Intro
Lactose intolerance is a common condition that affects millions of people worldwide, causing uncomfortable symptoms such as bloating, gas, and diarrhea after consuming lactose-containing products. The condition occurs when the body is unable to produce enough lactase, an enzyme that breaks down lactose, a sugar found in milk and other dairy products. If you suspect that you or a loved one may be lactose intolerant, it is essential to undergo a lactose intolerance test to confirm the diagnosis and develop an effective treatment plan.
Lactose intolerance can significantly impact an individual's quality of life, making it challenging to enjoy everyday activities and maintain a balanced diet. The condition can also lead to malnutrition, particularly in children and adolescents, if left undiagnosed or untreated. Fortunately, there are several lactose intolerance test options available, ranging from simple self-assessment tests to more comprehensive medical evaluations. By understanding the different test options and their benefits, individuals can take the first step towards managing their lactose intolerance and improving their overall health.
The importance of lactose intolerance testing cannot be overstated, as it enables individuals to make informed decisions about their diet and lifestyle. With the help of a healthcare professional, individuals can identify the best course of treatment, whether it involves avoiding lactose-containing products, taking lactase enzyme supplements, or exploring alternative dietary options. Moreover, lactose intolerance testing can also help individuals identify other underlying conditions that may be contributing to their symptoms, such as irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) or small intestine bacterial overgrowth (SIBO). By taking a proactive approach to lactose intolerance testing, individuals can regain control over their digestive health and enjoy a more balanced and fulfilling life.
Lactose Intolerance Test Types

There are several types of lactose intolerance tests available, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. The most common tests include the hydrogen breath test, lactose tolerance test, and stool acidity test. The hydrogen breath test measures the amount of hydrogen in the breath, which is produced when undigested lactose is fermented by bacteria in the colon. The lactose tolerance test, on the other hand, measures the body's ability to absorb lactose by monitoring blood sugar levels after consuming a lactose-containing drink. The stool acidity test, also known as the stool pH test, measures the acidity of the stool, which can indicate the presence of undigested lactose.
Hydrogen Breath Test
The hydrogen breath test is a non-invasive and relatively painless procedure that can be performed in a healthcare setting or at home. The test involves drinking a lactose-containing solution and then collecting breath samples at regular intervals to measure the amount of hydrogen present. The test is typically performed over a period of 2-3 hours, during which time the individual is required to fast and avoid physical activity. The results of the test are then used to determine the presence and severity of lactose intolerance.Lactose Intolerance Test Preparation

To prepare for a lactose intolerance test, individuals should follow a few simple steps. Firstly, it is essential to avoid consuming any lactose-containing products for at least 24 hours prior to the test. This includes milk, cheese, yogurt, and any other dairy products. Secondly, individuals should avoid eating any high-fiber foods, such as beans, cabbage, and broccoli, as these can interfere with the test results. Finally, individuals should avoid taking any medications that may affect the test results, such as antibiotics or antacids.
Lactose Intolerance Test Results
The results of a lactose intolerance test can be either positive or negative. A positive result indicates that the individual is lactose intolerant, while a negative result suggests that the individual is able to digest lactose normally. In some cases, the results may be inconclusive, in which case additional testing may be required to confirm the diagnosis. It is essential to discuss the test results with a healthcare professional, who can provide guidance on the best course of treatment and help develop a personalized plan to manage lactose intolerance.Lactose Intolerance Treatment Options

