Intro
Discover reliable vaccination and vaccine information, including vaccine types, schedules, and safety data, to make informed decisions about immunization and disease prevention, with expert insights on vaccine efficacy and potential side effects.
The importance of vaccination cannot be overstated, as it has been a crucial factor in the prevention and control of infectious diseases for centuries. Vaccines have saved countless lives and have been instrumental in the eradication of smallpox, a disease that once claimed millions of lives. The development and administration of vaccines have also led to significant reductions in the incidence of other serious diseases, such as polio, measles, and whooping cough. As a result, vaccination has become a cornerstone of public health policy, with widespread vaccination programs being implemented in countries around the world.
The benefits of vaccination extend far beyond the individual, as widespread vaccination can also prevent the spread of diseases within communities. This is because vaccines not only protect the person who receives them but also help to prevent the spread of disease to others, thereby reducing the risk of outbreaks. Furthermore, vaccination has also been shown to have economic benefits, as it can reduce the financial burden of treating and managing infectious diseases. With the rise of antimicrobial resistance, vaccination has become an increasingly important tool in the fight against infectious diseases.
The history of vaccination dates back to the late 18th century, when Edward Jenner developed the first vaccine against smallpox. Since then, numerous vaccines have been developed, including vaccines against diseases such as influenza, hepatitis B, and human papillomavirus (HPV). The development of vaccines involves a complex process, which includes identifying the causative agent of a disease, developing a vaccine candidate, and testing the vaccine for safety and efficacy. The process of vaccine development can take many years, if not decades, and requires significant investment and resources.
Vaccine Types And How They Work
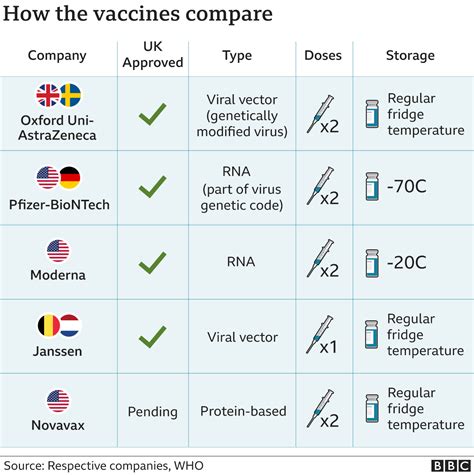
Vaccines can be broadly classified into several types, including inactivated vaccines, live attenuated vaccines, and subunit vaccines. Inactivated vaccines contain killed or inactivated pathogens, which are unable to cause disease. Live attenuated vaccines, on the other hand, contain weakened or attenuated pathogens, which can still cause a mild infection. Subunit vaccines, which are also known as conjugate vaccines, contain only specific components of a pathogen, such as proteins or sugars. Each type of vaccine works in a slightly different way, but they all stimulate the immune system to produce a protective response against a particular disease.
Live Attenuated Vaccines
Live attenuated vaccines are made from weakened or attenuated pathogens, which are able to cause a mild infection. This type of vaccine is often used to protect against diseases such as measles, mumps, and rubella. Live attenuated vaccines are highly effective and can provide long-term immunity against a disease. However, they can also cause mild side effects, such as fever and rash, in some individuals.Inactivated Vaccines
Inactivated vaccines, on the other hand, contain killed or inactivated pathogens. This type of vaccine is often used to protect against diseases such as influenza and hepatitis A. Inactivated vaccines are generally safe and well-tolerated, but they may require booster shots to maintain immunity.Vaccine Development And Approval

The development and approval of vaccines involve a complex and rigorous process. The process begins with the identification of a disease or condition that requires a vaccine. This is followed by the development of a vaccine candidate, which is then tested for safety and efficacy in preclinical trials. If the vaccine candidate shows promise, it is then tested in human clinical trials, which involve several phases. The first phase involves testing the vaccine in a small group of healthy individuals to assess its safety and tolerability. The second phase involves testing the vaccine in a larger group of individuals to assess its efficacy and side effects. The third phase involves testing the vaccine in an even larger group of individuals to confirm its efficacy and safety.
Clinical Trials
Clinical trials are a critical component of the vaccine development process. They involve testing the vaccine in human subjects to assess its safety and efficacy. Clinical trials are typically conducted in several phases, each of which is designed to answer specific questions about the vaccine. The first phase of clinical trials involves testing the vaccine in a small group of healthy individuals to assess its safety and tolerability. The second phase involves testing the vaccine in a larger group of individuals to assess its efficacy and side effects. The third phase involves testing the vaccine in an even larger group of individuals to confirm its efficacy and safety.Vaccine Safety And Side Effects

