Intro
Discover the potential Tb Skin Test Side Effects, including allergic reactions, skin irritation, and false positives, and learn about tuberculin testing, latent TB, and diagnostic procedures to ensure informed healthcare decisions.
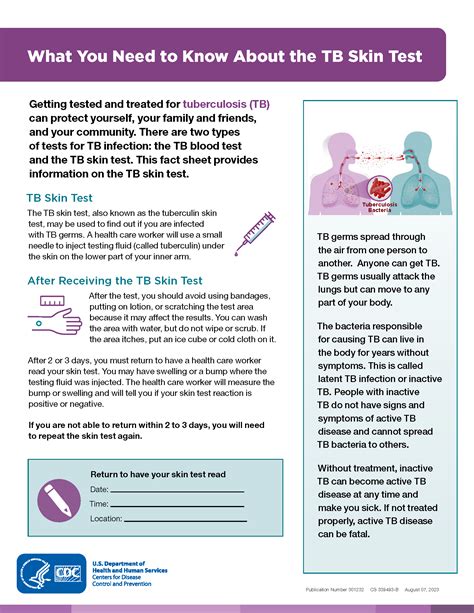
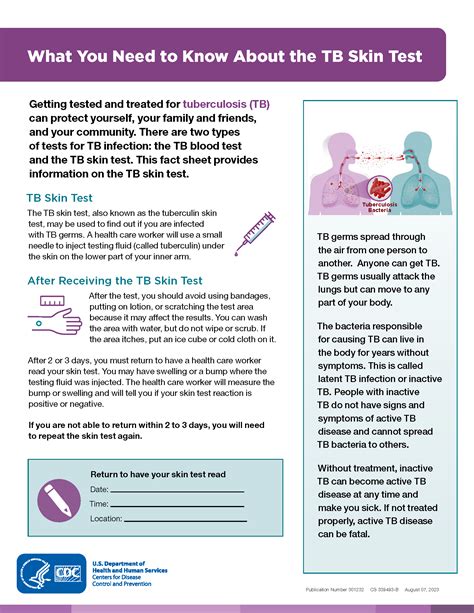
The TB skin test, also known as the Mantoux test, is a widely used method for detecting tuberculosis (TB) infection. It involves injecting a small amount of purified protein derivative (PPD) into the skin, usually on the forearm, and observing the reaction after 48-72 hours. While the test is generally safe and effective, it can cause some side effects, which will be discussed in this article.
The importance of understanding the TB skin test side effects cannot be overstated, as it is a crucial tool in the diagnosis and management of TB. TB is a serious infectious disease that can affect anyone, regardless of age, gender, or socioeconomic status. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), TB is one of the top 10 causes of death worldwide, with an estimated 10 million new cases and 1.5 million deaths annually. The TB skin test is a vital component of TB control programs, and being aware of its potential side effects can help individuals make informed decisions about their health.
The TB skin test is not only used for diagnostic purposes but also for screening individuals who are at high risk of developing TB, such as healthcare workers, prisoners, and people living with HIV/AIDS. The test is also used to monitor the effectiveness of TB treatment and to detect potential outbreaks. As the test is widely used, it is essential to be aware of the potential side effects, which can range from mild to severe. In this article, we will delve into the common and rare side effects of the TB skin test, as well as the factors that can influence the severity of the reaction.
Common Side Effects of the TB Skin Test
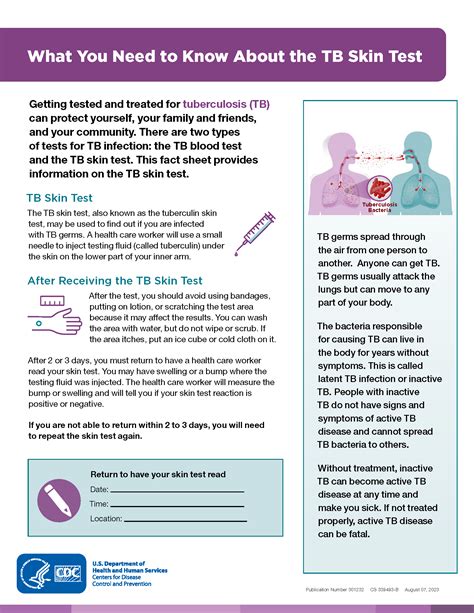
The most common side effects of the TB skin test are mild and temporary. These may include redness, swelling, and itching at the injection site. In some cases, a small bump or blister may form, which can be tender to the touch. These reactions are usually self-limiting and resolve on their own within a few days. In rare cases, the reaction can be more severe, causing significant discomfort and requiring medical attention.
Factors Influencing the Severity of the Reaction
The severity of the reaction to the TB skin test can be influenced by several factors, including the individual's immune response, the dose of PPD used, and the technique of the healthcare provider administering the test. People with a strong immune response may experience a more severe reaction, while those with a weakened immune system may have a milder reaction. Additionally, the use of certain medications, such as immunosuppressants, can affect the outcome of the test.Rare but Serious Side Effects of the TB Skin Test
While rare, there are some serious side effects associated with the TB skin test. These can include anaphylaxis, a severe allergic reaction that requires immediate medical attention. Symptoms of anaphylaxis may include difficulty breathing, rapid heartbeat, and a drop in blood pressure. Other rare side effects can include skin infections, such as cellulitis or abscesses, which can occur if the injection site becomes contaminated.
