Intro
Discover the top 5 thyroid medicines, including synthetic hormones and natural supplements, to manage hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism, and learn about thyroid medication side effects, dosage, and treatment options.
The thyroid gland plays a crucial role in regulating various bodily functions, including metabolism, growth, and development. When the thyroid gland does not produce enough thyroid hormones, it can lead to a condition known as hypothyroidism. Hypothyroidism can cause a range of symptoms, including fatigue, weight gain, and dry skin. Fortunately, there are several thyroid medicines available that can help manage the condition and alleviate its symptoms. In this article, we will discuss the importance of thyroid medicines and explore the different types of medications available.
Thyroid medicines are essential for individuals with hypothyroidism, as they help replace the missing thyroid hormones in the body. Without these medicines, individuals with hypothyroidism may experience a range of complications, including heart problems, nerve damage, and infertility. Thyroid medicines can help regulate metabolism, energy levels, and overall health. With the right medication and dosage, individuals with hypothyroidism can lead active and healthy lives.
The treatment of hypothyroidism typically involves taking thyroid hormone replacement medicines. These medicines work by replacing the missing thyroid hormones in the body, which can help alleviate symptoms and regulate bodily functions. There are several types of thyroid medicines available, each with its own unique characteristics and benefits. Some of the most common types of thyroid medicines include levothyroxine, liothyronine, and natural desiccated thyroid. In the following sections, we will explore these medicines in more detail and discuss their benefits, side effects, and dosage requirements.
Types of Thyroid Medicines

There are several types of thyroid medicines available, each with its own unique characteristics and benefits. Some of the most common types of thyroid medicines include:
- Levothyroxine (T4): This is the most commonly prescribed thyroid medicine, which works by replacing the missing T4 hormone in the body.
- Liothyronine (T3): This medicine works by replacing the missing T3 hormone in the body, which can help regulate metabolism and energy levels.
- Natural desiccated thyroid: This type of medicine is derived from animal thyroid glands and contains both T4 and T3 hormones.
- Thyroid extracts: These are derived from animal thyroid glands and contain a combination of T4 and T3 hormones.
Levothyroxine (T4)
Levothyroxine is the most commonly prescribed thyroid medicine, which works by replacing the missing T4 hormone in the body. It is available in various brand names, including Synthroid, Levoxyl, and Unithroid. Levothyroxine is usually taken orally, once a day, and is available in various dosage strengths. The dosage of levothyroxine may vary depending on the individual's age, weight, and medical condition.Benefits of Thyroid Medicines

Thyroid medicines can provide several benefits for individuals with hypothyroidism, including:
- Regulating metabolism and energy levels
- Alleviating symptoms such as fatigue, weight gain, and dry skin
- Improving heart health and reducing the risk of heart problems
- Regulating menstrual cycles and improving fertility
- Improving cognitive function and reducing the risk of depression
Liothyronine (T3)
Liothyronine is another type of thyroid medicine that works by replacing the missing T3 hormone in the body. It is available in various brand names, including Cytomel and Triostat. Liothyronine is usually taken orally, once a day, and is available in various dosage strengths. The dosage of liothyronine may vary depending on the individual's age, weight, and medical condition.Side Effects of Thyroid Medicines
While thyroid medicines can provide several benefits, they can also cause some side effects, including:
- Hair loss
- Weight loss
- Nervousness and anxiety
- Insomnia and sleep disturbances
- Increased heart rate and palpitations
Natural Desiccated Thyroid
Natural desiccated thyroid is a type of thyroid medicine that is derived from animal thyroid glands. It contains both T4 and T3 hormones and is available in various brand names, including Armour Thyroid and Nature-Throid. Natural desiccated thyroid is usually taken orally, once a day, and is available in various dosage strengths. The dosage of natural desiccated thyroid may vary depending on the individual's age, weight, and medical condition.Dosage and Administration
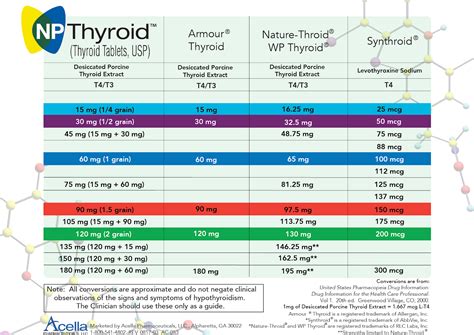
The dosage and administration of thyroid medicines may vary depending on the individual's age, weight, and medical condition. It is essential to follow the doctor's instructions and take the medicine as prescribed. Some general guidelines for taking thyroid medicines include:
- Taking the medicine at the same time every day
- Taking the medicine on an empty stomach, at least 30 minutes before breakfast
- Avoiding taking the medicine with other medications that may interact with it
- Monitoring thyroid hormone levels regularly to adjust the dosage as needed
Thyroid Extracts
Thyroid extracts are derived from animal thyroid glands and contain a combination of T4 and T3 hormones. They are available in various brand names, including Thyroid USP and Thyrolar. Thyroid extracts are usually taken orally, once a day, and are available in various dosage strengths. The dosage of thyroid extracts may vary depending on the individual's age, weight, and medical condition.Precautions and Interactions

While thyroid medicines can provide several benefits, they can also interact with other medications and have some precautions. Some of the precautions and interactions to consider include:
- Interactions with other medications, such as blood thinners and diabetes medications
- Allergic reactions to the medicine
- Pregnancy and breastfeeding precautions
- Pediatric and geriatric precautions
Pregnancy and Breastfeeding
Thyroid medicines are essential for pregnant and breastfeeding women with hypothyroidism. However, it is crucial to monitor thyroid hormone levels regularly and adjust the dosage as needed. Some thyroid medicines, such as levothyroxine, are safe to take during pregnancy and breastfeeding, while others, such as liothyronine, may require careful monitoring.Conclusion and Future Directions

In conclusion, thyroid medicines play a crucial role in managing hypothyroidism and alleviating its symptoms. With the right medication and dosage, individuals with hypothyroidism can lead active and healthy lives. Future directions in thyroid medicine research include developing new and more effective treatments, improving diagnostic techniques, and enhancing patient outcomes.
We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with thyroid medicines in the comments section below. If you have any questions or concerns, please do not hesitate to ask. You can also share this article with your friends and family to raise awareness about the importance of thyroid medicines.
What are the symptoms of hypothyroidism?
+The symptoms of hypothyroidism include fatigue, weight gain, dry skin, hair loss, and cold intolerance.
What are the different types of thyroid medicines?
+The different types of thyroid medicines include levothyroxine, liothyronine, natural desiccated thyroid, and thyroid extracts.
How do I take thyroid medicines?
+Thyroid medicines should be taken at the same time every day, on an empty stomach, and with a full glass of water.
Can I take thyroid medicines during pregnancy and breastfeeding?
+Yes, thyroid medicines are essential for pregnant and breastfeeding women with hypothyroidism. However, it is crucial to monitor thyroid hormone levels regularly and adjust the dosage as needed.
What are the side effects of thyroid medicines?
+The side effects of thyroid medicines include hair loss, weight loss, nervousness and anxiety, insomnia and sleep disturbances, and increased heart rate and palpitations.