Vaccines, like all medical products, can cause side effects. However, the vast majority of side effects are mild and temporary, such as pain, redness, and swelling at the injection site. In rare cases, vaccines can cause more serious side effects, such as allergic reactions and neurological disorders. However, the risk of serious side effects is extremely low, and the benefits of vaccination far outweigh the risks.
Common Side Effects
Common side effects of vaccines include: * Pain, redness, and swelling at the injection site * Fever * Headache * Fatigue * Nausea and vomiting * DiarrheaSerious Side Effects
Serious side effects of vaccines are rare, but can include: * Allergic reactions * Neurological disorders, such as seizures and Guillain-Barré syndrome * Blood clotting disorders * Immune system disordersVaccine Administration And Storage
Vaccines must be administered and stored properly to ensure their safety and efficacy. Vaccines are typically administered via injection, and the route of administration can vary depending on the type of vaccine. Some vaccines, such as the influenza vaccine, can be administered via a nasal spray. Vaccines must be stored at the correct temperature to maintain their potency, and they must be handled and administered by trained healthcare professionals.
Vaccine Storage
Vaccines must be stored at the correct temperature to maintain their potency. The storage temperature can vary depending on the type of vaccine, but most vaccines are stored at refrigerator temperatures (2-8°C) or freezer temperatures (-20°C or colder).Vaccine Handling
Vaccines must be handled and administered by trained healthcare professionals. This includes following proper procedures for vaccine preparation, administration, and disposal.Global Vaccination Efforts

Global vaccination efforts have been instrumental in reducing the incidence of infectious diseases worldwide. Organizations such as the World Health Organization (WHO) and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) have played a critical role in promoting vaccination and providing technical assistance to countries to improve their vaccination programs. Global vaccination efforts have also been supported by numerous non-governmental organizations, such as the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation, which has provided significant funding for vaccination programs in developing countries.
Global Vaccination Initiatives
Global vaccination initiatives include: * The Global Vaccine Action Plan (GVAP) * The WHO's immunization program * The CDC's global immunization program * The Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation's vaccination programVaccine-Preventable Diseases
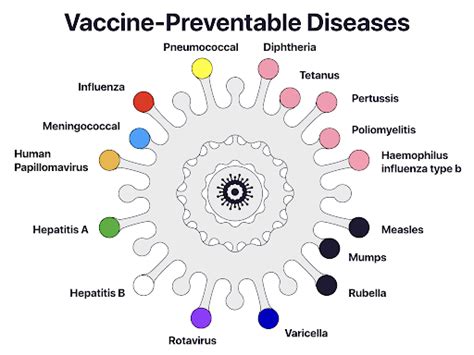
Vaccine-preventable diseases are diseases that can be prevented through vaccination. Examples of vaccine-preventable diseases include:
- Influenza
- Pneumococcal disease
- Human papillomavirus (HPV)
- Hepatitis B
- Measles, mumps, and rubella (MMR)
Disease Prevention
Vaccination is a critical tool in the prevention of infectious diseases. By vaccinating against vaccine-preventable diseases, individuals can protect themselves and their communities from the spread of disease.Future Of Vaccination
The future of vaccination holds much promise, with numerous new vaccines in development and innovative technologies being explored. One of the most promising areas of research is the development of mRNA vaccines, which have shown significant potential in the prevention of diseases such as COVID-19. Other areas of research include the development of vaccines against diseases such as HIV, tuberculosis, and malaria.
Emerging Technologies
Emerging technologies, such as mRNA vaccines and gene editing, hold much promise for the future of vaccination. These technologies have the potential to revolutionize the field of vaccination, enabling the rapid development of new vaccines and improving the efficacy and safety of existing vaccines.What is a vaccine?
+A vaccine is a medical product that stimulates the immune system to produce a protective response against a particular disease.
How do vaccines work?
+Vaccines work by stimulating the immune system to produce a protective response against a particular disease. This is achieved through the introduction of a small, harmless piece of a pathogen, such as a protein or sugar, which triggers an immune response.
What are the benefits of vaccination?
+The benefits of vaccination include the prevention of infectious diseases, the reduction of disease outbreaks, and the protection of vulnerable individuals, such as the elderly and young children.
In conclusion, vaccination is a critical tool in the prevention and control of infectious diseases. The benefits of vaccination are numerous, and the risks are minimal. As we look to the future, it is clear that vaccination will continue to play a vital role in protecting public health. We encourage readers to share this article with others, and to take action to protect themselves and their communities from the spread of infectious diseases. By working together, we can create a healthier, safer world for everyone.
