Intro
Diagnose gout accurately with our comprehensive guide on tests for gout diagnosis, including blood tests, joint fluid analysis, and medical imaging, to identify uric acid buildup and crystals, ensuring effective treatment and management of gout symptoms.
Gout is a type of arthritis that causes sudden and severe attacks of pain, swelling, and redness in the joints, often occurring at the base of the big toe. It is a complex condition that can be challenging to diagnose, as its symptoms can be similar to those of other conditions. However, there are several tests that can help diagnose gout and distinguish it from other conditions.
The importance of diagnosing gout cannot be overstated. If left untreated, gout can lead to serious complications, such as kidney damage, joint deformity, and increased risk of heart disease. Moreover, gout can significantly impact a person's quality of life, causing pain, discomfort, and limited mobility. Therefore, it is essential to seek medical attention if symptoms persist or worsen over time. In this article, we will delve into the various tests used for gout diagnosis, their benefits, and limitations, as well as provide an overview of the condition and its management.
Gout is a common condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It is caused by an excess of uric acid in the blood, which can form sharp crystals in the joints, leading to inflammation and pain. The condition can be triggered by various factors, including genetics, diet, obesity, and certain medical conditions. While gout can be managed with medication and lifestyle changes, early diagnosis is crucial to prevent long-term damage and improve treatment outcomes.
Introduction to Gout Diagnosis
Types of Tests for Gout Diagnosis
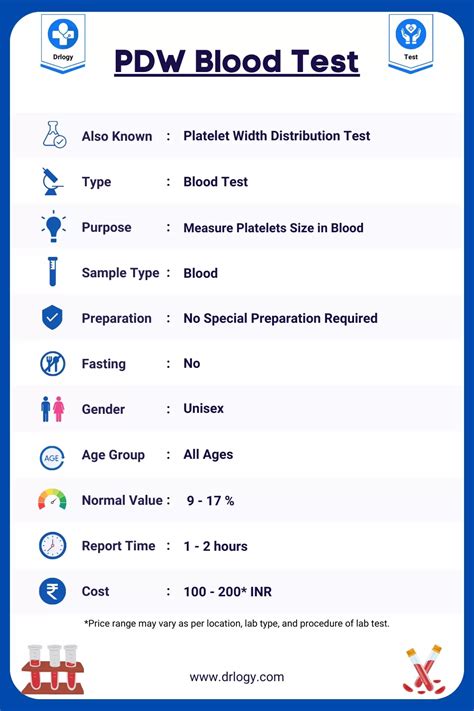
Blood Tests for Gout Diagnosis
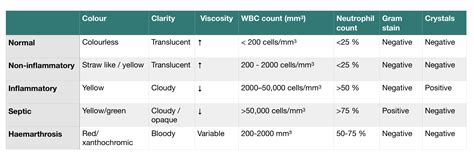
Joint Fluid Analysis for Gout Diagnosis
Imaging Studies for Gout Diagnosis

DECT Scan for Gout Diagnosis

Benefits and Limitations of Gout Diagnosis Tests
Gout Management and Treatment
Dietary Modifications for Gout Management

In conclusion, gout diagnosis and management require a comprehensive approach that involves a combination of physical examination, medical history, laboratory tests, and imaging studies. While there are several tests available for gout diagnosis, each has its benefits and limitations. Early diagnosis and treatment can help prevent long-term damage and improve treatment outcomes. By understanding the various tests and treatment options available, individuals with gout can take an active role in managing their condition and improving their quality of life.
We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with gout diagnosis and management. Have you or a loved one been diagnosed with gout? What tests were used to diagnose the condition? What treatment options have been effective in managing symptoms? Share your story in the comments below, and let's work together to raise awareness about gout and its management.
What are the common symptoms of gout?
+The common symptoms of gout include sudden and severe pain, swelling, and redness in the joints, often occurring at the base of the big toe.
How is gout diagnosed?
+Gout is diagnosed using a combination of physical examination, medical history, laboratory tests, and imaging studies.
What are the treatment options for gout?
+The treatment options for gout include medication, lifestyle changes, and dietary modifications.
Can gout be prevented?
+While gout cannot be completely prevented, the risk of gout attacks can be reduced by maintaining a healthy weight, exercising regularly, and avoiding foods high in purines.
What are the complications of untreated gout?
+The complications of untreated gout include kidney damage, joint deformity, and increased risk of heart disease.
