Intro
Identify 7 iron poisoning symptoms, including fatigue, pale skin, and shortness of breath, and learn about iron overdose effects, toxicity signs, and treatment options to prevent severe health complications.
Iron is an essential nutrient for the human body, playing a crucial role in the production of hemoglobin, which carries oxygen in the blood. However, excessive iron consumption can lead to iron poisoning, a potentially life-threatening condition. Iron poisoning symptoms can vary depending on the severity of the overdose and the individual's overall health. It is essential to recognize these symptoms to seek medical attention promptly.
Iron poisoning can occur due to accidental ingestion of iron supplements, especially in children, or as a result of intentional overdose. The severity of iron poisoning symptoms depends on the amount of iron consumed and the time elapsed since ingestion. Early recognition and treatment of iron poisoning are critical to prevent long-term complications and fatalities. In this article, we will delve into the common symptoms of iron poisoning, its causes, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention strategies.
The importance of understanding iron poisoning symptoms cannot be overstated. According to the American Association of Poison Control Centers, iron poisoning is a leading cause of poisoning-related deaths in children under the age of six. Moreover, iron poisoning can lead to severe health complications, including gastrointestinal damage, cardiovascular problems, and even death. Therefore, it is crucial to educate individuals about the risks associated with iron overdose and the importance of seeking medical attention if symptoms persist.
Introduction to Iron Poisoning

Causes of Iron Poisoning
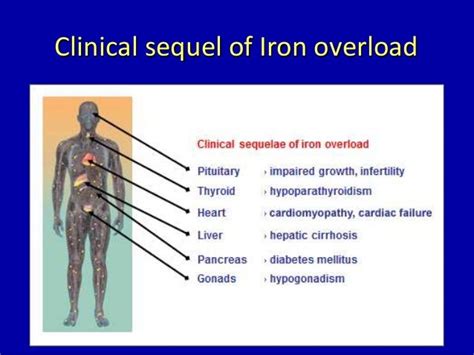
Genetic Disorders and Iron Poisoning
Genetic disorders, such as hemochromatosis, can increase the risk of iron poisoning by affecting the body's ability to regulate iron levels. Hemochromatosis is a genetic disorder characterized by excessive iron absorption, leading to iron overload in the body. Individuals with hemochromatosis are more susceptible to iron poisoning due to their impaired ability to regulate iron levels. Early diagnosis and treatment of genetic disorders can help prevent iron poisoning and related complications.Symptoms of Iron Poisoning
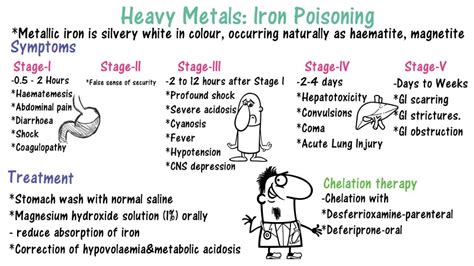
Early Symptoms of Iron Poisoning
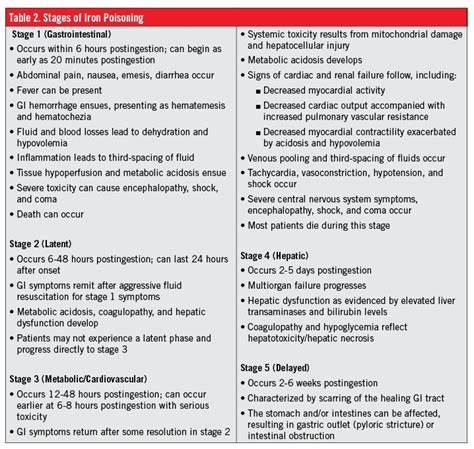
The early symptoms of iron poisoning can be mild and nonspecific, making diagnosis challenging. Early recognition of these symptoms is critical to prevent severe complications and fatalities. Common early symptoms of iron poisoning include: * Nausea and vomiting * Abdominal pain and diarrhea * Fatigue and weaknessDiagnosis and Treatment of Iron Poisoning

Treatment of iron poisoning depends on the severity of the overdose and the individual's overall health. Mild cases of iron poisoning may be treated with supportive care, such as hydration and monitoring of vital signs. Severe cases may require more aggressive treatment, including:
- Gastric lavage to remove iron from the stomach
- Activated charcoal to prevent iron absorption
- Chelation therapy to remove excess iron from the body
- Blood transfusions to treat anemia and other complications
Chelation Therapy for Iron Poisoning
Chelation therapy is a medical treatment that involves administering medications to remove excess iron from the body. Chelating agents, such as deferoxamine, bind to iron and facilitate its removal from the body. Chelation therapy is effective in treating iron poisoning, especially in severe cases. However, it requires close monitoring and adjustment of medication doses to prevent adverse effects.Prevention of Iron Poisoning
Safe Storage of Iron Supplements
Safe storage of iron supplements is critical to preventing accidental ingestion, especially in children. Iron supplements should be stored in a secure location, out of reach of children, and in their original packaging. Additionally, iron supplements should be labeled clearly, and their expiration dates should be checked regularly.What are the common causes of iron poisoning?
+Iron poisoning can be caused by accidental ingestion of iron supplements, intentional overdose, and genetic disorders that affect iron metabolism.
What are the symptoms of iron poisoning?
+The symptoms of iron poisoning include nausea and vomiting, abdominal pain and diarrhea, fatigue and weakness, dizziness and headache, rapid heartbeat and palpitations, and seizures and coma (in severe cases).
How is iron poisoning diagnosed and treated?
+Iron poisoning is diagnosed through a combination of physical examination, laboratory tests, and medical history. Treatment depends on the severity of the overdose and may involve supportive care, gastric lavage, activated charcoal, chelation therapy, and blood transfusions.
How can iron poisoning be prevented?
+Iron poisoning can be prevented by storing iron supplements out of reach of children, avoiding taking iron supplements without medical supervision, monitoring iron intake from foods and supplements, and following recommended dietary allowances for iron.
What is the importance of early recognition of iron poisoning symptoms?
+Early recognition of iron poisoning symptoms is critical to prevent severe complications and fatalities. Prompt medical attention can help alleviate symptoms, prevent long-term damage, and reduce the risk of mortality.
In conclusion, iron poisoning is a potentially life-threatening condition that requires prompt medical attention. Recognizing the symptoms of iron poisoning, understanding its causes, and taking measures to prevent it are essential for maintaining good health. By educating individuals about the risks associated with iron overdose and the importance of seeking medical attention if symptoms persist, we can reduce the incidence of iron poisoning and related complications. If you suspect someone has ingested an excessive amount of iron, call your local poison control center or seek immediate medical attention. Share this article with your friends and family to raise awareness about iron poisoning and its prevention.
