Intro
Identify 5 varicella symptoms, including rash, fever, and itching, to recognize chickenpox signs, causes, and treatment options for effective management.
The varicella virus, commonly known as chickenpox, is a highly contagious illness that affects millions of people worldwide, particularly children. It is essential to recognize the symptoms of varicella to provide timely treatment and prevent complications. Varicella symptoms can range from mild to severe, and understanding these symptoms is crucial for parents, caregivers, and individuals to take necessary precautions. In this article, we will delve into the importance of recognizing varicella symptoms, their effects on daily life, and the measures to prevent the spread of the virus.
Varicella is a viral infection that causes an itchy, blister-like rash, fever, and fatigue. The virus is highly contagious and can spread through direct contact with an infected person's rash, as well as through the air when an infected person coughs or sneezes. Recognizing the symptoms of varicella is vital to prevent the spread of the virus, especially among vulnerable individuals such as pregnant women, newborns, and people with weakened immune systems. By understanding the symptoms of varicella, individuals can take necessary precautions to prevent infection and seek medical attention if necessary.
The symptoms of varicella can be mild or severe, and they often appear within 10-21 days after exposure to the virus. The initial symptoms may include fever, headache, and fatigue, followed by the characteristic rash. The rash usually starts on the trunk, scalp, and face, and then spreads to other parts of the body. It is essential to recognize the symptoms of varicella to provide timely treatment and prevent complications, such as bacterial infections, pneumonia, and encephalitis. In severe cases, varicella can lead to life-threatening complications, especially among high-risk individuals.
Understanding Varicella Symptoms

Understanding varicella symptoms is crucial for providing timely treatment and preventing complications. The symptoms of varicella can be divided into two categories: primary and secondary. Primary symptoms include the characteristic rash, fever, and fatigue, while secondary symptoms may include headache, sore throat, and loss of appetite. Recognizing these symptoms is essential to distinguish varicella from other viral infections, such as measles or rubella.
Primary Varicella Symptoms
The primary symptoms of varicella include: * Rash: The characteristic rash of varicella is itchy, blister-like, and usually starts on the trunk, scalp, and face. * Fever: A low-grade fever is common in varicella, but it can be high in some cases. * Fatigue: Varicella can cause fatigue, which can last for several days.Secondary Varicella Symptoms

Secondary varicella symptoms may include:
- Headache: A headache is common in varicella, especially among adults.
- Sore throat: A sore throat can occur in some cases of varicella.
- Loss of appetite: Varicella can cause a loss of appetite, which can lead to dehydration and other complications.
Varicella Symptoms in Adults
Varicella symptoms in adults can be more severe than in children. Adults are more likely to experience: * High fever * Severe headache * Fatigue * Loss of appetiteDiagnosing Varicella

Diagnosing varicella is usually based on the characteristic rash and other symptoms. A doctor may perform a physical examination and take a medical history to confirm the diagnosis. In some cases, a blood test or viral culture may be necessary to confirm the diagnosis.
Treatment Options
Treatment for varicella usually focuses on relieving symptoms and preventing complications. Antiviral medications, such as acyclovir, may be prescribed to reduce the severity and duration of symptoms. Other treatment options include: * Rest and hydration * Over-the-counter pain relievers * Antihistamines to relieve itching * Antibiotics to treat bacterial infectionsPreventing Varicella

Preventing varicella is crucial to reduce the risk of infection and complications. The varicella vaccine is the most effective way to prevent varicella. The vaccine is usually given to children in two doses, with the first dose at 12-15 months and the second dose at 4-6 years. Adults who have not been vaccinated or have not had varicella can also receive the vaccine.
Varicella Vaccine
The varicella vaccine is a live, attenuated vaccine that is made from a weakened form of the varicella virus. The vaccine is usually given in combination with the measles, mumps, and rubella (MMR) vaccine. The varicella vaccine is: * Safe: The varicella vaccine is safe and well-tolerated. * Effective: The varicella vaccine is highly effective in preventing varicella. * Long-lasting: The varicella vaccine provides long-lasting immunity.Complications of Varicella
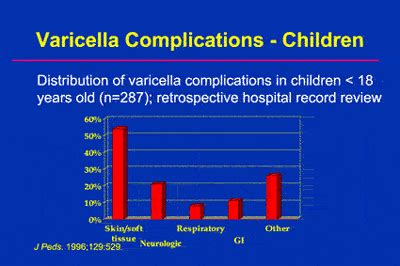
Complications of varicella can be severe and life-threatening, especially among high-risk individuals. Common complications include:
- Bacterial infections: Bacterial infections, such as strep throat or pneumonia, can occur in some cases of varicella.
- Pneumonia: Varicella can cause pneumonia, especially among adults and high-risk individuals.
- Encephalitis: Varicella can cause encephalitis, a rare but life-threatening complication.
Managing Complications
Managing complications of varicella requires prompt medical attention. Treatment may include: * Antibiotics to treat bacterial infections * Antiviral medications to treat varicella * Hospitalization to manage severe complicationsVaricella in High-Risk Individuals

Varicella can be severe and life-threatening in high-risk individuals, such as:
- Pregnant women
- Newborns
- People with weakened immune systems
- Adults over 50 years old
Precautions for High-Risk Individuals
Precautions for high-risk individuals include: * Avoiding contact with people who have varicella * Getting vaccinated against varicella * Taking antiviral medications to prevent varicellaWhat are the symptoms of varicella?
+The symptoms of varicella include a characteristic rash, fever, and fatigue. Secondary symptoms may include headache, sore throat, and loss of appetite.
How is varicella diagnosed?
+Varicella is usually diagnosed based on the characteristic rash and other symptoms. A doctor may perform a physical examination and take a medical history to confirm the diagnosis.
Can varicella be prevented?
+Yes, varicella can be prevented through vaccination. The varicella vaccine is the most effective way to prevent varicella and its complications.
In conclusion, recognizing the symptoms of varicella is essential to provide timely treatment and prevent complications. By understanding the primary and secondary symptoms of varicella, individuals can take necessary precautions to prevent infection and seek medical attention if necessary. We invite readers to share their experiences with varicella, ask questions, and provide feedback on this article. Additionally, we encourage readers to share this article with others who may be interested in learning more about varicella symptoms and prevention.
