Intro
Discover optimal 5 healthy TSH levels, thyroid function, and hormone balance, understanding normal TSH ranges, hypothyroidism, and hyperthyroidism for overall wellness.
Maintaining healthy thyroid function is crucial for overall well-being, and one key aspect of this is understanding and managing Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone (TSH) levels. TSH is a hormone produced by the pituitary gland that regulates the production of thyroid hormones by the thyroid gland. These hormones play a vital role in controlling metabolism, energy generation, and growth. Abnormal TSH levels can indicate thyroid disorders, which, if left untreated, can lead to various health issues.
The importance of TSH levels cannot be overstated, as they are a critical indicator of thyroid health. Both high and low TSH levels can have significant health implications, ranging from fatigue, weight changes, and mood alterations to more severe conditions like thyroiditis or thyroid cancer in extreme cases. Therefore, understanding what constitutes healthy TSH levels and how to maintain them is essential for preventing and managing thyroid-related diseases.
Thyroid function tests, including TSH tests, are commonly used to assess thyroid health. These tests measure the levels of TSH and thyroid hormones in the blood. The results help diagnose thyroid disorders such as hypothyroidism (underactive thyroid), hyperthyroidism (overactive thyroid), and other conditions. Healthy TSH levels typically range from 0.4 to 4.5 milliunits per liter (mU/L), though this range may slightly vary between laboratories. Maintaining TSH levels within this range is crucial for ensuring proper thyroid function and overall health.
Understanding TSH Levels
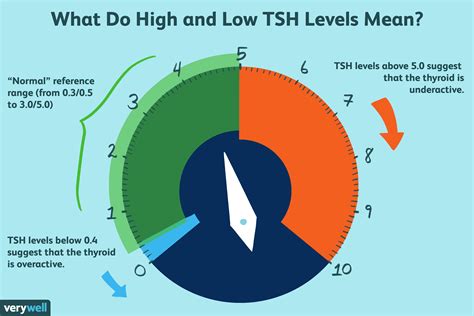
To grasp the concept of healthy TSH levels, it's essential to understand how TSH works. The pituitary gland releases TSH to stimulate the thyroid gland to produce thyroid hormones, primarily thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3). These hormones are vital for various bodily functions, including heart rate, metabolism, and muscle strength. The level of TSH in the blood is a reflection of the thyroid's ability to produce these hormones. High TSH levels may indicate that the thyroid is not producing enough thyroid hormones (hypothyroidism), prompting the pituitary gland to release more TSH to stimulate the thyroid. Conversely, low TSH levels may suggest that the thyroid is overproducing thyroid hormones (hyperthyroidism), leading the pituitary gland to reduce TSH production.
Factors Influencing TSH Levels
Several factors can influence TSH levels, including age, sex, and certain medical conditions. For instance, TSH levels naturally increase with age, and women are more likely than men to develop thyroid disorders. Pregnancy can also affect TSH levels, as the thyroid gland's function changes during pregnancy to support the fetus's development. Understanding these factors is crucial for interpreting TSH test results accurately.Benefits of Maintaining Healthy TSH Levels
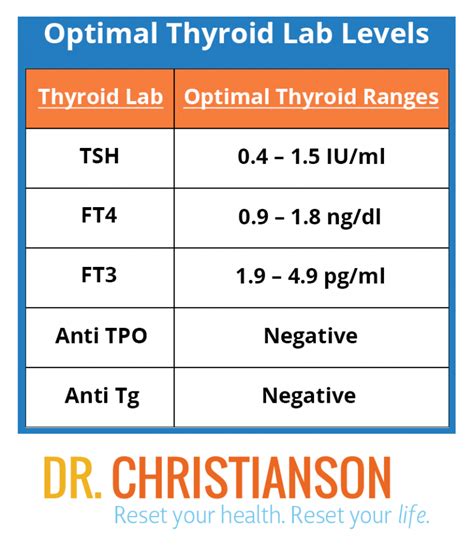
Maintaining healthy TSH levels offers numerous benefits, including improved energy levels, better weight management, enhanced mental clarity, and reduced risk of thyroid-related disorders. Healthy thyroid function also supports heart health by regulating cholesterol levels and maintaining a healthy heart rate. Furthermore, proper thyroid function is essential for bone health, as thyroid hormones help regulate calcium levels and bone metabolism.
