Intro
Learn about high triglycerides level, its causes, symptoms, and treatment. Manage elevated triglycerides with diet, exercise, and medication to reduce cardiovascular risk and improve overall health.
High triglycerides levels have become a significant health concern in recent years, affecting millions of people worldwide. Triglycerides are a type of fat found in the blood, and when their levels are elevated, it can increase the risk of heart disease, stroke, and other cardiovascular conditions. The importance of maintaining healthy triglyceride levels cannot be overstated, as it plays a crucial role in overall health and well-being. In this article, we will delve into the world of triglycerides, exploring what they are, the causes and symptoms of high triglycerides, and most importantly, the ways to manage and reduce them.
The prevalence of high triglycerides has been on the rise, and it is essential to understand the factors that contribute to this condition. A combination of genetic, lifestyle, and dietary factors can lead to elevated triglyceride levels. For instance, a diet high in saturated and trans fats, cholesterol, and carbohydrates can significantly increase triglyceride levels. Additionally, lack of physical activity, obesity, and certain medical conditions such as diabetes and hypothyroidism can also contribute to high triglycerides. It is crucial to identify these factors and take necessary steps to mitigate their impact on triglyceride levels.
Understanding the causes and symptoms of high triglycerides is vital in managing the condition. Symptoms may not always be apparent, but they can include fatigue, confusion, and abdominal pain. If left untreated, high triglycerides can lead to more severe health issues, such as pancreatitis and cardiovascular disease. Therefore, it is essential to monitor triglyceride levels regularly and take proactive steps to reduce them. This can be achieved through a combination of dietary changes, increased physical activity, and medication. By making informed lifestyle choices, individuals can significantly reduce their risk of developing high triglycerides and related health problems.
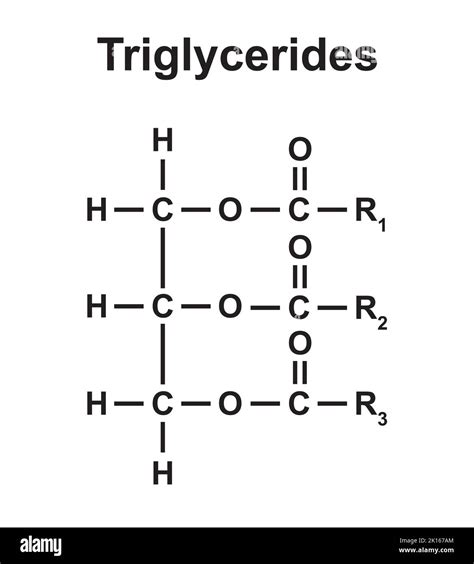
What are Triglycerides?
Normal Triglyceride Levels
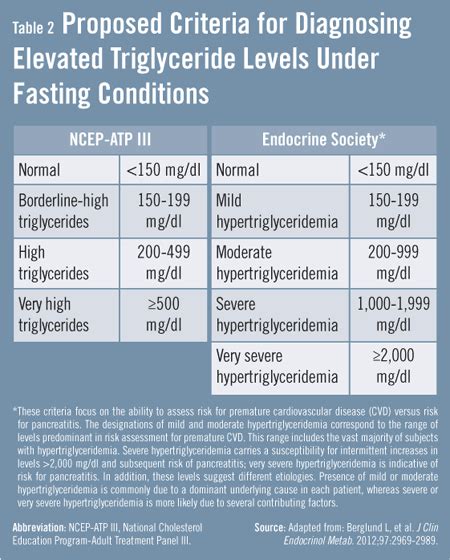
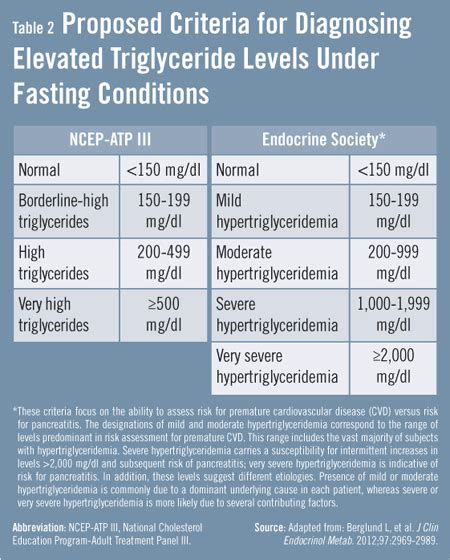
Normal triglyceride levels vary based on factors such as age, sex, and overall health. Generally, triglyceride levels are considered normal if they are below 150 milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL). Borderline high triglyceride levels range from 150 to 199 mg/dL, while high triglyceride levels are between 200 and 499 mg/dL. Very high triglyceride levels are above 500 mg/dL. It is essential to note that triglyceride levels can fluctuate throughout the day, and they may be affected by various factors, including diet, physical activity, and certain medications.Causes of High Triglycerides
Dietary Factors
Dietary factors play a significant role in determining triglyceride levels. Consuming high amounts of saturated and trans fats, cholesterol, and carbohydrates can increase triglyceride production in the liver. Foods high in these substances include red meat, full-fat dairy products, processed snacks, and sugary drinks. On the other hand, a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein sources can help lower triglyceride levels.Symptoms of High Triglycerides

