Intro
Learn about Tubal Ligation Surgery, a permanent birth control method, in our comprehensive guide, covering procedure, risks, recovery, and reversal options, to help women make informed decisions about female sterilization and family planning.
Tubal ligation, also known as "getting your tubes tied," is a surgical procedure that is used as a permanent birth control method. The procedure involves cutting, blocking, or tying the fallopian tubes to prevent pregnancy. This method is highly effective and is often considered by women who have completed their families or are sure they do not want to become pregnant in the future. Understanding the details of tubal ligation surgery is crucial for anyone considering this form of birth control.
The decision to undergo tubal ligation surgery is significant, and it's essential to weigh the benefits and risks. One of the primary benefits is that it provides a permanent solution to birth control, eliminating the need for daily, weekly, or monthly contraceptive measures. Additionally, the procedure is relatively quick, and many women can return to their normal activities within a few days. However, it's also important to consider the permanence of the procedure and the potential risks involved, such as infection, bleeding, and damage to surrounding organs.
For women considering tubal ligation, it's vital to have a comprehensive understanding of what the procedure entails, the benefits and risks, and what to expect during recovery. This includes understanding the different types of tubal ligation procedures available, the factors that might influence the decision to undergo surgery, and how the procedure might affect future fertility options. With the right information, women can make informed decisions about their reproductive health and choose the best birth control method for their needs and lifestyle.
Understanding Tubal Ligation
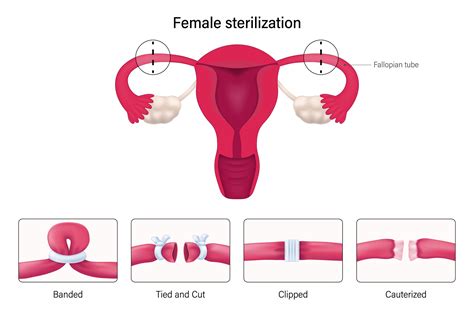
Tubal ligation is a surgical procedure that involves blocking or cutting the fallopian tubes to prevent sperm from reaching the egg. The procedure can be performed in a hospital or outpatient surgical center under general anesthesia or local anesthesia with sedation. There are several methods used for tubal ligation, including cutting and tying the tubes, using clips or bands to block the tubes, and using electrical current to cauterize a portion of the tubes. Each method has its own set of benefits and risks, and the choice of method often depends on the patient's overall health, the surgeon's preference, and the specific circumstances of the procedure.
Benefits of Tubal Ligation
The benefits of tubal ligation are numerous, making it a popular choice for permanent birth control. Some of the key benefits include: - **High effectiveness**: Tubal ligation is more than 99% effective in preventing pregnancy. - **Permanent solution**: Once the procedure is performed, it provides a lifelong solution to birth control, eliminating the need for ongoing contraceptive measures. - **Low maintenance**: Unlike other forms of birth control, tubal ligation does not require daily, weekly, or monthly maintenance. - **Reduced risk of ovarian cancer**: Some studies suggest that tubal ligation may reduce the risk of ovarian cancer.Types of Tubal Ligation Procedures
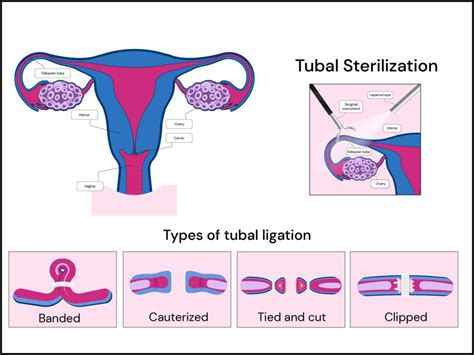
There are several types of tubal ligation procedures, each with its own technique and instruments. The choice of procedure often depends on the surgeon's preference, the patient's health status, and the specific circumstances of the surgery. Some of the most common types of tubal ligation procedures include:
- Laparoscopic tubal ligation: This is a minimally invasive procedure where a laparoscope (a thin, lighted tube) is inserted through a small incision in the abdomen to view the fallopian tubes. The tubes are then cut, tied, or blocked using clips or bands.
- Open tubal ligation: This procedure involves making a larger incision in the abdomen to access the fallopian tubes. It is often performed after childbirth or in situations where a laparoscopic approach is not feasible.