Steps to Maintain Healthy TSH Levels
To maintain healthy TSH levels, individuals can take several steps: - **Regular Health Check-ups**: Regular thyroid function tests can help identify any abnormalities in TSH levels early on. - **Balanced Diet**: Consuming a diet rich in iodine, selenium, and zinc can support thyroid health. Iodine is particularly important as it is a critical component of thyroid hormones. - **Exercise Regularly**: Physical activity can help improve thyroid function and overall health. - **Manage Stress**: High stress levels can negatively impact thyroid function. Engaging in stress-reducing activities like meditation or yoga can be beneficial.Diagnosing and Treating TSH Level Imbalances

Diagnosing TSH level imbalances typically involves a combination of physical examinations, medical history reviews, and thyroid function tests. Treatment options vary depending on whether the imbalance is due to hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism. For hypothyroidism, synthetic thyroid hormones are often prescribed to replace the missing hormones. In cases of hyperthyroidism, treatment may involve medications to reduce thyroid hormone production, radioactive iodine to destroy part of the thyroid gland, or surgery to remove part or all of the thyroid gland.
Practical Examples of TSH Level Management
Real-life examples of managing TSH levels include: - **Lifestyle Changes**: Making dietary changes, such as increasing iodine intake, and engaging in regular physical activity can help manage mild thyroid disorders. - **Medication Adherence**: For those on thyroid hormone replacement therapy, adhering to the prescribed medication regimen is crucial for maintaining healthy TSH levels. - **Regular Monitoring**: Regular follow-up appointments with healthcare providers to monitor TSH levels and adjust treatment plans as necessary are essential for effective management.Statistical Data on TSH Levels and Thyroid Health
According to various studies, approximately 4.6% of the U.S. population has hypothyroidism, with a higher prevalence among women and individuals over 50 years old. The prevalence of hyperthyroidism is significantly lower, affecting about 1.3% of the population. Understanding these statistics highlights the importance of thyroid health awareness and the need for regular check-ups to detect and manage thyroid disorders early.
FAQs on TSH Levels and Thyroid Health
Given the complexity of thyroid health and TSH levels, many individuals have questions about what constitutes healthy TSH levels, how TSH is tested, and the implications of abnormal TSH levels. Here are some frequently asked questions:What are the symptoms of high TSH levels?
+High TSH levels can indicate hypothyroidism, which may cause symptoms such as fatigue, weight gain, dry skin, hair loss, and cold intolerance.
How often should I get my TSH levels checked?
+The frequency of TSH level checks depends on age, health status, and whether you have a history of thyroid disorders. Generally, adults should have their TSH levels checked every 5 years, while those with thyroid conditions may need more frequent monitoring.
Can diet alone manage TSH level imbalances?
+While diet plays a crucial role in thyroid health, it may not be enough to manage TSH level imbalances on its own. In many cases, especially for significant imbalances, medical treatment under the guidance of a healthcare provider is necessary.
Conclusion and Call to Action
In conclusion, maintaining healthy TSH levels is vital for overall health and well-being. By understanding the importance of TSH, recognizing the factors that influence TSH levels, and taking proactive steps to manage thyroid health, individuals can significantly reduce their risk of thyroid-related disorders. If you suspect you have a thyroid issue or are concerned about your TSH levels, consult with a healthcare provider. They can provide personalized advice and treatment options tailored to your specific needs.
We invite you to share your experiences with managing TSH levels and thyroid health in the comments below. Your stories can provide valuable insights and support to others who may be facing similar challenges. Additionally, consider sharing this article with friends and family to raise awareness about the importance of thyroid health and the steps individuals can take to maintain healthy TSH levels. Together, we can promote better health and well-being for everyone.