Managing Side Effects and Complications
If you experience any side effects or complications after receiving a TB skin test, it is essential to seek medical attention. Your healthcare provider can assess the severity of the reaction and provide guidance on how to manage any discomfort or complications. In some cases, over-the-counter medications, such as antihistamines or pain relievers, may be recommended to alleviate symptoms. In rare cases, more severe reactions may require hospitalization or specialized treatment.Precautions and Contraindications
While the TB skin test is generally safe, there are some precautions and contraindications to be aware of. Individuals with a history of severe allergic reactions or anaphylaxis should inform their healthcare provider before receiving the test. Additionally, people with certain medical conditions, such as skin infections or eczema, may need to take special precautions or avoid the test altogether. Pregnant or breastfeeding women should also consult with their healthcare provider before receiving the test, as there is limited data on its safety in these populations.
Special Considerations for High-Risk Groups
Certain groups, such as healthcare workers, prisoners, and people living with HIV/AIDS, may require special consideration when it comes to the TB skin test. These individuals may be at higher risk of developing TB or experiencing severe side effects, and their healthcare providers should take this into account when administering the test. Additionally, individuals who have received the Bacille Calmette-Guérin (BCG) vaccine may have a false-positive reaction to the TB skin test, which can affect the interpretation of the results.Interpreting TB Skin Test Results
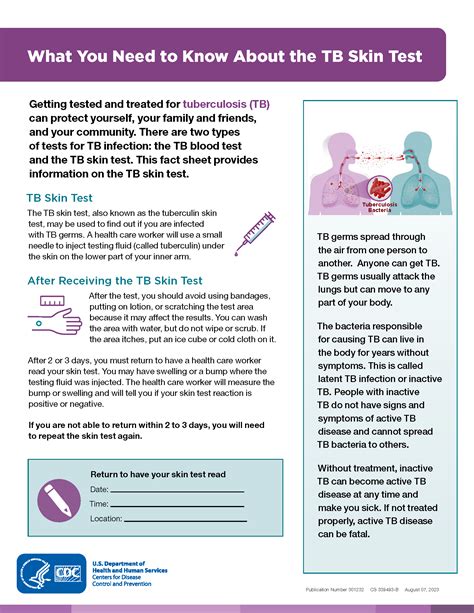
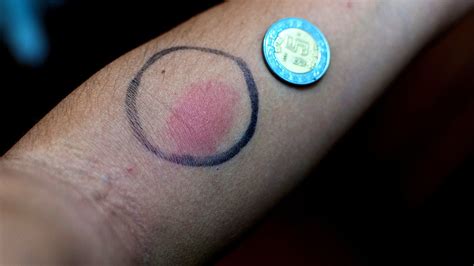
The results of the TB skin test are typically interpreted 48-72 hours after the injection. A positive result is indicated by a raised, firm, and reddened area at the injection site, which can range in size from 5-20 mm. The size of the reaction can help determine the likelihood of TB infection, with larger reactions indicating a higher probability of infection. However, the results should be interpreted in the context of the individual's medical history, risk factors, and symptoms.
Follow-Up Testing and Treatment
If the TB skin test is positive, further testing and treatment may be necessary. This can include chest X-rays, sputum tests, and blood tests to confirm the diagnosis and assess the extent of the infection. Treatment for TB typically involves a combination of antibiotics, which can be taken for several months to ensure that the infection is fully cleared. It is essential to complete the full course of treatment to prevent the development of drug-resistant TB and to reduce the risk of transmission to others.Conclusion and Next Steps
In conclusion, the TB skin test is a valuable tool for detecting TB infection, but it is essential to be aware of the potential side effects and complications. By understanding the common and rare side effects, as well as the precautions and contraindications, individuals can make informed decisions about their health. If you have received a TB skin test or are considering getting one, it is crucial to follow up with your healthcare provider to discuss the results and any necessary next steps.
What are the common side effects of the TB skin test?
+The common side effects of the TB skin test include redness, swelling, and itching at the injection site. In some cases, a small bump or blister may form, which can be tender to the touch.
Can the TB skin test cause serious side effects?
+Yes, the TB skin test can cause serious side effects, such as anaphylaxis, a severe allergic reaction that requires immediate medical attention. Other rare side effects can include skin infections, such as cellulitis or abscesses.
How is the TB skin test interpreted?
+The results of the TB skin test are typically interpreted 48-72 hours after the injection. A positive result is indicated by a raised, firm, and reddened area at the injection site, which can range in size from 5-20 mm.
We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of the TB skin test and its potential side effects. If you have any further questions or concerns, please do not hesitate to reach out to your healthcare provider. Additionally, we invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with the TB skin test in the comments section below. Your input can help others better understand the test and its implications.
