Intro
Discover the importance of testing breast cancer gene mutations, including BRCA1 and BRCA2, to assess genetic risk and prevent breast cancer through early detection and targeted therapy.
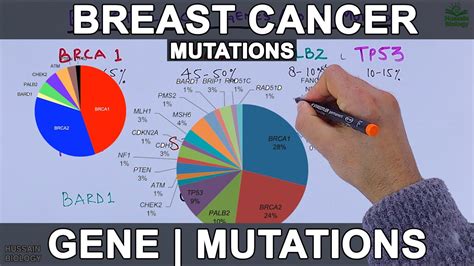
Breast cancer is a complex and multifaceted disease that affects millions of people worldwide. While there are many factors that contribute to the development of breast cancer, genetic mutations play a significant role in the onset of this disease. In recent years, there has been a growing interest in testing for breast cancer genes, particularly the BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes. These genes are responsible for producing proteins that help repair damaged DNA, and mutations in these genes can increase the risk of developing breast and ovarian cancer.
The importance of testing for breast cancer genes cannot be overstated. For individuals who have a family history of breast or ovarian cancer, testing for these genes can provide valuable information about their risk of developing the disease. Additionally, testing can help identify individuals who may be at risk of passing on genetic mutations to their children. With this information, individuals can take proactive steps to reduce their risk of developing breast cancer, such as undergoing regular screening, taking preventive medications, or considering surgical options.
The process of testing for breast cancer genes is relatively straightforward. A simple blood test or saliva sample is typically used to collect a DNA sample, which is then sent to a laboratory for analysis. The laboratory will examine the DNA sample for any mutations in the BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes, as well as other genes that may be associated with an increased risk of breast cancer. The results of the test can take several weeks to several months to receive, and they will typically indicate whether an individual has a mutation in one of the breast cancer genes.
Understanding Breast Cancer Genes
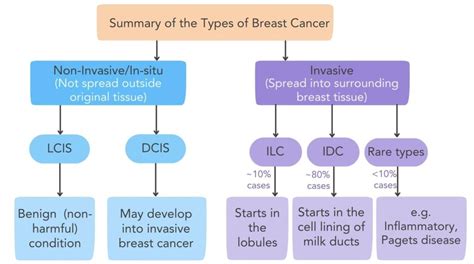
Breast cancer genes, such as BRCA1 and BRCA2, play a critical role in the development and growth of breast tissue. These genes produce proteins that help repair damaged DNA, which can contribute to the development of cancer. When these genes are mutated, the proteins they produce may not function properly, leading to an increased risk of breast cancer. There are several types of breast cancer genes, including tumor suppressor genes, oncogenes, and DNA repair genes. Tumor suppressor genes, such as BRCA1 and BRCA2, help prevent the growth of cancer cells, while oncogenes can promote the growth of cancer cells. DNA repair genes, such as ATM and CHEK2, help repair damaged DNA, which can contribute to the development of cancer.
Types of Breast Cancer Genes
There are several types of breast cancer genes, including: * BRCA1 and BRCA2: These genes are the most well-known breast cancer genes and are responsible for producing proteins that help repair damaged DNA. * ATM: This gene produces a protein that helps repair damaged DNA and is associated with an increased risk of breast cancer. * CHEK2: This gene produces a protein that helps regulate the cell cycle and is associated with an increased risk of breast cancer. * PALB2: This gene produces a protein that helps repair damaged DNA and is associated with an increased risk of breast cancer.Benefits of Testing for Breast Cancer Genes
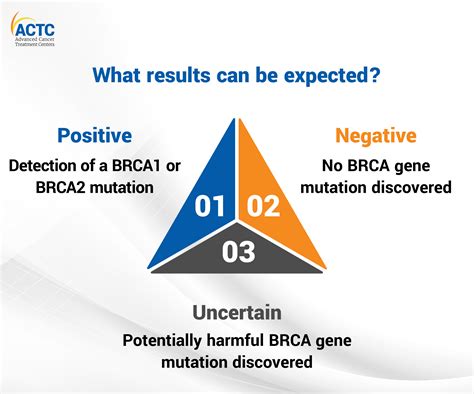
Testing for breast cancer genes can provide several benefits, including:
- Identification of genetic mutations: Testing can identify genetic mutations that increase the risk of breast cancer, allowing individuals to take proactive steps to reduce their risk.
- Risk assessment: Testing can help individuals understand their risk of developing breast cancer, which can inform decisions about screening and prevention.
- Family planning: Testing can provide information about the risk of passing on genetic mutations to children, which can inform decisions about family planning.
- Targeted therapy: Testing can help identify individuals who may be eligible for targeted therapies, such as PARP inhibitors, which can be effective in treating breast cancer.
