Intro
Understand a positive tuberculin skin test result, including its implications, causes, and relation to latent tuberculosis infection, TB disease, and BCG vaccination effects.
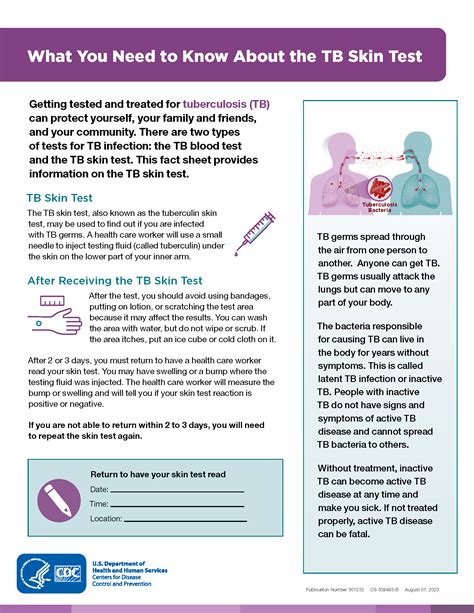
The tuberculin skin test, also known as the Mantoux test, is a widely used diagnostic tool to detect tuberculosis (TB) infection. It involves injecting a small amount of tuberculin, a substance derived from the bacteria that cause TB, into the skin of the forearm. After 48-72 hours, the skin is examined for a reaction, which can indicate the presence of TB infection. A positive result can be alarming, but it's essential to understand what it means and the next steps to take.
A positive tuberculin skin test result indicates that the individual has been exposed to TB bacteria at some point in their lives. This exposure can be due to various factors, such as close contact with someone who has active TB, traveling to areas where TB is common, or working in a healthcare setting where TB is present. However, a positive result does not necessarily mean that the person has active TB disease. In many cases, the immune system can contain the bacteria, and the individual may not exhibit any symptoms.
The significance of a positive tuberculin skin test result lies in its ability to identify individuals who are at risk of developing active TB disease. This is particularly important for people who are more susceptible to TB, such as those with weakened immune systems, young children, and older adults. By identifying those who are infected, healthcare providers can take steps to prevent the development of active TB disease, which can be life-threatening if left untreated.
Understanding the Tuberculin Skin Test
Interpreting the Results
The interpretation of the tuberculin skin test results depends on various factors, including the size of the induration, the individual's medical history, and their risk factors for TB. In general, a positive result is defined as an induration of 10 mm or more in diameter. However, for individuals with certain medical conditions, such as HIV/AIDS, or those who are taking immunosuppressive medications, a positive result may be defined as an induration of 5 mm or more.What Does a Positive Result Mean?
Latent TB Infection (LTBI)
LTBI is a condition in which the TB bacteria are present in the body, but the individual does not exhibit any symptoms. People with LTBI are not contagious, and they do not have active TB disease. However, they are at risk of developing active TB disease if the bacteria become active. This can occur due to various factors, such as a weakened immune system, age, or certain medical conditions.Next Steps After a Positive Result

Treatment for Latent TB Infection (LTBI)
If an individual is found to have LTBI, their healthcare provider may recommend treatment to prevent the development of active TB disease. This typically involves taking antibiotics for a period of 3-9 months. The goal of treatment is to kill the TB bacteria and prevent them from becoming active.Prevention and Control

- Avoiding close contact with individuals who have active TB disease
- Wearing masks or respirators in healthcare settings where TB is present
- Ensuring good ventilation in enclosed spaces
- Avoiding sharing food, drinks, or utensils with individuals who have active TB disease
Vaccination
The Bacillus Calmette-Guérin (BCG) vaccine is a widely used vaccine to prevent TB. It is typically administered to children in countries where TB is common. However, the vaccine is not 100% effective, and it may not provide lifelong protection.Challenges and Limitations

- False-positive results, which can occur due to cross-reactivity with other bacteria
- False-negative results, which can occur in individuals with weakened immune systems
- The need for multiple visits to a healthcare provider to administer and read the test
- The potential for skin reactions or other adverse effects
Future Directions
Researchers are working to develop new diagnostic tools and treatments for TB. These include:- Blood tests that can detect TB infection more accurately and quickly
- New antibiotics that can treat TB more effectively
- Vaccines that can provide better protection against TB
Conclusion and Recommendations

We recommend that individuals who test positive for TB follow their healthcare provider's recommendations for further testing and treatment. Additionally, we encourage individuals to take steps to prevent the spread of TB, such as avoiding close contact with individuals who have active TB disease and wearing masks or respirators in healthcare settings where TB is present.
What is the tuberculin skin test used for?
+The tuberculin skin test is used to diagnose tuberculosis (TB) infection. It involves injecting a small amount of tuberculin into the skin, and the reaction is measured after 48-72 hours.
What does a positive result mean?
+A positive result indicates that the individual has been infected with TB bacteria. However, it does not necessarily mean that they have active TB disease.
How is latent TB infection (LTBI) treated?
+LTBI is typically treated with antibiotics for a period of 3-9 months. The goal of treatment is to kill the TB bacteria and prevent them from becoming active.
Can the tuberculin skin test be used to diagnose active TB disease?
+No, the tuberculin skin test is not used to diagnose active TB disease. Further testing, such as chest X-rays and sputum tests, is necessary to confirm the presence of active disease.
Is the BCG vaccine effective in preventing TB?
+The BCG vaccine is not 100% effective in preventing TB, and it may not provide lifelong protection. However, it is widely used in countries where TB is common to prevent the spread of the disease.
We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of the tuberculin skin test and its significance in diagnosing TB infection. If you have any further questions or concerns, please do not hesitate to comment below. Additionally, we encourage you to share this article with others who may be interested in learning more about TB and the tuberculin skin test. By working together, we can help prevent the spread of TB and promote better health outcomes for individuals around the world.
