Intro
Identify Intestinal Blockage Symptoms, including bowel obstruction signs, abdominal pain, and digestive issues, to seek timely medical help and prevent complications like ischemia and perforation.
Intestinal blockage is a serious medical condition that occurs when there is a partial or complete obstruction in the small or large intestine, preventing the normal flow of food, fluid, and gas. This condition can be caused by a variety of factors, including hernias, adhesions, tumors, and certain medications. Intestinal blockage symptoms can vary depending on the severity and location of the blockage, but it's essential to recognize the warning signs to seek prompt medical attention.
The importance of recognizing intestinal blockage symptoms cannot be overstated. If left untreated, intestinal blockage can lead to severe complications, such as tissue death, perforation, and peritonitis, which can be life-threatening. Moreover, intestinal blockage can cause significant discomfort, pain, and distress, affecting a person's quality of life. By understanding the symptoms and seeking medical help promptly, individuals can prevent long-term damage and ensure a speedy recovery.
Intestinal blockage symptoms can be subtle at first, but they can escalate quickly. Common symptoms include severe abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, bloating, and constipation. In some cases, people may experience diarrhea or abdominal tenderness. It's crucial to pay attention to these symptoms, especially if they persist or worsen over time. By seeking medical attention early, individuals can receive a timely diagnosis and treatment, reducing the risk of complications and improving outcomes.
Causes of Intestinal Blockage
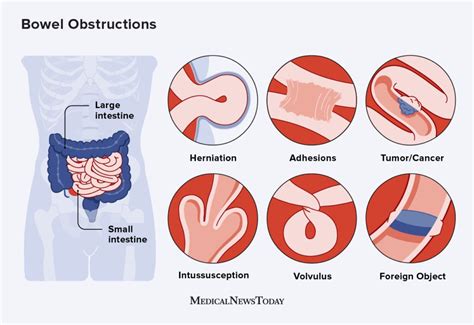
Types of Intestinal Blockage
There are two main types of intestinal blockage: partial and complete. Partial blockage occurs when the intestine is only partially obstructed, allowing some food, fluid, and gas to pass through. Complete blockage, on the other hand, occurs when the intestine is completely obstructed, preventing any food, fluid, or gas from passing through. Both types of blockage require medical attention, and the treatment approach depends on the severity and location of the blockage.Symptoms of Intestinal Blockage
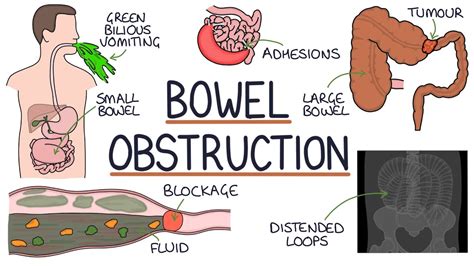
Diagnosing Intestinal Blockage
Diagnosing intestinal blockage requires a combination of physical examination, medical history, and diagnostic tests. The doctor will perform a physical examination to check for abdominal tenderness, distension, and bowel sounds. The doctor will also ask about the patient's medical history, including any previous surgeries, illnesses, or medications. Diagnostic tests, such as X-rays, CT scans, and MRI scans, may be ordered to confirm the diagnosis and determine the location and severity of the blockage.Treatment Options for Intestinal Blockage
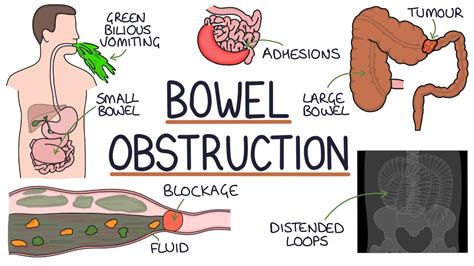
Preventing Intestinal Blockage
Preventing intestinal blockage requires a combination of lifestyle changes and medical interventions. Individuals can reduce their risk of intestinal blockage by: * Eating a high-fiber diet * Staying hydrated * Avoiding heavy lifting and straining * Managing chronic conditions, such as diabetes and hypertension * Avoiding certain medications, such as opioids and anticholinergics * Getting regular check-ups and screeningsComplications of Intestinal Blockage
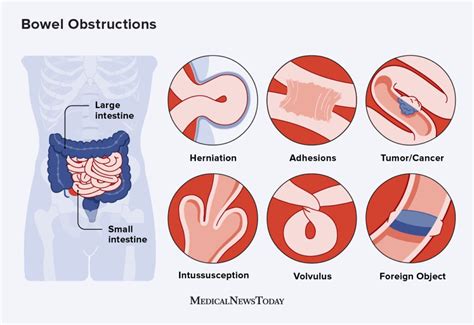
Managing Intestinal Blockage
Managing intestinal blockage requires a comprehensive approach that includes medical treatment, lifestyle changes, and emotional support. Individuals with intestinal blockage should: * Follow a bowel rest diet * Stay hydrated * Manage pain and discomfort * Get regular check-ups and follow-up care * Seek emotional support from family, friends, and support groupsLiving with Intestinal Blockage

Coping with Intestinal Blockage
Coping with intestinal blockage requires a combination of emotional support, lifestyle changes, and medical interventions. Individuals with intestinal blockage should: * Seek support from family and friends * Join support groups and online forums * Practice stress-reducing techniques, such as meditation and yoga * Get regular exercise and physical activity * Stay connected with their healthcare teamWhat are the symptoms of intestinal blockage?
+The symptoms of intestinal blockage include severe abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, bloating, and constipation. In some cases, people may experience diarrhea or abdominal tenderness.
What causes intestinal blockage?
+Intestinal blockage can be caused by various factors, including mechanical and non-mechanical causes. Mechanical causes include physical obstructions, such as hernias, adhesions, and tumors, while non-mechanical causes include conditions that affect the intestinal muscles, such as paralytic ileus.
How is intestinal blockage diagnosed?
+Diagnosing intestinal blockage requires a combination of physical examination, medical history, and diagnostic tests, such as X-rays, CT scans, and MRI scans.
What are the treatment options for intestinal blockage?
+The treatment options for intestinal blockage depend on the severity and location of the blockage. In some cases, the blockage may resolve on its own with bowel rest, fluid replacement, and medication, while in more severe cases, surgery may be necessary to remove the blockage and restore normal intestinal function.
How can I prevent intestinal blockage?
+Individuals can reduce their risk of intestinal blockage by eating a high-fiber diet, staying hydrated, avoiding heavy lifting and straining, managing chronic conditions, and getting regular check-ups and screenings.
In conclusion, intestinal blockage is a serious medical condition that requires prompt attention and treatment. By understanding the symptoms, causes, and treatment options, individuals can take proactive steps to prevent complications and ensure a speedy recovery. If you or someone you know is experiencing symptoms of intestinal blockage, don't hesitate to seek medical help. Share this article with others to raise awareness about intestinal blockage and encourage them to take action to protect their digestive health.
