Intro
Type II diabetes is a chronic and complex health condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It is a metabolic disorder characterized by high blood sugar levels, insulin resistance, and impaired insulin secretion. The prevalence of type II diabetes has been increasing rapidly over the past few decades, and it is now considered a major public health concern. In this article, we will delve into the world of type II diabetes, exploring its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options, and management strategies.
The importance of understanding type II diabetes cannot be overstated. This condition can have severe consequences if left untreated or poorly managed, including cardiovascular disease, kidney damage, nerve damage, and even blindness. Moreover, type II diabetes is a significant economic burden on individuals, families, and societies as a whole. According to the International Diabetes Federation, the global healthcare expenditure on diabetes was estimated to be over $1.3 trillion in 2020. Therefore, it is essential to raise awareness about type II diabetes, promote early detection, and encourage individuals to adopt healthy lifestyle habits to prevent or manage the condition.
As we explore the topic of type II diabetes, it is crucial to recognize the impact of lifestyle factors, such as diet, physical activity, and stress, on the development and progression of the disease. A sedentary lifestyle, poor eating habits, and excessive weight gain can all contribute to insulin resistance, a hallmark of type II diabetes. Furthermore, certain ethnic groups, such as African Americans, Hispanics, and Native Americans, are at a higher risk of developing type II diabetes due to genetic and environmental factors. By understanding these risk factors, individuals can take proactive steps to reduce their likelihood of developing type II diabetes and improve their overall health and well-being.
Causes and Risk Factors of Type II Diabetes
Type II diabetes is a multifactorial disease, and its causes and risk factors are complex and interrelated. Some of the key causes and risk factors include:
- Insulin resistance: This occurs when the body's cells become less responsive to insulin, a hormone produced by the pancreas that regulates blood sugar levels.
- Impaired insulin secretion: This occurs when the pancreas is unable to produce enough insulin to meet the body's needs.
- Obesity: Excess weight, particularly around the abdominal area, can lead to insulin resistance and increase the risk of type II diabetes.
- Physical inactivity: A sedentary lifestyle can contribute to insulin resistance and increase the risk of type II diabetes.
- Genetics: Certain genetic mutations can increase the risk of type II diabetes.
- Age: The risk of type II diabetes increases with age, particularly after the age of 45.
- Ethnicity: Certain ethnic groups, such as African Americans, Hispanics, and Native Americans, are at a higher risk of developing type II diabetes.
Genetic and Environmental Factors
Genetic and environmental factors can also play a significant role in the development of type II diabetes. For example, individuals with a family history of type II diabetes are more likely to develop the condition. Additionally, environmental factors, such as exposure to pollutants and stress, can contribute to insulin resistance and increase the risk of type II diabetes.Symptoms and Diagnosis of Type II Diabetes

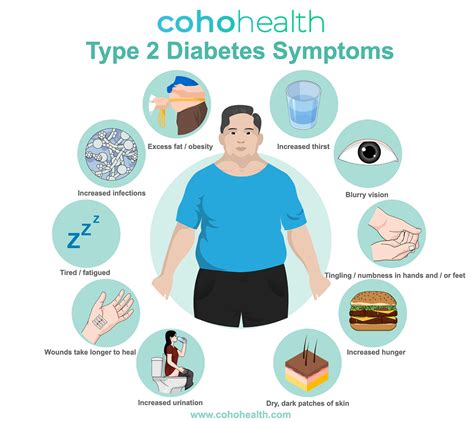
The symptoms of type II diabetes can be subtle and may develop gradually over time. Some common symptoms include:
- Increased thirst and urination
- Fatigue
- Blurred vision
- Slow healing of cuts and wounds
- Tingling or numbness in the hands and feet
- Recurring skin, gum, or bladder infections
Diagnosing type II diabetes typically involves a combination of physical examination, medical history, and laboratory tests. The most common diagnostic tests include:
- Fasting plasma glucose test: This measures blood glucose levels after an overnight fast.
- Oral glucose tolerance test: This measures blood glucose levels after consuming a sugary drink.
- Hemoglobin A1c test: This measures average blood glucose levels over the past 2-3 months.
