Intro
Discover the ultimate Type 1 Diabetes Guide, covering symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, and management, including insulin therapy, blood sugar control, and lifestyle changes for a healthy living with T1D, autoimmune disease, and insulin dependence.
Type 1 diabetes is a chronic autoimmune condition where the pancreas produces little to no insulin, a hormone that regulates blood sugar levels. This condition requires constant management and attention to maintain a healthy lifestyle. Understanding the intricacies of type 1 diabetes is crucial for those living with the condition, as well as their loved ones and caregivers. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the world of type 1 diabetes, exploring its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options, and management strategies.
Living with type 1 diabetes can be challenging, but with the right knowledge and support, individuals can lead active, healthy lives. The condition affects people of all ages, from children to adults, and its impact extends beyond the individual to their families and communities. By shedding light on the complexities of type 1 diabetes, we hope to empower those affected by the condition to take control of their health and well-being. Whether you are newly diagnosed or have been living with type 1 diabetes for years, this guide aims to provide you with the information and resources you need to navigate the ups and downs of this condition.
The importance of understanding type 1 diabetes cannot be overstated. By recognizing the signs and symptoms of the condition, individuals can seek medical attention promptly, reducing the risk of complications and improving health outcomes. Moreover, a deep understanding of type 1 diabetes enables individuals to make informed decisions about their care, from diet and exercise to medication and technology. As we embark on this journey through the world of type 1 diabetes, we invite you to join us in exploring the many facets of this complex condition.
What is Type 1 Diabetes?

Causes of Type 1 Diabetes
The exact causes of type 1 diabetes are still not fully understood, but research suggests that a combination of genetic and environmental factors contributes to the development of the condition. Genetic predisposition, viral infections, and other environmental triggers may stimulate the immune system to attack the pancreas, leading to the destruction of insulin-producing cells. While the exact causes of type 1 diabetes are still unclear, ongoing research aims to uncover the underlying mechanisms of the condition, paving the way for new treatments and potential cures.Symptoms of Type 1 Diabetes

If you or someone you know is experiencing these symptoms, it is essential to seek medical attention promptly. Early diagnosis and treatment can significantly improve health outcomes and reduce the risk of complications.
Diagnosis of Type 1 Diabetes
Diagnosing type 1 diabetes typically involves a combination of physical examinations, medical history, and laboratory tests. Healthcare providers may use the following tests to diagnose type 1 diabetes: * Fasting blood glucose test * Oral glucose tolerance test * Random blood glucose test * Glycated hemoglobin (A1C) test * Autoantibody testsThese tests help healthcare providers determine the presence and severity of type 1 diabetes, enabling them to develop an effective treatment plan.
Treatment and Management of Type 1 Diabetes

Treatment plans may include:
- Insulin therapy: administering insulin via injections or an insulin pump
- Blood glucose monitoring: tracking blood sugar levels to adjust treatment
- Diet and exercise: following a healthy diet and engaging in regular physical activity
- Medications: taking medications to manage related conditions, such as high blood pressure or cholesterol
Lifestyle Modifications for Type 1 Diabetes
Making lifestyle modifications is crucial for managing type 1 diabetes. These modifications may include: * Eating a balanced diet: focusing on whole, nutrient-dense foods * Engaging in regular physical activity: aiming for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise per week * Maintaining a healthy weight: achieving and maintaining a healthy weight to reduce the risk of complications * Quitting smoking: avoiding tobacco products to reduce the risk of cardiovascular diseaseBy incorporating these lifestyle modifications into daily life, individuals with type 1 diabetes can better manage their condition and reduce the risk of complications.
Complications of Type 1 Diabetes
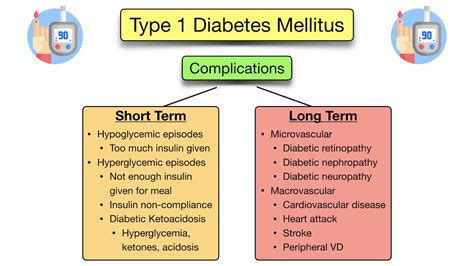
Regular monitoring and management of type 1 diabetes can significantly reduce the risk of these complications, enabling individuals to lead healthy, active lives.
Emerging Trends and Technologies in Type 1 Diabetes
The field of type 1 diabetes is constantly evolving, with emerging trends and technologies offering new hope for improved management and potential cures. Some of these advancements include: * Artificial pancreas systems: using automated insulin delivery systems to regulate blood sugar levels * Stem cell therapies: exploring the potential of stem cells to regenerate insulin-producing cells * Gene therapies: investigating the use of gene editing technologies to modify the genes responsible for type 1 diabetes * Immunotherapies: developing treatments that target the immune system to prevent or reverse type 1 diabetesThese innovative approaches hold promise for improving the lives of individuals with type 1 diabetes, offering new avenues for research and potential breakthroughs.
Living with Type 1 Diabetes

Some tips for living with type 1 diabetes include:
- Staying organized: using tools and resources to track blood sugar levels, medication, and appointments
- Building a support network: surrounding yourself with loved ones, healthcare providers, and peers who understand the condition
- Prioritizing self-care: engaging in activities that promote physical and emotional well-being
- Staying informed: staying up-to-date with the latest research, treatments, and technologies
By embracing these strategies, individuals with type 1 diabetes can lead fulfilling, active lives, despite the challenges posed by the condition.
Conclusion and Next Steps
In conclusion, type 1 diabetes is a complex condition that requires careful management and attention to maintain a healthy lifestyle. By understanding the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options, and management strategies, individuals can take control of their health and well-being. As research continues to uncover new insights and innovations, the future of type 1 diabetes management looks promising.We invite you to share your thoughts, experiences, and questions about type 1 diabetes in the comments below. Whether you are living with the condition or supporting a loved one, your voice and perspective are valuable contributions to the conversation. Together, we can work towards a brighter future for those affected by type 1 diabetes.
What are the symptoms of type 1 diabetes?
+The symptoms of type 1 diabetes include increased thirst and urination, fatigue and weakness, blurred vision, cuts or wounds that are slow to heal, tingling or numbness in the hands and feet, and recurring skin, gum, or bladder infections.
How is type 1 diabetes diagnosed?
+Type 1 diabetes is diagnosed using a combination of physical examinations, medical history, and laboratory tests, including fasting blood glucose tests, oral glucose tolerance tests, random blood glucose tests, glycated hemoglobin (A1C) tests, and autoantibody tests.
What are the treatment options for type 1 diabetes?
+Treatment options for type 1 diabetes include insulin therapy, blood glucose monitoring, diet and exercise, and medications to manage related conditions, such as high blood pressure or cholesterol.
Can type 1 diabetes be prevented?
+Currently, there is no known way to prevent type 1 diabetes, but researchers are exploring potential strategies, including immunotherapies and gene therapies, to prevent or reverse the condition.
What are the complications of type 1 diabetes?
+The complications of type 1 diabetes include cardiovascular disease, nerve damage, kidney damage, eye damage, and foot damage, which can be reduced or prevented with proper management and care.
