Intro
Discover 5 effective ways to test PCOS, including hormone level checks, ultrasound, and physical exams, to diagnose and manage Polycystic Ovary Syndrome symptoms, insulin resistance, and infertility issues.
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is a complex hormonal disorder that affects women of reproductive age. It is characterized by a range of symptoms, including irregular menstrual cycles, weight gain, acne, and excess hair growth. Diagnosing PCOS can be challenging, as the symptoms can vary widely from woman to woman. However, there are several tests that can help diagnose PCOS. In this article, we will explore the different ways to test for PCOS and what to expect from each test.
The importance of diagnosing PCOS cannot be overstated. If left untreated, PCOS can lead to a range of serious health problems, including infertility, type 2 diabetes, and heart disease. Early diagnosis and treatment can help manage symptoms and reduce the risk of long-term complications. With the right diagnosis and treatment, women with PCOS can lead healthy and fulfilling lives.
PCOS is a common endocrine disorder that affects up to 10% of women of childbearing age. The exact cause of PCOS is not known, but it is thought to be related to a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Women with a family history of PCOS are more likely to develop the condition, and certain lifestyle factors, such as obesity and insulin resistance, can also increase the risk. By understanding the causes and symptoms of PCOS, women can take steps to manage their symptoms and reduce their risk of long-term complications.
Understanding PCOS Symptoms
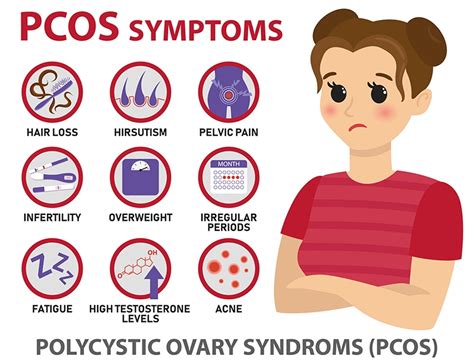
Physical Exam and Medical History

What to Expect from a Physical Exam
A physical exam for PCOS will typically include a pelvic exam to check for any abnormalities in the reproductive organs. The healthcare provider may also check for signs of insulin resistance, such as high blood pressure and high cholesterol. A physical exam can help diagnose PCOS, but it is not definitive. Further testing is usually needed to confirm a diagnosis.Hormone Level Tests

Types of Hormone Level Tests
There are several types of hormone level tests that can be used to diagnose PCOS. These include: * Androgen tests: These tests measure the levels of androgen in the blood. High levels of androgen can indicate PCOS. * Estrogen tests: These tests measure the levels of estrogen in the blood. Low levels of estrogen can indicate PCOS. * Progesterone tests: These tests measure the levels of progesterone in the blood. Low levels of progesterone can indicate PCOS. * Thyroid function tests: These tests measure the levels of thyroid hormones in the blood. Abnormal thyroid function can affect hormone levels and mimic PCOS symptoms.Ultrasound
What to Expect from an Ultrasound
An ultrasound for PCOS will typically involve a transvaginal ultrasound, which involves inserting a probe into the vagina to get a closer look at the ovaries. The test is usually painless and takes about 30 minutes to complete. The ultrasound technician will take images of the ovaries and check for any abnormalities, such as cysts or tumors.Glucose Tolerance Test

What to Expect from a Glucose Tolerance Test
A glucose tolerance test for PCOS will typically involve drinking a sugary drink and then having blood drawn at regular intervals to measure blood sugar levels. The test usually takes about 2 hours to complete and can help diagnose insulin resistance and PCOS.Lipid Profile Test
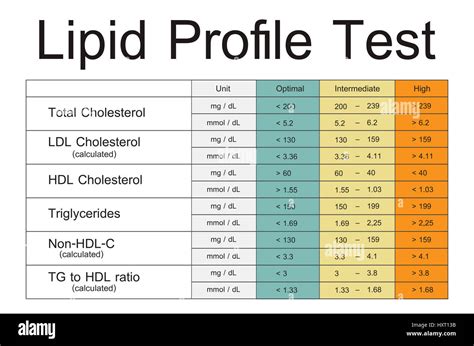
What to Expect from a Lipid Profile Test
A lipid profile test for PCOS will typically involve a blood test to measure cholesterol and triglyceride levels. The test is usually painless and takes about 10 minutes to complete. The results can help diagnose PCOS and identify any potential cardiovascular risks.In conclusion, diagnosing PCOS can be challenging, but there are several tests that can help. A physical exam and medical history are the first steps in diagnosing PCOS, followed by hormone level tests, ultrasound, glucose tolerance test, and lipid profile test. By understanding the different tests used to diagnose PCOS, women can take steps to manage their symptoms and reduce their risk of long-term complications.
We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with PCOS in the comments below. If you have any questions or concerns, please don't hesitate to ask. You can also share this article with anyone who may be experiencing symptoms of PCOS.
What are the symptoms of PCOS?
+The symptoms of PCOS can vary widely, but common symptoms include irregular menstrual cycles, weight gain, acne, and excess hair growth.
How is PCOS diagnosed?
+PCOS is diagnosed using a combination of physical exam, medical history, hormone level tests, ultrasound, glucose tolerance test, and lipid profile test.
Can PCOS be treated?
+Yes, PCOS can be treated using a combination of lifestyle changes, such as diet and exercise, and medication to manage symptoms and reduce the risk of long-term complications.
What are the risks of untreated PCOS?
+Untreated PCOS can increase the risk of long-term complications, such as infertility, type 2 diabetes, and heart disease.
How can I manage my PCOS symptoms?
+Managing PCOS symptoms involves a combination of lifestyle changes, such as diet and exercise, and medication to manage symptoms and reduce the risk of long-term complications.
