Intro
The development and administration of vaccine shots have been crucial in preventing the spread of infectious diseases and protecting public health. Vaccines have been instrumental in saving millions of lives and have played a significant role in eradicating diseases such as smallpox. With the advancement of medical technology and research, various types of vaccine shots have been developed to combat different diseases. In this article, we will delve into the world of vaccines and explore five types of vaccine shots that have been widely used to prevent infectious diseases.
Vaccines work by introducing a small, harmless piece of a pathogen, such as a virus or bacteria, to the body, which triggers an immune response. This immune response helps the body to recognize and fight the pathogen, providing immunity against future infections. The importance of vaccines cannot be overstated, as they have been instrumental in preventing the spread of infectious diseases and saving countless lives. With the rise of vaccine-preventable diseases, it is essential to understand the different types of vaccine shots available and their role in protecting public health.
The development of vaccines has been a long and challenging process, with scientists and researchers working tirelessly to create effective and safe vaccines. From the early days of vaccine development to the present day, significant progress has been made in creating vaccines that can prevent a wide range of infectious diseases. With the advancement of medical technology and research, new vaccines are being developed to combat emerging diseases, and existing vaccines are being improved to provide better protection against infectious diseases.
Types of Vaccine Shots
There are several types of vaccine shots available, each with its unique characteristics and advantages. The five types of vaccine shots that we will discuss in this article are inactivated vaccines, live attenuated vaccines, conjugate vaccines, subunit vaccines, and mRNA vaccines. Each of these vaccine types has been developed to combat specific diseases and has been widely used to prevent infectious diseases.
Inactivated Vaccines
Inactivated vaccines are made from killed pathogens and are often used to prevent diseases such as flu, hepatitis A, and rabies. These vaccines are created by killing the pathogen using heat, chemicals, or radiation, which renders it incapable of causing disease. Inactivated vaccines are generally safe and effective, but they may require multiple doses to provide long-term immunity.Inactivated Vaccine Mechanism
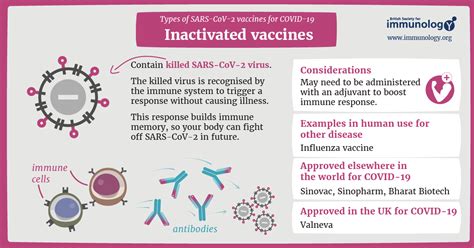
Inactivated vaccines work by introducing the killed pathogen to the body, which triggers an immune response. The immune system recognizes the killed pathogen as foreign and mounts an immune response to eliminate it. This immune response provides immunity against future infections, making it an effective way to prevent infectious diseases.
Live Attenuated Vaccines
Live attenuated vaccines are made from weakened pathogens and are often used to prevent diseases such as measles, mumps, and rubella. These vaccines are created by weakening the pathogen through various methods, such as growing it in a laboratory or using genetic engineering. Live attenuated vaccines are generally effective and provide long-term immunity, but they may pose a risk to people with weakened immune systems.Live Attenuated Vaccine Benefits

Live attenuated vaccines have several benefits, including providing long-term immunity and being easy to administer. They are also relatively inexpensive to produce and can be used to prevent a wide range of infectious diseases. However, live attenuated vaccines may pose a risk to people with weakened immune systems, and their use must be carefully considered.
Conjugate Vaccines
Conjugate vaccines are made by combining a weakened pathogen with a carrier protein. These vaccines are often used to prevent diseases such as Haemophilus influenzae type b (Hib) and pneumococcal disease. Conjugate vaccines are generally safe and effective, and they provide long-term immunity against infectious diseases.Conjugate Vaccine Mechanism
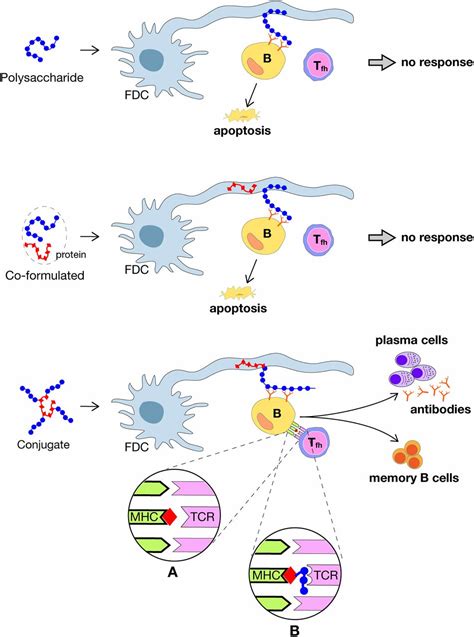
Conjugate vaccines work by introducing the weakened pathogen and carrier protein to the body, which triggers an immune response. The immune system recognizes the weakened pathogen and carrier protein as foreign and mounts an immune response to eliminate them. This immune response provides immunity against future infections, making it an effective way to prevent infectious diseases.