There are several treatment options available for lactose intolerance, ranging from dietary modifications to enzyme supplements. The most effective treatment plan will depend on the individual's specific needs and circumstances. Some common treatment options include avoiding lactose-containing products, taking lactase enzyme supplements, and exploring alternative dietary options, such as lactose-free milk or soy milk. In some cases, individuals may also benefit from probiotics, which can help regulate the gut microbiome and improve lactose digestion.
Lactose Intolerance Diet
A lactose intolerance diet involves avoiding or reducing lactose-containing products, such as milk, cheese, and yogurt. This can be challenging, particularly for individuals who are accustomed to consuming dairy products as part of their regular diet. However, there are many lactose-free alternatives available, including lactose-free milk, soy milk, and almond milk. Individuals can also explore other calcium-rich foods, such as leafy greens, fortified cereals, and tofu, to ensure they are getting enough calcium in their diet.Lactose Intolerance Symptoms
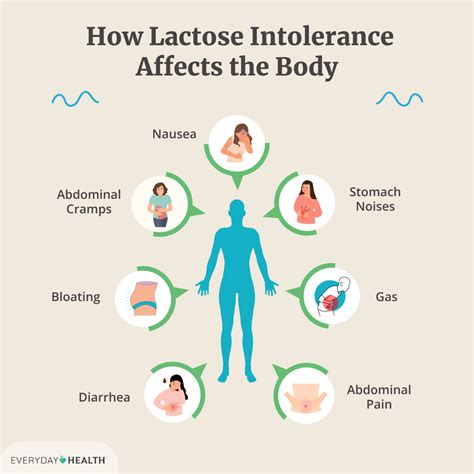
The symptoms of lactose intolerance can vary in severity and frequency, but common symptoms include bloating, gas, diarrhea, stomach cramps, and nausea. In some cases, individuals may also experience vomiting, headaches, and fatigue. The symptoms typically occur within 30 minutes to 2 hours after consuming lactose-containing products and can last for several hours. If left untreated, lactose intolerance can lead to malnutrition, particularly in children and adolescents, as well as other complications, such as osteoporosis and anemia.
Lactose Intolerance Complications
If left untreated, lactose intolerance can lead to several complications, including malnutrition, osteoporosis, and anemia. Malnutrition can occur when individuals avoid dairy products and other calcium-rich foods, leading to a deficiency in essential nutrients. Osteoporosis can occur when the body is unable to absorb enough calcium, leading to weak and brittle bones. Anemia can occur when the body is unable to absorb enough iron, leading to fatigue, weakness, and shortness of breath.Lactose Intolerance Prevention

While lactose intolerance cannot be prevented, there are several steps individuals can take to reduce their risk of developing the condition. Firstly, individuals can avoid consuming large amounts of lactose-containing products, particularly if they are prone to digestive issues. Secondly, individuals can explore lactose-free alternatives, such as lactose-free milk or soy milk. Finally, individuals can maintain a balanced diet that includes a variety of calcium-rich foods, such as leafy greens, fortified cereals, and tofu.
Lactose Intolerance Management
Managing lactose intolerance requires a comprehensive approach that includes dietary modifications, enzyme supplements, and lifestyle changes. Individuals can start by avoiding lactose-containing products and exploring lactose-free alternatives. They can also take lactase enzyme supplements to help digest lactose. Additionally, individuals can maintain a food diary to track their symptoms and identify trigger foods. By taking a proactive approach to managing lactose intolerance, individuals can reduce their symptoms and improve their overall quality of life.What is lactose intolerance?
+Lactose intolerance is a condition in which the body is unable to produce enough lactase, an enzyme that breaks down lactose, a sugar found in milk and other dairy products.
What are the symptoms of lactose intolerance?
+The symptoms of lactose intolerance include bloating, gas, diarrhea, stomach cramps, and nausea, and can vary in severity and frequency.
How is lactose intolerance diagnosed?
+Lactose intolerance is typically diagnosed using a hydrogen breath test, lactose tolerance test, or stool acidity test, which measure the body's ability to digest lactose.
What are the treatment options for lactose intolerance?
+The treatment options for lactose intolerance include avoiding lactose-containing products, taking lactase enzyme supplements, and exploring alternative dietary options, such as lactose-free milk or soy milk.
Can lactose intolerance be prevented?
+While lactose intolerance cannot be prevented, individuals can reduce their risk of developing the condition by avoiding consuming large amounts of lactose-containing products and maintaining a balanced diet that includes a variety of calcium-rich foods.
In summary, lactose intolerance is a common condition that can significantly impact an individual's quality of life. By understanding the different lactose intolerance test options and treatment plans, individuals can take the first step towards managing their condition and improving their overall health. If you suspect that you or a loved one may be lactose intolerant, it is essential to consult with a healthcare professional to discuss the best course of treatment and develop a personalized plan to manage lactose intolerance. We encourage you to share your experiences and ask questions in the comments below, and to share this article with others who may be struggling with lactose intolerance. By working together, we can raise awareness and promote education about lactose intolerance, and help individuals take control of their digestive health.
