Intro
Protect against chickenpox with the Varicella vaccine for adults, preventing shingles, herpes zoster, and varicella infections, ensuring adult immunity and public health safety.
The varicella vaccine, also known as the chickenpox vaccine, is a highly effective way to prevent varicella, a common and highly contagious illness caused by the varicella-zoster virus. While it is often associated with children, the varicella vaccine is also important for adults, particularly those who have not had chickenpox or have not been vaccinated against it. In fact, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommends that all adults who have not had chickenpox or have not been vaccinated against it should receive two doses of the varicella vaccine, given at least 4 weeks apart.
The importance of the varicella vaccine for adults cannot be overstated. Chickenpox can be a serious illness in adults, leading to complications such as pneumonia, encephalitis, and even death. According to the CDC, adults are more likely to experience severe complications from chickenpox than children, with the risk of hospitalization and death increasing with age. Furthermore, adults who have not had chickenpox or have not been vaccinated against it can spread the virus to others, including children and individuals with weakened immune systems, who are at increased risk of severe illness.
In addition to protecting against chickenpox, the varicella vaccine also has the potential to prevent other illnesses caused by the varicella-zoster virus, such as shingles. Shingles is a painful rash that can occur in individuals who have had chickenpox, typically later in life. The varicella vaccine has been shown to reduce the risk of developing shingles and its associated complications, such as postherpetic neuralgia, a condition characterized by persistent pain after the rash has resolved.
Benefits of the Varicella Vaccine for Adults
How the Varicella Vaccine Works
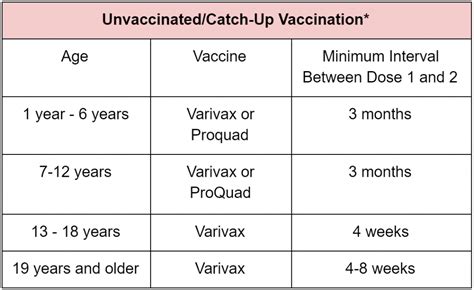
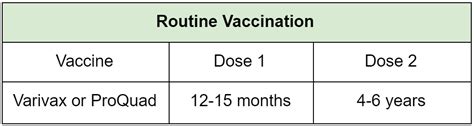
The varicella vaccine works by introducing a weakened or killed form of the varicella-zoster virus to the body, which stimulates the immune system to produce antibodies against the virus. These antibodies provide protection against future infections, reducing the risk of severe illness and complications. The varicella vaccine is typically given in two doses, with the second dose given at least 4 weeks after the first dose. This allows the immune system to produce a strong and lasting response to the vaccine, providing long-term protection against chickenpox and shingles.Who Should Receive the Varicella Vaccine
Contraindications and Precautions
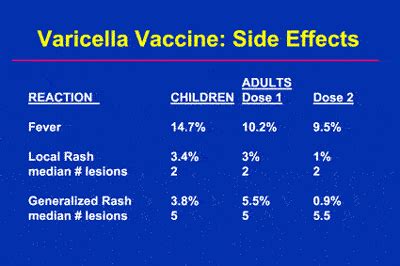
While the varicella vaccine is generally safe and effective, there are certain contraindications and precautions that should be considered. These include: * Allergy to any component of the vaccine, such as gelatin or neomycin * Pregnancy or breastfeeding, as the safety of the vaccine in these populations has not been established * Weakened immune system, such as those with HIV/AIDS or cancer * Taking immunosuppressive medications, such as corticosteroids or chemotherapy * Recent receipt of blood or plasma transfusions, as these may interfere with the vaccine's effectivenessSide Effects of the Varicella Vaccine
Serious Side Effects
While rare, serious side effects can occur after receiving the varicella vaccine. These include: * Allergic reactions, such as anaphylaxis or hives * Seizures or convulsions * Encephalitis or meningitis * Guillain-Barré syndrome, a rare autoimmune disorderEffectiveness of the Varicella Vaccine
Duration of Protection
The duration of protection provided by the varicella vaccine is not fully understood, although it is believed to last for many years. Booster doses may be necessary to maintain immunity, particularly in individuals who are at high risk of exposure to the varicella-zoster virus.Conclusion and Recommendations
What is the varicella vaccine and how does it work?
+The varicella vaccine is a vaccine that protects against chickenpox and its complications. It works by introducing a weakened or killed form of the varicella-zoster virus to the body, which stimulates the immune system to produce antibodies against the virus.
Who should receive the varicella vaccine?
+The varicella vaccine is recommended for all adults who have not had chickenpox or have not been vaccinated against it, particularly those who are at high risk of exposure to the varicella-zoster virus.
What are the side effects of the varicella vaccine?
+Common side effects of the varicella vaccine include redness, swelling, or pain at the injection site, fever, headache, fatigue, muscle or joint pain, and nausea or vomiting. Serious side effects are rare, but can be severe.
How effective is the varicella vaccine?
+The varicella vaccine is highly effective in preventing chickenpox and its complications. Studies have shown that the vaccine is 85-90% effective in preventing chickenpox in individuals who have not had the disease.
Do I need to get a booster dose of the varicella vaccine?
+The duration of protection provided by the varicella vaccine is not fully understood, although it is believed to last for many years. Booster doses may be necessary to maintain immunity, particularly in individuals who are at high risk of exposure to the varicella-zoster virus.
We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with the varicella vaccine in the comments below. Have you received the varicella vaccine? What were your experiences with the vaccine? Do you have any questions or concerns about the vaccine? Share your comments and help us build a community of informed and engaged individuals.
