Intro
Discover Tizanidine side effects, including muscle weakness, drowsiness, and hallucinations. Learn about common and rare effects, interactions, and warnings to ensure safe usage of this muscle relaxant medication.
Tizanidine is a muscle relaxant used to treat muscle spasms caused by conditions such as multiple sclerosis or spinal injury. It works by blocking nerve impulses that cause muscles to tighten, helping to relieve pain and discomfort. However, like all medications, tizanidine can have side effects, some of which can be serious. Understanding the potential side effects of tizanidine is crucial for patients who are considering taking this medication or are already on it.
The importance of being aware of tizanidine's side effects cannot be overstated. While for many people, the benefits of taking tizanidine outweigh the risks, knowing what to expect can help patients manage their condition more effectively and seek medical help if needed. Side effects can range from mild and temporary to severe and potentially life-threatening. Moreover, being informed allows patients to take preventive measures, adhere to their treatment plan, and maintain open communication with their healthcare provider about any changes in their condition or concerns they may have.
Tizanidine's impact on daily life can also be significant. By alleviating muscle spasms, it can improve mobility, reduce pain, and enhance overall quality of life. However, the presence of side effects can sometimes counteract these benefits, leading to a decrease in physical activity, increased fatigue, or emotional distress. Therefore, it's essential to weigh the benefits against the potential drawbacks and to manage side effects effectively to ensure that tizanidine use is optimized.
Tizanidine Mechanism of Action
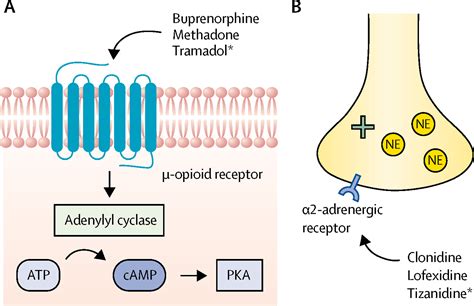
How Tizanidine Works
The mechanism through which tizanidine exerts its effects involves the activation of α2 adrenergic receptors in the spinal cord. These receptors are part of the body's natural pain modulation system. When tizanidine binds to these receptors, it mimics the action of natural chemicals in the body that help to reduce pain and muscle tension. This action not only helps in relieving muscle spasms but can also contribute to its side effect profile, as the effects of tizanidine are not limited to the spinal cord but can also influence other bodily functions.Common Side Effects of Tizanidine

Less Common but Serious Side Effects
While less common, tizanidine can also cause more serious side effects. These include hallucinations, fever, sore throat, and unusual bruising or bleeding. Patients should seek immediate medical attention if they experience any of these symptoms. It's also important to note that tizanidine can cause a condition called hypotension (low blood pressure), which may lead to dizziness or fainting, especially when standing up from a sitting or lying position.Tizanidine Dosage and Administration

Factors Influencing Dosage
Several factors can influence the appropriate dosage of tizanidine for a patient. These include the patient's age, kidney function, and whether they are taking other medications that could interact with tizanidine. For example, patients with renal impairment may require lower doses due to the decreased ability of the kidneys to clear the drug from the body. Similarly, elderly patients may be more susceptible to the side effects of tizanidine and may require dose adjustments.Interactions with Other Medications
Managing Interactions
To manage potential interactions, healthcare providers may need to adjust the dosage of tizanidine or the other medication. In some cases, an alternative medication may be prescribed to avoid interactions altogether. Patients should also be vigilant about monitoring their condition and reporting any changes or side effects to their healthcare provider promptly.Pregnancy and Breastfeeding

Considerations for Women of Childbearing Age
Women of childbearing age who are taking tizanidine should discuss contraception options with their healthcare provider to prevent unintended pregnancy. If a woman becomes pregnant while taking tizanidine, she should immediately inform her healthcare provider. The decision to continue or discontinue tizanidine during pregnancy should be made under the guidance of a healthcare professional, weighing the benefits of the medication against the potential risks to the fetus.Withdrawal from Tizanidine
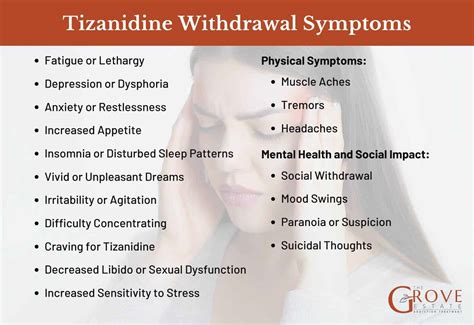
Managing Withdrawal Symptoms
Managing withdrawal symptoms requires careful planning and monitoring by a healthcare provider. In some cases, medications may be prescribed to alleviate withdrawal symptoms. Patients should be advised to report any symptoms promptly and to follow the tapering schedule as directed. It's also important for patients to understand that withdrawal is a sign of physical dependence and not a reflection of addiction, as tizanidine is not typically associated with abuse.Conclusion and Future Directions

Final Thoughts
As with any medication, the key to successful treatment with tizanidine is a thorough understanding of its benefits and risks. By being proactive, patients can take an active role in their healthcare, ensuring that they receive the most effective treatment for their condition while safeguarding their overall health and well-being.What is the most common side effect of tizanidine?
+The most common side effects of tizanidine include drowsiness, dizziness, and weakness.
Can tizanidine be taken with other medications?
+Tizanidine can interact with other medications, so it's essential to inform your healthcare provider about all the medications you are taking to minimize the risk of adverse interactions.
Is tizanidine safe during pregnancy?
+The safety of tizanidine during pregnancy is not well established. It should only be used if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus.
How should tizanidine be discontinued?
+Tizanidine should be tapered off gradually under the supervision of a healthcare provider to avoid withdrawal symptoms.
What should I do if I experience side effects from tizanidine?
+If you experience side effects from tizanidine, you should discuss them with your healthcare provider, who may adjust your dosage or recommend alternative treatments.
We hope this comprehensive overview of tizanidine has provided you with valuable insights into its uses, benefits, and potential side effects. If you have any further questions or would like to share your experiences with tizanidine, please don't hesitate to comment below. Your feedback is invaluable in helping us improve our content and serve our readers better. Additionally, if you found this article informative, please consider sharing it with others who might benefit from this information. Together, we can work towards creating a community that is well-informed and supportive of individuals managing muscle spasms and related conditions.