Early Detection and Prevention
Early detection and prevention of type II diabetes are crucial in reducing the risk of complications and improving health outcomes. Individuals can take proactive steps to prevent type II diabetes by adopting healthy lifestyle habits, such as:- Eating a balanced diet that is low in sugar and saturated fats
- Engaging in regular physical activity, such as walking or cycling
- Maintaining a healthy weight
- Getting enough sleep and managing stress
Treatment and Management of Type II Diabetes
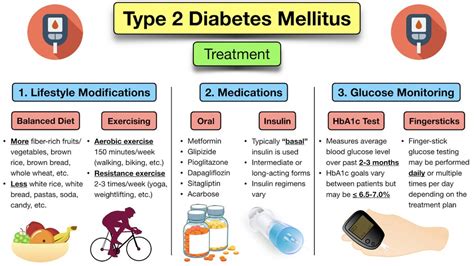
The treatment and management of type II diabetes typically involve a combination of lifestyle modifications, medications, and monitoring. Some common treatment options include:
- Metformin: This is a commonly prescribed medication that helps to improve insulin sensitivity and reduce blood glucose levels.
- Sulfonylureas: These medications stimulate the pancreas to produce more insulin.
- Pioglitazone: This medication helps to improve insulin sensitivity and reduce blood glucose levels.
- Insulin therapy: This may be necessary for individuals with type II diabetes who are unable to produce enough insulin.
Lifestyle modifications are also essential in managing type II diabetes. These may include:
- Eating a healthy and balanced diet that is low in sugar and saturated fats
- Engaging in regular physical activity, such as walking or cycling
- Maintaining a healthy weight
- Getting enough sleep and managing stress
Monitoring and Adjusting Treatment
Monitoring and adjusting treatment are critical in managing type II diabetes. This may involve:- Regular blood glucose monitoring to track blood sugar levels
- Adjusting medication dosages or types as needed
- Making lifestyle changes, such as increasing physical activity or improving diet
- Regular health check-ups to monitor for complications and adjust treatment as needed
Complications of Type II Diabetes
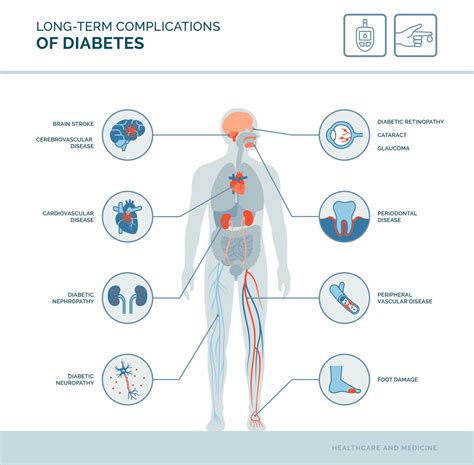
Type II diabetes can lead to a range of complications if left untreated or poorly managed. Some common complications include:
- Cardiovascular disease: This is the leading cause of death in individuals with type II diabetes.
- Kidney damage: Type II diabetes can damage the kidneys and increase the risk of kidney failure.
- Nerve damage: This can cause numbness, tingling, and pain in the hands and feet.
- Blindness: Type II diabetes can cause damage to the blood vessels in the eyes and increase the risk of blindness.
- Foot damage: Type II diabetes can cause nerve damage and poor circulation, leading to foot ulcers and amputations.
Preventing Complications
Preventing complications is essential in managing type II diabetes. This may involve:- Regular health check-ups to monitor for complications
- Making lifestyle changes, such as increasing physical activity or improving diet
- Taking medications as prescribed
- Monitoring blood glucose levels regularly
What are the symptoms of type II diabetes?
+The symptoms of type II diabetes can be subtle and may develop gradually over time. Common symptoms include increased thirst and urination, fatigue, blurred vision, slow healing of cuts and wounds, tingling or numbness in the hands and feet, and recurring skin, gum, or bladder infections.
How is type II diabetes diagnosed?
+Diagnosing type II diabetes typically involves a combination of physical examination, medical history, and laboratory tests. The most common diagnostic tests include fasting plasma glucose test, oral glucose tolerance test, and hemoglobin A1c test.
What are the treatment options for type II diabetes?
+The treatment and management of type II diabetes typically involve a combination of lifestyle modifications, medications, and monitoring. Common treatment options include metformin, sulfonylureas, pioglitazone, and insulin therapy. Lifestyle modifications, such as eating a healthy and balanced diet, engaging in regular physical activity, and maintaining a healthy weight, are also essential in managing type II diabetes.
In conclusion, type II diabetes is a complex and multifactorial disease that requires a comprehensive approach to management. By understanding the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options, and management strategies, individuals can take proactive steps to prevent or manage the condition. It is essential to raise awareness about type II diabetes, promote early detection, and encourage individuals to adopt healthy lifestyle habits to reduce the risk of complications and improve health outcomes. We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with type II diabetes in the comments section below and to share this article with others who may benefit from this information.