Diagnosis of High Triglycerides
Diagnosing high triglycerides typically involves a blood test, which measures the level of triglycerides in the blood. The test is usually performed after an overnight fast, and the results are used to determine the severity of the condition. In some cases, additional tests, such as a liver function test or a thyroid function test, may be necessary to rule out underlying medical conditions that may be contributing to high triglycerides.Treatment and Management of High Triglycerides
Lifestyle Changes
Lifestyle changes play a crucial role in managing high triglycerides. Increasing physical activity, losing weight, and quitting smoking can help reduce triglyceride levels. Additionally, reducing stress, getting enough sleep, and practicing relaxation techniques, such as meditation or yoga, can also help lower triglyceride levels.Reducing Triglycerides through Diet
Foods that Help Lower Triglycerides
Certain foods can help lower triglyceride levels. These include: * Fatty fish, such as salmon and sardines * Flaxseeds and walnuts, which are rich in omega-3 fatty acids * Avocados, which are rich in healthy fats * Fruits, such as berries and citrus fruits * Vegetables, such as leafy greens and cruciferous vegetables * Whole grains, such as brown rice and quinoa * Lean protein sources, such as chicken and turkeyMedications for High Triglycerides
Side Effects of Medications
Medications for high triglycerides can have side effects, such as: * Abdominal pain and diarrhea * Headache and dizziness * Muscle pain and weakness * Increased risk of bleeding * Liver damageConclusion and Final Thoughts

We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with high triglycerides in the comments below. Have you or someone you know been affected by high triglycerides? What steps have you taken to manage and reduce them? Your input can help others who may be struggling with this condition. Additionally, if you found this article informative and helpful, please share it with your friends and family on social media.
What are the normal triglyceride levels?
+Normal triglyceride levels vary based on factors such as age, sex, and overall health. Generally, triglyceride levels are considered normal if they are below 150 milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL).
What are the causes of high triglycerides?
+Causes of high triglycerides include dietary, lifestyle, and genetic factors. A diet high in saturated and trans fats, cholesterol, and carbohydrates can significantly increase triglyceride levels. Additionally, lack of physical activity, obesity, and certain medical conditions such as diabetes and hypothyroidism can also contribute to high triglycerides.
How can I reduce my triglyceride levels?
+Reducing triglyceride levels can be achieved through a combination of lifestyle changes and medication. Dietary changes, such as reducing intake of saturated and trans fats, cholesterol, and carbohydrates, can help lower triglyceride levels. Increasing physical activity, losing weight, and quitting smoking can also help reduce triglyceride levels.
