Intro
Discover how Torsemide treats edema effectively, reducing swelling with its potent diuretic properties, managing fluid retention and congestion, a common symptom of heart failure and renal disease, promoting healthy circulation and overall well-being.
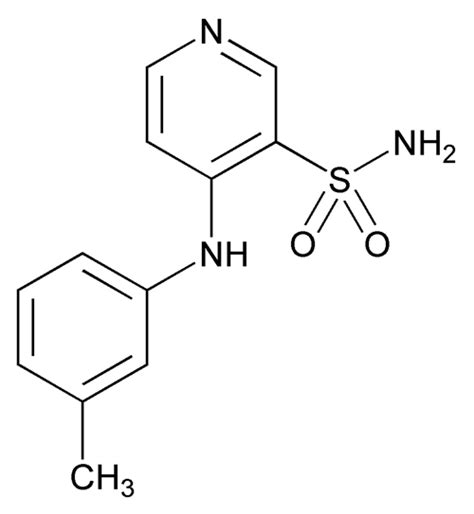
Edema, a condition characterized by the accumulation of excess fluid in the body's tissues, can be a debilitating and painful experience for those affected. It can result from a variety of factors, including heart failure, kidney disease, liver disease, and certain medications. One of the most effective treatments for edema is the use of diuretics, specifically torsemide. Torsemide is a loop diuretic that has been widely used to treat edema associated with various conditions. In this article, we will delve into the world of torsemide, exploring its mechanisms, benefits, and potential side effects, as well as its role in edema treatment.
The importance of effective edema management cannot be overstated. If left untreated, edema can lead to serious complications, such as skin ulcers, infections, and even organ damage. Torsemide, with its potent diuretic properties, has become a crucial component in the treatment arsenal against edema. By promoting the excretion of excess fluid and sodium, torsemide helps to alleviate the symptoms of edema, improving the quality of life for those affected. Understanding how torsemide works and its benefits is essential for both healthcare professionals and patients seeking to manage edema effectively.
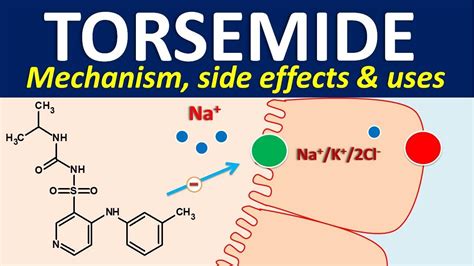
Torsemide's effectiveness in treating edema is attributed to its ability to inhibit the reabsorption of sodium and chloride in the ascending loop of Henle, a critical part of the kidney's nephron. This inhibition leads to an increased excretion of sodium, chloride, and water, thereby reducing fluid accumulation in the body's tissues. The result is a significant reduction in edema, offering relief to patients suffering from this condition. Moreover, torsemide has been shown to have a more favorable pharmacokinetic profile compared to other loop diuretics, making it a preferred choice for many clinicians.
Torsemide Mechanism of Action
Benefits of Torsemide in Edema Treatment

Steps for Effective Torsemide Use
For torsemide to be used effectively, several steps must be followed: - **Initial Assessment**: Patients should undergo a thorough medical evaluation to determine the underlying cause of edema. - **Dose Titration**: The dose of torsemide should be titrated based on the patient's response to treatment, with careful monitoring of urine output and electrolyte levels. - **Regular Monitoring**: Regular follow-up appointments are crucial to monitor the patient's condition, adjust the dose as necessary, and manage potential side effects. - **Lifestyle Modifications**: Patients should be advised on lifestyle modifications, such as dietary changes and increased physical activity, to complement torsemide treatment.Potential Side Effects of Torsemide

Managing Side Effects
To manage the side effects associated with torsemide, the following strategies can be employed: - **Close Monitoring**: Regular monitoring of electrolyte levels, blood pressure, and urine output can help identify potential side effects early. - **Dose Adjustment**: Adjusting the dose of torsemide can help mitigate side effects while maintaining therapeutic efficacy. - **Supplementation**: In some cases, supplementation with potassium or other electrolytes may be necessary to prevent deficiencies.Comparison with Other Diuretics
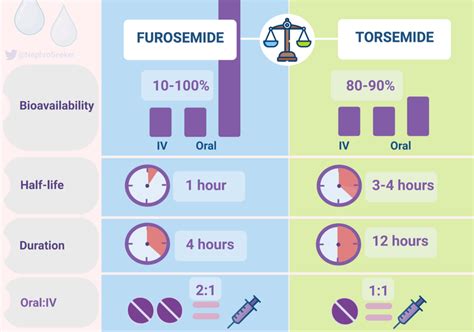
Advantages Over Furosemide
Torsemide has several advantages over furosemide, including: - **Pharmacokinetic Profile**: Torsemide has a more favorable pharmacokinetic profile, with a longer half-life and a more consistent bioavailability. - **Efficacy**: Torsemide has been shown to be more effective in patients with resistant edema or those with decreased renal function. - **Tolerability**: Torsemide may have a better tolerability profile, with fewer reports of side effects such as ototoxicity.Conclusion and Future Directions
Final Thoughts
As we move forward in the management of edema, it is essential to consider the individual needs of each patient. By tailoring treatment to the underlying cause of edema and the patient's response to therapy, clinicians can optimize outcomes and improve the quality of life for those affected. Torsemide, with its proven efficacy and safety profile, is poised to remain a cornerstone in the treatment of edema for years to come.We invite readers to share their thoughts and experiences with torsemide and edema treatment in the comments below. Your insights can help others better understand the complexities of edema management and the role of torsemide in improving patient outcomes. Please feel free to ask questions, share personal stories, or provide feedback on this article. Your engagement is invaluable in creating a community that supports and informs those affected by edema.
What is the primary mechanism of action of torsemide?
+Torsemide works by inhibiting the sodium-potassium-chloride cotransporter (NKCC2) in the thick ascending limb of the loop of Henle, preventing the reabsorption of sodium, potassium, and chloride ions.
What are the benefits of using torsemide in edema treatment?
+The benefits of torsemide include rapid and effective diuresis, improvement in symptoms associated with edema, and a favorable effect on patients with heart failure, reducing the need for hospitalization and improving survival rates.
How should torsemide be used effectively?
+For torsemide to be used effectively, patients should undergo a thorough medical evaluation, the dose should be titrated based on response, and regular monitoring of urine output and electrolyte levels should be performed.
What are the potential side effects of torsemide?
+Potential side effects include electrolyte imbalances, dehydration, increased urination, hypotension, dizziness, and gastrointestinal disturbances.
How does torsemide compare to other diuretics?
+Torsemide has a more favorable pharmacokinetic profile and is more effective in patients with resistant edema or decreased renal function compared to other loop diuretics like furosemide.
