Intro
Discover the 5 ways TSH test impacts thyroid function, including diagnosis, treatment, and management of hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism, with insights into thyroid-stimulating hormone levels and hormone imbalance.
The TSH test, also known as the Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone test, is a crucial diagnostic tool used to assess the functioning of the thyroid gland. The thyroid gland plays a vital role in regulating various bodily functions, including metabolism, growth, and development. An abnormal TSH level can indicate thyroid disorders, such as hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism. In this article, we will delve into the world of TSH testing, exploring its importance, benefits, and the various ways it can be utilized to diagnose and manage thyroid-related conditions.
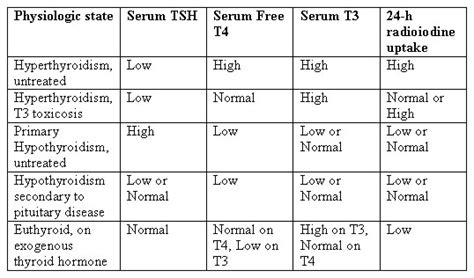
The TSH test measures the level of thyroid-stimulating hormone in the blood, which is produced by the pituitary gland. This hormone stimulates the thyroid gland to produce thyroid hormones, namely triiodothyronine (T3) and thyroxine (T4). The TSH test is essential for diagnosing and monitoring thyroid disorders, as it helps healthcare professionals determine whether the thyroid gland is producing adequate amounts of thyroid hormones. An abnormal TSH level can indicate a range of thyroid-related conditions, from mild hypothyroidism to severe hyperthyroidism.
Thyroid disorders can have a significant impact on an individual's quality of life, causing symptoms such as fatigue, weight gain or loss, hair loss, and mood changes. Therefore, it is crucial to diagnose and manage these conditions effectively. The TSH test is a vital tool in this process, providing healthcare professionals with valuable insights into thyroid function and enabling them to develop personalized treatment plans. In the following sections, we will explore the different ways the TSH test can be used to diagnose and manage thyroid-related conditions.
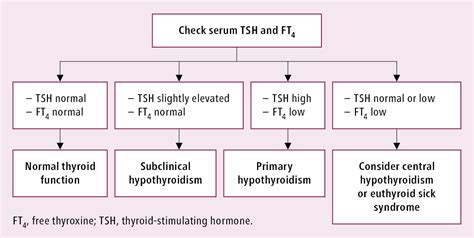
Understanding TSH Test Results
Factors Influencing TSH Test Results
Several factors can influence TSH test results, including: * Certain medications, such as thyroid hormones, steroids, and dopamine * Pregnancy, which can affect thyroid function and TSH levels * Underlying medical conditions, such as pituitary gland disorders or thyroid nodules * Age, as TSH levels tend to increase with age * Time of day, as TSH levels tend to be higher in the morning and lower in the eveningDiagnosing Hypothyroidism with TSH Test

TSH Test Results in Hypothyroidism
In hypothyroidism, the TSH test results typically show: * Elevated TSH levels, often above 10 mU/L * Low free T4 (FT4) and free T3 (FT3) levels * Presence of thyroid antibodies, which can indicate an autoimmune thyroid disorderDiagnosing Hyperthyroidism with TSH Test
TSH Test Results in Hyperthyroidism
In hyperthyroidism, the TSH test results typically show: * Suppressed TSH levels, often below 0.1 mU/L * Elevated FT4 and FT3 levels * Presence of thyroid-stimulating immunoglobulins, which can indicate an autoimmune thyroid disorderMonitoring Thyroid Function with TSH Test

Frequency of TSH Testing
The frequency of TSH testing depends on various factors, including: * Age and overall health * Presence of underlying medical conditions * Type and severity of thyroid disorder * Medication regimen and dosageInterpreting TSH Test Results in Special Populations
TSH Test Results in Pregnancy
In pregnancy, the TSH test results typically show: * Elevated TSH levels, often above 2.5 mU/L * Low FT4 and FT3 levels * Presence of thyroid antibodies, which can indicate an autoimmune thyroid disorderWhat is the normal range for TSH test results?
+The normal range for TSH test results is typically between 0.4 and 4.5 milliunits per liter (mU/L).
What are the symptoms of hypothyroidism?
+The symptoms of hypothyroidism include fatigue, weight gain, hair loss, cold intolerance, and dry skin.
How often should I get a TSH test?
+The frequency of TSH testing depends on various factors, including age, overall health, and presence of underlying medical conditions. Your healthcare professional will determine the best testing schedule for you.
In conclusion, the TSH test is a vital diagnostic tool for assessing thyroid function and diagnosing thyroid-related conditions. By understanding the importance of TSH testing, individuals can take an active role in managing their thyroid health. If you have any concerns about your thyroid health or would like to learn more about TSH testing, we encourage you to consult with a healthcare professional. Additionally, we invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with TSH testing in the comments section below. By working together, we can promote greater awareness and understanding of thyroid health and the importance of TSH testing.
