Intro
Discover the 5 ways elevated TSH happens, including thyroid disorders, iodine deficiency, and pituitary gland issues, and learn how to manage hypothyroidism symptoms and thyroid function for optimal health.
Elevated TSH, or Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone, is a condition where the thyroid gland does not produce enough thyroid hormones, leading to a range of health issues. The thyroid gland plays a crucial role in regulating various bodily functions, including metabolism, growth, and development. When the thyroid gland is not functioning properly, it can have a significant impact on overall health and wellbeing. In this article, we will explore the 5 ways elevated TSH happens, its causes, symptoms, and treatment options.
The importance of understanding elevated TSH cannot be overstated. Thyroid disorders are common, affecting millions of people worldwide. According to the American Thyroid Association, approximately 20 million Americans have some form of thyroid disease, with many cases going undiagnosed. Elevated TSH is a common indicator of hypothyroidism, a condition where the thyroid gland does not produce enough thyroid hormones. If left untreated, hypothyroidism can lead to a range of health problems, including weight gain, fatigue, and increased risk of heart disease.
The causes of elevated TSH are varied and complex. In some cases, it may be caused by an autoimmune disorder, such as Hashimoto's thyroiditis, where the immune system attacks the thyroid gland. In other cases, it may be caused by iodine deficiency, radiation therapy, or certain medications. Understanding the underlying causes of elevated TSH is crucial for developing effective treatment plans. By exploring the 5 ways elevated TSH happens, we can gain a deeper understanding of this complex condition and how to manage it.
Introduction to Elevated TSH
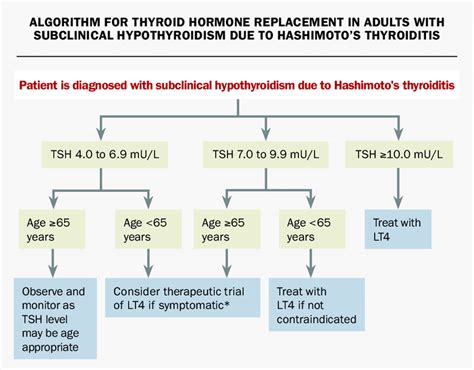
Causes of Elevated TSH
The causes of elevated TSH are varied and complex. Some of the common causes include: * Autoimmune disorders, such as Hashimoto's thyroiditis * Iodine deficiency * Radiation therapy * Certain medications, such as lithium and amiodarone * Thyroid surgery or radioactive iodine treatment * Pituitary gland problems, such as a tumor or hypopituitarism5 Ways Elevated TSH Happens

Symptoms of Elevated TSH
The symptoms of elevated TSH can vary depending on the underlying cause. Some common symptoms include: * Fatigue and weakness * Weight gain * Cold intolerance * Dry skin and hair * Hair loss * Memory problems and difficulty concentrating * Heavy or irregular menstrual periodsTreatment Options for Elevated TSH
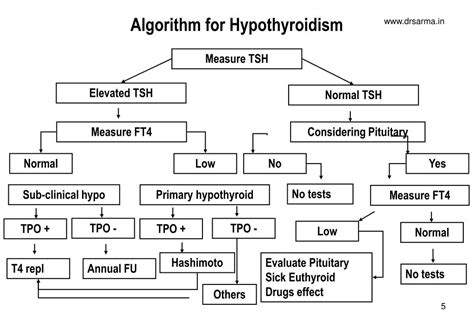
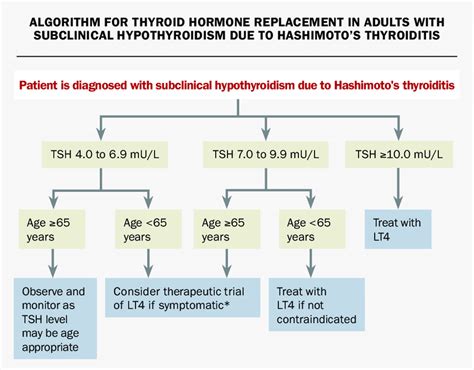
Prevention and Management
Preventing and managing elevated TSH requires a comprehensive approach. Some strategies include: * **Getting regular check-ups**: Regular check-ups with a healthcare provider can help detect thyroid problems early on. * **Maintaining a healthy diet**: Eating a healthy diet that includes iodine-rich foods, such as seafood and dairy products, can help support thyroid function. * **Avoiding certain medications**: Avoiding certain medications, such as lithium and amiodarone, can help prevent thyroid problems. * **Managing stress**: Managing stress through techniques, such as meditation and yoga, can help support thyroid function.Conclusion and Next Steps
What are the common symptoms of elevated TSH?
+The common symptoms of elevated TSH include fatigue and weakness, weight gain, cold intolerance, dry skin and hair, hair loss, memory problems and difficulty concentrating, and heavy or irregular menstrual periods.
How is elevated TSH diagnosed?
+Elevated TSH is diagnosed through a blood test that measures TSH levels. A healthcare provider may also perform a physical exam and take a medical history to rule out other underlying conditions.
What are the treatment options for elevated TSH?
+The treatment options for elevated TSH include thyroid hormone replacement therapy, medications, surgery, and radioactive iodine treatment. The treatment approach depends on the underlying cause of the elevated TSH.
Can elevated TSH be prevented?
+While elevated TSH cannot be completely prevented, individuals can take steps to reduce their risk of developing thyroid problems. This includes getting regular check-ups, maintaining a healthy diet, avoiding certain medications, and managing stress.
What is the prognosis for individuals with elevated TSH?
+The prognosis for individuals with elevated TSH depends on the underlying cause and the effectiveness of treatment. With proper treatment and management, individuals with elevated TSH can lead healthy and active lives.
We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of elevated TSH and its causes, symptoms, and treatment options. If you have any further questions or concerns, please do not hesitate to reach out to a healthcare provider. Additionally, we encourage you to share this article with others who may be experiencing thyroid problems, and to join the conversation by commenting below. Together, we can raise awareness about thyroid health and support individuals in their journey towards wellness.
