Intro
Discover 5 Vitamin B1 benefits, including energy boosts, nerve function support, and heart health improvements, with this essential nutrient also known as Thiamine, playing a crucial role in carbohydrate metabolism and overall wellness.
Vitamin B1, also known as thiamine, is an essential nutrient that plays a critical role in various bodily functions. It is a water-soluble vitamin that is not stored in the body, making it necessary to consume it regularly through a balanced diet or supplements. Thiamine is involved in energy production, nerve function, and heart health, among other processes. In this article, we will delve into the numerous benefits of vitamin B1 and explore its importance in maintaining overall health and well-being.
The human body relies heavily on vitamin B1 to convert carbohydrates into energy, which is then used to power the body's various functions. This process is crucial for the proper functioning of the nervous system, muscles, and heart. Moreover, thiamine helps to maintain healthy skin, hair, and mucous membranes, making it an essential nutrient for overall health. With its numerous benefits and functions, it is no wonder that vitamin B1 is often referred to as the "energy vitamin."
Vitamin B1 deficiency can lead to a range of health problems, including beriberi, a condition characterized by weakness, fatigue, and nerve damage. In severe cases, thiamine deficiency can cause more serious health issues, such as heart failure, seizures, and even death. However, with a balanced diet that includes thiamine-rich foods, such as whole grains, legumes, and nuts, it is possible to maintain adequate levels of vitamin B1 and reap its numerous benefits.
Vitamin B1 Benefits for Energy Production
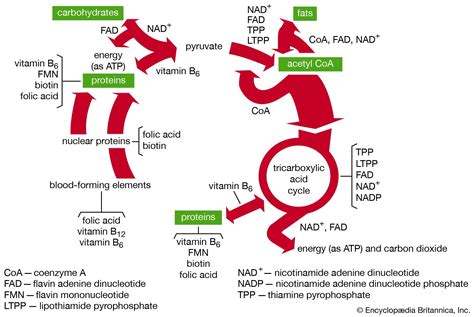
The benefits of vitamin B1 for energy production are numerous. For instance, thiamine helps to:
- Convert carbohydrates into energy
- Produce ATP, the primary energy currency of the body
- Support the proper functioning of the nervous system, muscles, and heart
- Maintain healthy skin, hair, and mucous membranes
- Support immune function and overall health
Vitamin B1-Rich Foods
Some of the richest sources of vitamin B1 include: * Whole grains, such as brown rice, quinoa, and whole wheat bread * Legumes, such as black beans, chickpeas, and lentils * Nuts and seeds, such as sunflower seeds, flaxseeds, and almonds * Lean proteins, such as chicken, fish, and turkey * Fortified cereals and energy barsVitamin B1 Benefits for Nerve Function
The benefits of vitamin B1 for nerve function are numerous. For instance, thiamine helps to:
- Maintain healthy nerve cells and support the transmission of nerve impulses
- Produce myelin, the fatty substance that surrounds and protects nerve fibers
- Support the proper functioning of the nervous system, including the brain and spinal cord
- Reduce the risk of neurodegenerative diseases, such as Alzheimer's and Parkinson's
- Improve cognitive function and memory
Vitamin B1 Deficiency and Nerve Damage
Vitamin B1 deficiency can lead to nerve damage and a range of health problems, including: * Beriberi, a condition characterized by weakness, fatigue, and nerve damage * Peripheral neuropathy, a condition characterized by numbness, tingling, and muscle weakness * Wernicke-Korsakoff syndrome, a condition characterized by memory loss, confusion, and difficulty with coordination and balanceVitamin B1 Benefits for Heart Health

The benefits of vitamin B1 for heart health are numerous. For instance, thiamine helps to:
- Maintain healthy blood vessels and support the proper functioning of the cardiovascular system
- Produce nitric oxide, a molecule that helps to relax and dilate blood vessels
- Reduce the risk of heart disease, including high blood pressure, heart failure, and stroke
- Improve blood flow and reduce the risk of blood clots
- Support the overall health and well-being of the cardiovascular system
Vitamin B1 and Blood Pressure
Vitamin B1 has been shown to have a positive effect on blood pressure, as it helps to relax and dilate blood vessels, improving blood flow and reducing blood pressure. Some studies have suggested that thiamine supplementation may be beneficial for individuals with high blood pressure, as it may help to reduce blood pressure and improve cardiovascular health.Vitamin B1 Benefits for Skin, Hair, and Mucous Membranes

