age, sex, and level of physical activity. Older individuals are more prone to groin pull symptoms due to decreased muscle mass and flexibility. Men are more likely to experience groin pull symptoms than women, particularly in sports that involve contact or collision. Individuals who engage in high-level physical activity, such as professional athletes, are also at increased risk of developing groin pull symptoms.Diagnosis of Groin Pull Symptoms
Treatment Complications
Treatment complications can arise if groin pull symptoms are not properly managed. Untreated groin pull symptoms can lead to chronic pain, limited mobility, and decreased athletic performance. In severe cases, untreated groin pull symptoms can result in permanent damage to the muscles or tendons, requiring surgical intervention. Additionally, inadequate treatment can lead to recurrence of symptoms, making it challenging to achieve full recovery.Recovery from Groin Pull Symptoms

Returning to Activity after Groin Pull Symptoms
Returning to activity after groin pull symptoms requires a gradual and structured approach. Individuals should not return to activity until they have achieved full range of motion, strength, and flexibility. A gradual progression of exercise intensity and volume can help prevent recurrence of symptoms and promote long-term recovery. It is essential to listen to the body and not push too hard, as this can lead to further injury.Conclusion and Final Thoughts

What are the common symptoms of a groin pull?
+The common symptoms of a groin pull include pain, swelling, bruising, and limited mobility. The pain associated with a groin pull can range from mild to severe and can be felt in the groin area, thigh, or lower abdomen.
How can I prevent groin pull symptoms?
+Prevention is key to reducing the risk of groin pull symptoms. Individuals can take several steps to prevent groin pull symptoms, including warming up properly before physical activity, stretching regularly, and strengthening the muscles in the groin area.
What are the treatment options for groin pull symptoms?
+Treatment options for groin pull symptoms depend on the severity of the injury. Mild groin pull symptoms can be treated with rest, ice, compression, and elevation (RICE). Moderate to severe groin pull symptoms may require physical therapy, pain management, and in some cases, surgery.
We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of groin pull symptoms, their causes, treatment options, and prevention strategies. If you have any further questions or concerns, please do not hesitate to comment below. Share this article with your friends and family to help raise awareness about the importance of proper diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of groin pull symptoms. Take the first step towards optimal athletic performance and overall health by prioritizing your groin health today!