- Postpartum tubal ligation: This procedure is performed shortly after childbirth, usually within 48 hours. It is often done vaginally, without the need for an abdominal incision.
Risks and Complications
While tubal ligation is generally safe, there are potential risks and complications to consider. Some of the possible risks include: - **Infection**: As with any surgical procedure, there is a risk of infection with tubal ligation. - **Bleeding**: Excessive bleeding during or after the procedure can occur. - **Damage to surrounding organs**: The bowel, bladder, or blood vessels can be inadvertently damaged during the procedure. - **Failure of the procedure**: In rare cases, the procedure may not be 100% effective, and pregnancy can still occur.Preparation for Tubal Ligation Surgery
Preparation for tubal ligation surgery involves several steps to ensure that the patient is ready for the procedure. This includes:
- Consultation with a healthcare provider: Discussing the procedure, its benefits and risks, and ensuring that tubal ligation is the right choice for the patient.
- Physical examination and testing: Undergoing a physical examination and any necessary tests to ensure that the patient is in good health for the surgery.
- Stopping certain medications: Stopping any medications that may increase the risk of bleeding during surgery.
- Arranging for post-operative care: Ensuring that there is someone to provide care and support after the procedure.
Recovery After Tubal Ligation
Recovery after tubal ligation surgery can vary depending on the type of procedure performed and the individual's overall health. Generally, patients can expect: - **Mild discomfort**: Some discomfort, cramping, and spotting are common after the procedure. - **Rest**: Resting for a few days to allow the body to heal. - **Follow-up care**: Following up with the healthcare provider to ensure that the incisions are healing properly and to discuss any concerns.Alternatives to Tubal Ligation
For women who are seeking permanent birth control but are hesitant about tubal ligation, there are alternatives to consider. Some of these alternatives include:
- Vasectomy: A surgical procedure for men that cuts or blocks the vas deferens to prevent sperm from reaching the penis.
- Essure: A non-surgical procedure that involves inserting small coils into the fallopian tubes to block sperm. However, Essure is no longer available in the US due to safety concerns.
- Adiana: A non-surgical procedure that involves using a catheter to insert small implants into the fallopian tubes to block sperm. This method is also not widely available due to similar concerns as Essure.
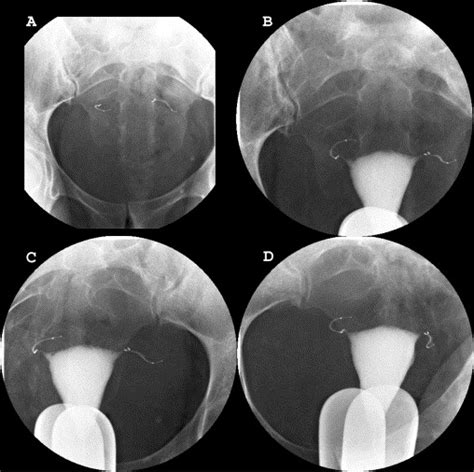
Reversal of Tubal Ligation
In some cases, women who have undergone tubal ligation may later decide that they want to become pregnant. Tubal ligation reversal is a surgical procedure that attempts to restore the fallopian tubes to their normal function. However, the success of the reversal depends on several factors, including the type of tubal ligation procedure performed, the length of the remaining fallopian tube, and the age of the patient.Conclusion and Final Thoughts

Tubal ligation is a highly effective and permanent method of birth control that can provide peace of mind for women who have completed their families or are sure they do not want to become pregnant in the future. While the procedure is generally safe, it's essential to understand the potential risks and complications and to carefully consider the decision before proceeding. For those who are considering tubal ligation, discussing the procedure with a healthcare provider and weighing the benefits and risks can help make an informed decision.
We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with tubal ligation in the comments below. If you found this article informative, please consider sharing it with others who may be considering their birth control options.
What is the effectiveness of tubal ligation in preventing pregnancy?
+Tubal ligation is more than 99% effective in preventing pregnancy, making it one of the most reliable forms of birth control.
Can tubal ligation be reversed if I change my mind about having more children?
+Yes, tubal ligation can be reversed, but the success of the reversal depends on several factors, including the type of tubal ligation procedure performed and the age of the patient.
What are the potential risks and complications of tubal ligation?
+Potential risks and complications of tubal ligation include infection, bleeding, damage to surrounding organs, and failure of the procedure.
