Intro
Identify lead poisoning symptoms, including developmental delays, abdominal pain, and headaches. Learn about exposure risks, testing, and treatment to prevent long-term effects like neurological damage and organ failure.
Lead poisoning is a serious and potentially life-threatening condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It occurs when lead, a toxic metal, accumulates in the body and causes damage to various organs and systems. The symptoms of lead poisoning can be subtle and may not appear immediately, making it essential to understand the risks and signs of exposure. In this article, we will delve into the world of lead poisoning, exploring its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention.
Lead poisoning can affect anyone, regardless of age, sex, or socioeconomic status. However, children under the age of six are particularly vulnerable due to their developing brains and bodies. Pregnant women, workers in industries that involve lead-based materials, and people living in older homes with lead-based paint are also at higher risk. The effects of lead poisoning can be devastating, ranging from mild cognitive impairment to severe neurological damage, organ failure, and even death.
The importance of recognizing lead poisoning symptoms cannot be overstated. Early detection and treatment can significantly reduce the risk of long-term damage and improve outcomes. Moreover, understanding the causes of lead poisoning can help individuals and communities take proactive steps to prevent exposure. By raising awareness about lead poisoning and its consequences, we can work together to create a safer and healthier environment for everyone.
Introduction to Lead Poisoning

Causes of Lead Poisoning

Risk Factors for Lead Poisoning
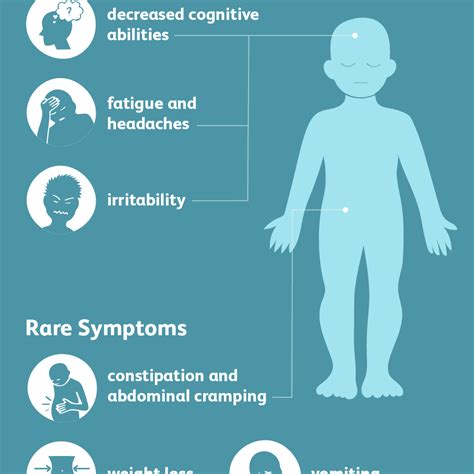
Certain individuals are more susceptible to lead poisoning due to various risk factors. These include: * Age: Children under the age of six are at higher risk due to their developing brains and bodies. * Pregnancy: Pregnant women are at risk of exposing their unborn babies to lead. * Occupation: Workers in industries that involve lead-based materials are at risk of exposure. * Socioeconomic status: People living in older homes or in areas with high levels of environmental pollution may be at higher risk.Symptoms of Lead Poisoning
Acute vs. Chronic Lead Poisoning
Lead poisoning can be acute or chronic, depending on the level and duration of exposure. Acute lead poisoning occurs when a person is exposed to a high level of lead over a short period, resulting in severe symptoms. Chronic lead poisoning, on the other hand, occurs when a person is exposed to low levels of lead over a prolonged period, resulting in subtle and often unnoticed symptoms.Diagnosis and Treatment of Lead Poisoning
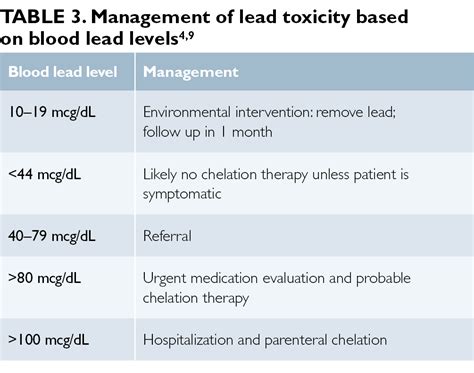
Chelation Therapy
Chelation therapy involves the use of medications that bind to lead, allowing it to be excreted from the body. This treatment is usually reserved for severe cases of lead poisoning or for individuals with high levels of lead in their blood.Prevention of Lead Poisoning

Community-Based Initiatives
Community-based initiatives can play a crucial role in preventing lead poisoning. These initiatives may include: * Lead screening programs * Public awareness campaigns * Environmental remediation projects * Policy changes to reduce lead exposureConclusion and Next Steps

We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with lead poisoning in the comments section below. If you have any questions or concerns, please do not hesitate to reach out. Together, we can make a difference and create a lead-free future for all.
What are the most common symptoms of lead poisoning?
+The most common symptoms of lead poisoning include headaches, fatigue, irritability, abdominal pain, constipation, memory loss, difficulty concentrating, mood changes, seizures, and coma.
How can I prevent lead poisoning in my home?
+To prevent lead poisoning in your home, remove lead-based paint and contaminated soil, use lead-free products, avoid exposure to lead-based materials, and implement safety protocols when renovating or repairing your home.
What are the long-term effects of lead poisoning?
+The long-term effects of lead poisoning can include cognitive impairment, neurological damage, organ failure, and even death. Early detection and treatment can significantly reduce the risk of long-term damage and improve outcomes.
Can lead poisoning be treated?
+Yes, lead poisoning can be treated. Treatment typically involves removing the source of exposure, providing supportive care, and administering chelation therapy to remove lead from the body.
How can I get my child tested for lead poisoning?
+To get your child tested for lead poisoning, consult with your pediatrician or healthcare provider. They can perform a blood test to check for lead levels and provide guidance on next steps.