Subunit Vaccines
Subunit vaccines are made from specific components of a pathogen, such as proteins or sugars. These vaccines are often used to prevent diseases such as hepatitis B and human papillomavirus (HPV). Subunit vaccines are generally safe and effective, and they provide long-term immunity against infectious diseases.Subunit Vaccine Benefits
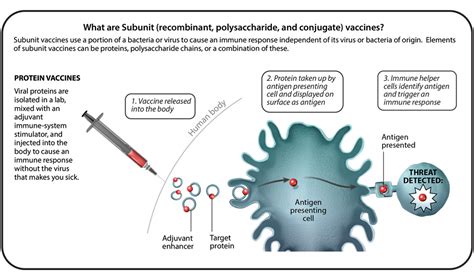
Subunit vaccines have several benefits, including being relatively inexpensive to produce and easy to administer. They are also safe and effective, providing long-term immunity against infectious diseases. However, subunit vaccines may require multiple doses to provide long-term immunity, and their use must be carefully considered.
mRNA Vaccines
mRNA vaccines are a new type of vaccine that uses a piece of genetic material called messenger RNA (mRNA) to instruct cells to produce a specific protein. These vaccines are often used to prevent diseases such as COVID-19 and influenza. mRNA vaccines are generally safe and effective, and they provide long-term immunity against infectious diseases.mRNA Vaccine Mechanism
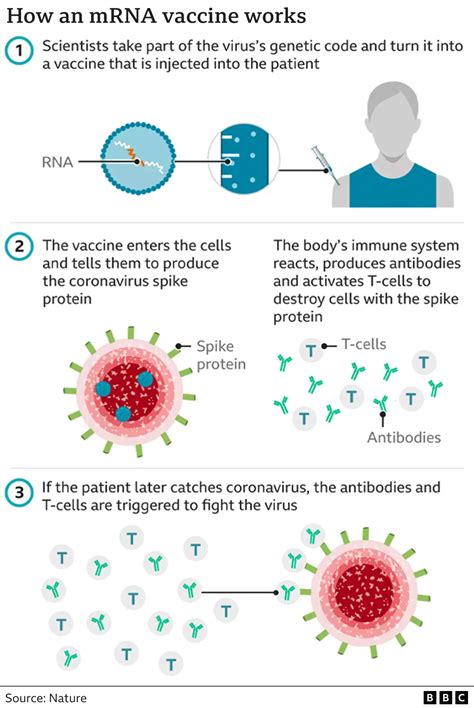
mRNA vaccines work by introducing the mRNA to the body, which instructs cells to produce a specific protein. The immune system recognizes the protein as foreign and mounts an immune response to eliminate it. This immune response provides immunity against future infections, making it an effective way to prevent infectious diseases.
What are the benefits of vaccine shots?
+Vaccine shots provide immunity against infectious diseases, preventing the spread of diseases and saving countless lives. They are also relatively inexpensive to produce and easy to administer, making them a crucial tool in public health.
How do vaccine shots work?
+Vaccine shots work by introducing a small, harmless piece of a pathogen to the body, which triggers an immune response. The immune system recognizes the pathogen as foreign and mounts an immune response to eliminate it, providing immunity against future infections.
What are the different types of vaccine shots available?
+There are several types of vaccine shots available, including inactivated vaccines, live attenuated vaccines, conjugate vaccines, subunit vaccines, and mRNA vaccines. Each of these vaccine types has been developed to combat specific diseases and has been widely used to prevent infectious diseases.
Are vaccine shots safe?
+Vaccine shots are generally safe and effective, but they may pose a risk to people with weakened immune systems. It is essential to consult with a healthcare professional before receiving a vaccine shot to discuss any potential risks or concerns.
How often should I get vaccinated?
+The frequency of vaccination depends on the type of vaccine and the individual's risk factors. It is essential to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the best vaccination schedule for your specific needs.
In conclusion, vaccine shots have been instrumental in preventing the spread of infectious diseases and saving countless lives. With the advancement of medical technology and research, various types of vaccine shots have been developed to combat different diseases. By understanding the different types of vaccine shots available and their role in protecting public health, we can make informed decisions about our health and well-being. We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with vaccine shots, and to take action to protect yourself and your loved ones against infectious diseases.