Who Should Be Tested for Breast Cancer Genes
Testing for breast cancer genes is typically recommended for individuals who have a family history of breast or ovarian cancer, as well as those who have been diagnosed with breast cancer at a young age. Additionally, testing may be recommended for individuals who have a personal history of breast cancer, as well as those who have a history of radiation exposure. The following individuals may be candidates for testing: * Women with a family history of breast or ovarian cancer * Women who have been diagnosed with breast cancer at a young age * Women who have a personal history of breast cancer * Women who have a history of radiation exposure * Men with a family history of breast or ovarian cancerHow to Get Tested for Breast Cancer Genes

Getting tested for breast cancer genes is a relatively straightforward process. The first step is to speak with a healthcare provider, such as a primary care physician or a genetic counselor, to discuss the risks and benefits of testing. The healthcare provider will typically ask about family history, medical history, and other factors that may increase the risk of breast cancer. If testing is recommended, a blood test or saliva sample will be collected and sent to a laboratory for analysis. The results of the test will typically be available within several weeks to several months.
What to Expect from the Testing Process
The testing process typically involves the following steps: * Consultation with a healthcare provider: The first step is to speak with a healthcare provider to discuss the risks and benefits of testing. * Collection of a DNA sample: A blood test or saliva sample will be collected and sent to a laboratory for analysis. * Analysis of the DNA sample: The laboratory will examine the DNA sample for any mutations in the BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes, as well as other genes that may be associated with an increased risk of breast cancer. * Receipt of test results: The results of the test will typically be available within several weeks to several months.Interpretation of Test Results
The interpretation of test results can be complex and may require the expertise of a genetic counselor or other healthcare professional. The results of the test will typically indicate whether an individual has a mutation in one of the breast cancer genes. If a mutation is detected, the individual may be at increased risk of developing breast cancer, and may need to take proactive steps to reduce their risk. If no mutation is detected, the individual may still be at risk of developing breast cancer, and should continue to follow recommended screening guidelines.
Understanding the Risks and Benefits of Testing
Testing for breast cancer genes can provide valuable information about an individual's risk of developing breast cancer. However, testing is not without risks and benefits. The following are some of the potential risks and benefits of testing: * Risks: + Emotional distress: Receiving a positive test result can be emotionally distressing, and may lead to anxiety and depression. + Insurance discrimination: In some cases, individuals who test positive for a breast cancer gene may face insurance discrimination. + Surgical risks: Individuals who test positive for a breast cancer gene may be at increased risk of surgical complications, such as infection and scarring. * Benefits: + Identification of genetic mutations: Testing can identify genetic mutations that increase the risk of breast cancer, allowing individuals to take proactive steps to reduce their risk. + Risk assessment: Testing can help individuals understand their risk of developing breast cancer, which can inform decisions about screening and prevention. + Family planning: Testing can provide information about the risk of passing on genetic mutations to children, which can inform decisions about family planning.Living with a Breast Cancer Gene Mutation
Living with a breast cancer gene mutation can be challenging, but there are several steps that individuals can take to reduce their risk of developing breast cancer. The following are some of the ways that individuals can manage their risk:
- Regular screening: Individuals with a breast cancer gene mutation should undergo regular screening, such as mammograms and MRI scans, to detect any changes in the breast tissue.
- Preventive medications: Individuals with a breast cancer gene mutation may be eligible for preventive medications, such as tamoxifen or raloxifene, which can help reduce the risk of breast cancer.
- Surgical options: In some cases, individuals with a breast cancer gene mutation may choose to undergo surgical options, such as a mastectomy or oophorectomy, to reduce their risk of developing breast cancer.
Coping with the Emotional Impact of Testing
Receiving a positive test result can be emotionally distressing, and may lead to anxiety and depression. The following are some of the ways that individuals can cope with the emotional impact of testing: * Seek support: Individuals who receive a positive test result should seek support from family, friends, and healthcare professionals. * Consider counseling: Counseling can provide individuals with a safe and supportive environment to discuss their feelings and concerns. * Join a support group: Joining a support group can provide individuals with a sense of community and connection with others who are going through similar experiences.What are the benefits of testing for breast cancer genes?
+Testing for breast cancer genes can provide several benefits, including identification of genetic mutations, risk assessment, and family planning.
Who should be tested for breast cancer genes?
+Testing for breast cancer genes is typically recommended for individuals who have a family history of breast or ovarian cancer, as well as those who have been diagnosed with breast cancer at a young age.
What are the risks and benefits of testing for breast cancer genes?
+Testing for breast cancer genes can provide valuable information about an individual's risk of developing breast cancer, but it is not without risks and benefits. The potential risks of testing include emotional distress, insurance discrimination, and surgical risks, while the potential benefits include identification of genetic mutations, risk assessment, and family planning.
In conclusion, testing for breast cancer genes is an important step in understanding an individual's risk of developing breast cancer. While testing is not without risks and benefits, it can provide valuable information about an individual's risk of developing breast cancer, and can inform decisions about screening and prevention. If you are considering testing for breast cancer genes, it is essential to speak with a healthcare provider to discuss the risks and benefits of testing, and to determine whether testing is right for you. We encourage you to share your thoughts and experiences with testing for breast cancer genes in the comments below, and to share this article with anyone who may be interested in learning more about this topic.
