Intro
Discover the ultimate Thyroid Stimulating Test Guide, covering thyroid function, hormone regulation, and hypothyroidism diagnosis, with expert insights on TSH levels, thyroid disorders, and treatment options.
The thyroid stimulating test, also known as the thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) test, is a crucial diagnostic tool used to evaluate the functioning of the thyroid gland. Located in the neck, the thyroid gland plays a vital role in regulating various bodily functions, including metabolism, growth, and development. An imbalance of thyroid hormones can lead to a range of health problems, from mild discomfort to life-threatening conditions. In this article, we will delve into the world of thyroid stimulating tests, exploring their importance, benefits, and what to expect during the testing process.
Thyroid disorders are more common than one might think, affecting millions of people worldwide. Hypothyroidism, a condition characterized by an underactive thyroid gland, can cause symptoms such as fatigue, weight gain, and dry skin. On the other hand, hyperthyroidism, a condition where the thyroid gland is overactive, can lead to symptoms like weight loss, rapid heartbeat, and anxiety. The thyroid stimulating test is a valuable tool in diagnosing and managing these conditions, allowing healthcare professionals to develop effective treatment plans and monitor patient progress.
The thyroid stimulating test is a relatively simple and non-invasive procedure, involving a blood sample drawn from a vein in the arm. The blood sample is then sent to a laboratory for analysis, where the levels of TSH and other thyroid hormones, such as triiodothyronine (T3) and thyroxine (T4), are measured. The results of the test can provide valuable insights into thyroid function, helping healthcare professionals to diagnose and manage a range of thyroid-related disorders.
Understanding Thyroid Stimulating Test
The thyroid stimulating test is a crucial component of thyroid function testing, providing a comprehensive picture of thyroid health. The test measures the levels of TSH, a hormone produced by the pituitary gland that stimulates the thyroid gland to produce T3 and T4. By analyzing TSH levels, healthcare professionals can determine if the thyroid gland is producing adequate amounts of thyroid hormones. Elevated TSH levels may indicate hypothyroidism, while low TSH levels may suggest hyperthyroidism.
Benefits of Thyroid Stimulating Test
The thyroid stimulating test offers several benefits, including: * Early detection and diagnosis of thyroid disorders * Monitoring of thyroid hormone levels during treatment * Evaluation of thyroid function in patients with symptoms of thyroid disease * Detection of thyroid problems in pregnant women, which is crucial for fetal developmentPreparation and Procedure

To prepare for the thyroid stimulating test, patients are typically required to:
- Fast for several hours before the test
- Avoid taking certain medications, such as thyroid supplements or steroids
- Inform their healthcare provider about any medications they are currently taking
- Wear comfortable clothing and arrive at least 15 minutes before the scheduled test time
The procedure itself is relatively quick and straightforward, involving a blood sample drawn from a vein in the arm. The blood sample is then sent to a laboratory for analysis, and the results are typically available within a few days.
Interpreting Test Results
Interpreting the results of the thyroid stimulating test requires a comprehensive understanding of thyroid function and hormone levels. The results are typically evaluated in conjunction with symptoms, medical history, and other diagnostic tests. The following are some general guidelines for interpreting TSH levels: * Normal TSH levels: 0.4-4.5 milliunits per liter (mU/L) * Elevated TSH levels: above 4.5 mU/L, which may indicate hypothyroidism * Low TSH levels: below 0.4 mU/L, which may suggest hyperthyroidismThyroid Disorders and Treatment Options
Thyroid disorders can be effectively managed with a range of treatment options, including:
- Medications, such as synthetic thyroid hormones or anti-thyroid medications
- Radioactive iodine therapy, which involves ingesting a small amount of radioactive iodine to destroy part or all of the thyroid gland
- Surgery, which may be necessary to remove a portion or all of the thyroid gland
Treatment Considerations
When considering treatment options, healthcare professionals take into account several factors, including: * The underlying cause of the thyroid disorder * The severity of symptoms * The patient's overall health and medical history * The potential risks and benefits of each treatment optionLiving with Thyroid Disorders
Living with a thyroid disorder can be challenging, but with the right treatment and support, it is possible to manage symptoms and maintain a high quality of life. Patients with thyroid disorders can take several steps to manage their condition, including:
- Following a healthy diet and exercise routine
- Monitoring thyroid hormone levels regularly
- Attending regular follow-up appointments with their healthcare provider
- Connecting with others who have thyroid disorders, either in person or online
Coping with Thyroid-Related Symptoms
Coping with thyroid-related symptoms can be difficult, but there are several strategies that can help, including: * Practicing stress-reducing techniques, such as meditation or yoga * Getting enough sleep and maintaining a consistent sleep schedule * Engaging in regular physical activity, such as walking or swimming * Seeking support from friends, family, or a mental health professionalConclusion and Next Steps
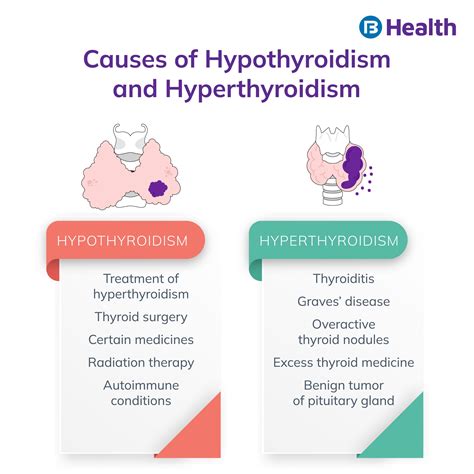
In conclusion, the thyroid stimulating test is a valuable diagnostic tool that plays a critical role in evaluating thyroid function and managing thyroid-related disorders. By understanding the benefits, preparation, and procedure of the test, patients can take an active role in their healthcare and work with their healthcare provider to develop an effective treatment plan. If you have concerns about your thyroid health or would like to learn more about thyroid stimulating tests, consult with your healthcare provider or a qualified medical professional.
What is the purpose of a thyroid stimulating test?
+The purpose of a thyroid stimulating test is to evaluate the functioning of the thyroid gland and diagnose thyroid-related disorders, such as hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism.
How do I prepare for a thyroid stimulating test?
+To prepare for a thyroid stimulating test, patients are typically required to fast for several hours, avoid taking certain medications, and inform their healthcare provider about any medications they are currently taking.
What are the benefits of a thyroid stimulating test?
+The benefits of a thyroid stimulating test include early detection and diagnosis of thyroid disorders, monitoring of thyroid hormone levels during treatment, and evaluation of thyroid function in patients with symptoms of thyroid disease.
How long does it take to get the results of a thyroid stimulating test?
+The results of a thyroid stimulating test are typically available within a few days, although this may vary depending on the laboratory and healthcare provider.
Can I take the test if I am pregnant or breastfeeding?
+Yes, the thyroid stimulating test is safe for pregnant and breastfeeding women, although it is essential to inform your healthcare provider about your pregnancy or breastfeeding status before taking the test.
We hope this comprehensive guide to thyroid stimulating tests has provided you with valuable insights and information. If you have any further questions or concerns, please do not hesitate to reach out to your healthcare provider or a qualified medical professional. Share this article with friends and family who may be interested in learning more about thyroid health, and take the first step towards maintaining a healthy and balanced lifestyle.