The benefits of vitamin B1 for skin, hair, and mucous membranes are numerous. For instance, thiamine helps to:
- Maintain healthy skin, hair, and mucous membranes
- Produce collagen, a protein that gives structure and strength to skin, hair, and connective tissue
- Support the proper functioning of the skin, including the production of sebum and sweat
- Improve the health and appearance of skin, hair, and mucous membranes
- Reduce the risk of skin problems, such as acne, eczema, and psoriasis
Vitamin B1 and Wound Healing
Vitamin B1 has been shown to have a positive effect on wound healing, as it helps to support the proper functioning of the skin and promote the production of collagen. Some studies have suggested that thiamine supplementation may be beneficial for individuals with wounds, as it may help to improve wound healing and reduce the risk of infection.Vitamin B1 Benefits for Immune Function

The benefits of vitamin B1 for immune function are numerous. For instance, thiamine helps to:
- Support the proper functioning of the immune system
- Produce white blood cells, which are critical for fighting off infections and diseases
- Reduce the risk of illness and infection
- Improve the overall health and well-being of the immune system
- Support the production of antibodies, which are proteins that help to fight off infections and diseases
Vitamin B1 and Infections
Vitamin B1 has been shown to have a positive effect on infections, as it helps to support the proper functioning of the immune system and reduce the risk of illness and infection. Some studies have suggested that thiamine supplementation may be beneficial for individuals with infections, as it may help to improve immune function and reduce the risk of complications.Vitamin B1 Benefits for Cognitive Function
The benefits of vitamin B1 for cognitive function are numerous. For instance, thiamine helps to:
- Support the proper functioning of the brain and nervous system
- Produce neurotransmitters, which are chemicals that help to transmit signals between nerve cells
- Improve memory, concentration, and focus
- Reduce the risk of neurodegenerative diseases, such as Alzheimer's and Parkinson's
- Support the overall health and well-being of the brain and nervous system
Vitamin B1 and Neurodegenerative Diseases
Vitamin B1 has been shown to have a positive effect on neurodegenerative diseases, as it helps to support the proper functioning of the brain and nervous system and reduce the risk of cognitive decline. Some studies have suggested that thiamine supplementation may be beneficial for individuals with neurodegenerative diseases, as it may help to improve cognitive function and reduce the risk of complications.What are the symptoms of vitamin B1 deficiency?
+The symptoms of vitamin B1 deficiency include weakness, fatigue, numbness, tingling, and muscle weakness. In severe cases, thiamine deficiency can cause more serious health problems, such as heart failure, seizures, and even death.
What are the best sources of vitamin B1?
+The best sources of vitamin B1 include whole grains, legumes, nuts, and seeds. Fortified cereals and energy bars are also good sources of thiamine.
Can vitamin B1 supplements help to improve energy levels?
+Yes, vitamin B1 supplements may help to improve energy levels, as thiamine is involved in the production of ATP, the primary energy currency of the body. However, it is essential to consult with a healthcare professional before taking any supplements.
Can vitamin B1 deficiency cause nerve damage?
+Yes, vitamin B1 deficiency can cause nerve damage, as thiamine is essential for the proper functioning of the nervous system. Nerve damage can lead to problems such as numbness, tingling, and muscle weakness.
Can vitamin B1 supplements help to improve cognitive function?
+Yes, vitamin B1 supplements may help to improve cognitive function, as thiamine is involved in the production of neurotransmitters, which are chemicals that help to transmit signals between nerve cells. However, it is essential to consult with a healthcare professional before taking any supplements.
In conclusion, vitamin B1 is an essential nutrient that plays a critical role in various bodily functions, including energy production, nerve function, heart health, and immune function. The benefits of vitamin B1 are numerous, and it is essential to maintain adequate levels of thiamine through a balanced diet or supplements. By understanding the importance of vitamin B1 and its numerous benefits, individuals can take steps to support their overall health and well-being. We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with vitamin B1 in the comments section below.
